AMD PowerTune
 | |
| Design firm | Advanced Micro Devices |
|---|---|
| Introduced | December 2011 |
| Type | Dynamic frequency scaling |
AMD PowerTune is a trademark for a series of dynamic frequency scaling technologies built into some AMD GPUs and APUs that allow the clock speed of the processor to be dynamically changed (to different P-states) by software. This allows the processor to meet the instantaneous performance needs of the operation being performed, while minimizing power draw, heat generation and noise. AMD PowerTune aims to solve thermal design power and performance constraints.[1]
Besides the reduced energy consumption, AMD PowerTune helps to lower the noise levels created by the cooling in desktop computers, and extends battery life in mobile devices. AMD PowerTune is the successor to AMD PowerPlay.[2]
Support for "PowerPlay" was added to the Linux kernel driver "amdgpu" on November, 11 2015.[3]
As a lecture from CCC in 2014 nicely shows, AMD's x86-64 SMU firmware is executed on some LatticeMico32 and PowerTune was modeled using Matlab.[4] This is similar to Nvidia's PDAEMON, the RTOS responsible for power on their GPUs.[5]
Overview
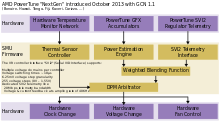
AMD PowerTune was introduced in the TeraScale 3 (VLIW4) with Radeon HD 6900 in Dec 15, 2010 and has been available in different development stages on Radeon- and AMD FirePro-branded products ever since.
Over the years, reviews which document the development of AMD PowerTune have been published by AnandTech.[6][7][8][9]
An additional technology named AMD ZeroCore Power has been available since the Radeon HD 7000 Series, implementing the Graphics Core Next microarchitecture.
The pointlessness of a fixed clock frequency was accredited in January 2014 by SemiAccurate.[10]
Operating system support
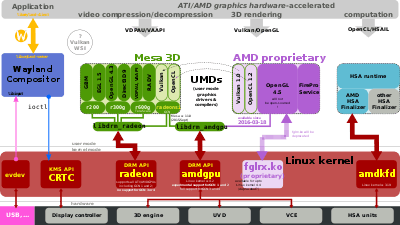
AMD Catalyst is available for Microsoft Windows and Linux and supports AMD PowerTune since version.
The free and open-source "Radeon" graphics device driver has some support for AMD PowerTune, see "Enduro".[11]
Feature overview for AMD APUs
| Brand | Llano | Trinity | Richland | Kaveri | Carrizo | Bristol Ridge | Raven Ridge | Desna, Ontario, Zacate | Kabini, Temash | Beema, Mullins | Carrizo-L | Stoney Ridge | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Platform | Desktop, Mobile | Mobile | Desktop, Mobile | Ultra-mobile | |||||||||
| Released | Aug 2011 | Oct 2012 | Jun 2013 | Jan 2014 | Jun 2015 | Jun 2016 | May 2017 | Jan 2011 | May 2013 | Q2 2014 | May 2015 | June 2016 | |
| Fab. (nm) | GlobalFoundries 32 SOI | 28 | 14 | TSMC 40 | 28 | ||||||||
| Die size (mm2) | 228 | 246 | 245 | 244.62 | 250.04 | TBA | 75 (+ 28 FCH) | ~107 | TBA | 125 | |||
| Socket | FM1, FS1 | FM2, FS1+, FP2 | FM2+, FP3 | FM2+, FP4 | FP4 | AM4, FP5 | FT1 | AM1, FT3 | FT3b | FP4 | FP4 | ||
| CPU architecture | AMD 10h | Piledriver | Steamroller | Excavator | Zen | Bobcat | Jaguar | Puma | Puma+[12] | Excavator | |||
| Memory support | DDR3-1866 DDR3-1600 DDR3-1333 | DDR3-2133 DDR3-1866 DDR3-1600 DDR3-1333 | DDR4-2400 DDR4-2133 DDR4-1866 DDR4-1600 | DDR3L-1333 DDR3L-1066 | DDR3L-1866 DDR3L-1600 DDR3L-1333 DDR3L-1066 | DDR3L-1866 DDR3L-1600 DDR3L-1333 | Up to DDR4-2133 | ||||||
