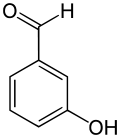
3-Hydroxybenzaldehyde
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3-Hydroxybenzaldehyde | |
| Other names
m-Hydroxybenzaldehyde; m-Formylphenol; 3-Formylphenol | |
| Identifiers | |
| 100-83-4 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:16207 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL243816 |
| ChemSpider | 21105795 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.630 |
| KEGG | C03067 |
| PubChem | 101 |
| UNII | 8Z2819J40E |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H6O2 | |
| Molar mass | 122.12 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | light-tan crystals |
| Melting point | 100 to 103 °C (212 to 217 °F; 373 to 376 K) |
| Boiling point | 191 °C (376 °F; 464 K) (50 mmHg) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
3-Hydroxybenzaldehyde is one of the three isomers of hydroxybenzaldehyde.
Chemistry
It has been prepared from 3-nitrobenzaldehyde in a sequence of nitro group reduction, diazotization of the amine, and hydrolysis.[1][2]
Metabolism
3-hydroxybenzyl-alcohol dehydrogenase is an enzyme that uses 3-hydroxybenzyl alcohol and NADP+ to produce 3-hydroxybenzaldehyde, NADPH and H+.
Uses
A known use of 3-Hydroxybenzaldehyde is in the synthesis of Monastrol.
See also
- Salicylaldehyde (2-hydroxybenzaldehyde)
- 4-Hydroxybenzaldehyde
References
- ↑ m-HYDROXYBENZALDEHYDE, Organic Syntheses, Coll. Vol. 3, p.453 (1955); Vol. 25, p.55 (1945)
- ↑ m-METHOXYBENZALDEHYDE, Organic Syntheses, Coll. Vol. 3, p.564 (1955); Vol. 29, p.63 (1949)
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 8/1/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.