| 3D engine[lower-alpha 1] | TeraScale (VLIW5) | TeraScale (VLIW4) | GCN 2nd Gen (Mantle, HSA) | GCN 3rd Gen (Mantle, HSA) | GCN 4th Gen[13] (Mantle, HSA) | TeraScale (VLIW5) | GCN 2nd Gen | GCN 3rd Gen[14] | |||||
| Up to 400:20:8 | Up to 384:24:6 | Up to 512:32:8 | Up to 768:48:12 | 80:8:4 | 128:8:4 | Up to 192:?:? | |||||||
| IOMMUv1 | IOMMUv2 | IOMMUv1[15] | TBA | TBA | |||||||||
| Unified Video Decoder | UVD 3 | UVD 4.2 | UVD 6 | TBA | UVD 3 | UVD 4 | UVD 4.2 | UVD 6 | UVD 6.3 | ||||
| Video Coding Engine | N/A | VCE 1.0 | VCE 2.0 | VCE 3.1 | TBA | N/A | VCE 2.0 | VCE 3.1 | |||||
| GPU power saving | PowerPlay | PowerTune | N/A | PowerTune[16] | |||||||||
| Max. displays[lower-alpha 2] | 2–3 | 2–4 | 2–4 | 3 | 4 | TBA | 2 | TBA | TBA | ||||
| TrueAudio | N/A | ✔[18] | N/A[15] | TBA | |||||||||
| FreeSync | N/A | ✔ | N/A | TBA | |||||||||
/drm/radeon[19][11] |
✔ | N/A | ✔ | N/A | |||||||||
/drm/amd/amdgpu[20] |
N/A | ✔[21] | ✔ | N/A | ✔[21] | ✔ | |||||||
- ↑ Unified shaders : texture mapping units : render output units
- ↑ To feed more than two displays, the additional panels must have native DisplayPort support.[17] Alternatively active DisplayPort-to-DVI/HDMI/VGA adapters can be employed.
Feature overview for AMD graphics cards
| R100 | R200 | R300 | R400 | R500 | R600 | RV670 | R700 | Evergreen | Northern Islands |
Southern Islands |
Sea Islands |
Volcanic Islands |
Polaris | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Released | Apr 2000 | Aug 2001 | Sep 2002 | May 2004 | Oct 2005 | May 2007 | Nov 2007 | Jun 2008 | Sep 2009 | Oct 2010 | Jan 2012 | Sep 2013 | Jun 2015 | Jun 2016 |
| Instruction set | not publicly known | TeraScale instruction set | GCN instruction set | |||||||||||
| Microarchitecture | TeraScale 1 (VLIW5) | TeraScale 2 (VLIW5) | TeraScale 3 (VLIW4) | GCN 1st gen | GCN 2nd gen | GCN 3rd gen | GCN 4th gen | |||||||
| Microarchitecture type | Fixed pipeline | Unified shader model | ||||||||||||
| Direct3D | 7.0 | 8.1 | 9.0 | 9.0b | 9.0c | 10.0 | 10.1 | 11.0 | 12.0 | |||||
| Shader Model | 1.1 | 1.4 | 2.0+ | 2.0b | 3.0 | 4.0 | 4.1 | 5.0 | 5.1 | |||||
| OpenGL | 1.3 | 2.0 | 3.3 | 4.4 | 4.5 | |||||||||
| Vulkan | N/A | WIP in Linux, Windows 7+ Full support for 1.0 | 1.0 | |||||||||||
| OpenCL | N/A | APP Stream | 1.1 | 1.2 | 2.0 | |||||||||
| Power saving | ? | PowerPlay | PowerTune | PowerTune & ZeroCore Power | ||||||||||
| Unified Video Decoder | N/A | Avivo/UVD | UVD+ | UVD 2 | UVD 2.2 | UVD 3 | UVD 4 | UVD 4.2 | UVD 5.0 or 6.0 | UVD 6.3 | ||||
| Video Coding Engine | N/A | VCE 1.0 | VCE 2.0 | VCE 3.0 or 3.1 | VCE 3.4 | |||||||||
| TrueAudio | N/A | Dedicated DSP | Run on the shaders | |||||||||||
| FreeSync | N/A | ✔ | ||||||||||||
| Max. displays[lower-alpha 1] | 1–2 | 2 | 2–6 | |||||||||||
| Max. resolution | ? | 2–6x 2560×1600 | 2–6x 4096×2160 @ 60 Hz | 2–6x 5120x2880 @ 60 Hz | ||||||||||
/drm/radeon |
✔ | N/A | ||||||||||||
/drm/amd/amdgpu |
N/A | WIP[22] | experimental | ✔ | ||||||||||
- ↑ More displays may be supported with native DisplayPort connections, or splitting the maximum resolution between multiple monitors with active converters.
See also
- AMD Cool'n'Quiet (for desktop CPUs)
- AMD PowerNow! (for laptop CPUs)
- AMD Turbo Core (for CPUs)
- Dynamic frequency scaling
- Intel SpeedStep (for CPUs)
- Intel Turbo Boost (for CPUs)
References
- ↑ "AMD PowerTune Technology" (pdf). AMD. 2012-03-23.
- ↑ "AMD PowerTune vs PowerPlay" (pdf). AMD. 2010-12-01.
- ↑ "Add amdgpu powerplay support". 2015-11-11.
- ↑ "AMD x86 SMU firmware analysis". 2014-12-27.
- ↑ "Reverse engineering power management on Nvidia GPUs" (PDF).
- ↑ "Redefining TDP With PowerTune". AnandTech. 2010-12-15.
- ↑ "Introducing PowerTune Technology With Boost". AnandTech. 2012-06-22.
- ↑ "The New PowerTune: Adding Further States". AnandTech. 2013-03-22.
- ↑ "PowerTune: Improved Flexibility & Fan Speed Throttling". AnandTech. 2014-10-23.
- ↑ "What is AMD's PowerTune 2.0 and what does it do?". SemiAccurate. 2013-12-16.
- 1 2 "Radeon feature matrix". freedesktop.org. Retrieved 2016-01-10.
- ↑ "AMD Mobile "Carrizo" Family of APUs Designed to Deliver Significant Leap in Performance, Energy Efficiency in 2015" (Press release). 2014-11-20. Retrieved 2015-02-16.
- ↑ "AMD VEGA10 and VEGA11 GPUs spotted in OpenCL driver". VideoCardz.com. Retrieved 3 September 2016.
- ↑ "AMD VEGA10 and VEGA11 GPUs spotted in OpenCL driver". VideoCardz.com. Retrieved 3 September 2016.
- 1 2 Thomas De Maesschalck (2013-11-14). "AMD teases Mullins and Beema tablet/convertibles APU". Retrieved 2015-02-24.
- ↑ Tony Chen; Jason Greaves, "AMD's Graphics Core Next (GCN) Architecture" (PDF), AMD, retrieved 2016-08-13
- ↑ "How do I connect three or More Monitors to an AMD Radeon™ HD 5000, HD 6000, and HD 7000 Series Graphics Card?". AMD. Retrieved 2014-12-08.
- ↑ "A technical look at AMD's Kaveri architecture". Semi Accurate. Retrieved 6 July 2014.
- ↑ Airlie, David (2009-11-26). "DisplayPort supported by KMS driver mainlined into Linux kernel 2.6.33". Retrieved 2016-01-16.
- ↑ Deucher, Alexander (2015-09-16). "XDC2015: AMDGPU" (PDF). Retrieved 2016-01-16.
- 1 2 Michel Dänzer (2016-11-17). "[ANNOUNCE] xf86-video-amdgpu 1.2.0". lists.x.org.
- ↑ Larabel, Michael (9 May 2016). "AMD Soon Might Have Out AMDGPU Support For The Original GCN GPUs". Phoronix. Retrieved 10 May 2016.