Airbag launching
Airbag launching refers to a method to launch vessels with marine air bags. It a methodology for ship launching utilizing air bags.[1]
The Xiao Qinghe shipyard launched a tank barge with marine airbags on January 20, 1981 and it is known as the first use of marine airbags.
This kind ship launching method has the advantages of requiring less permanent infrastructure, risk, and cost. The airbags provide support to the hull of the ship,air bags rolling motion take a vessel launch into water, thus it is arguably safer than other options like sideways launching.
The arrangements of air bags
Launching type
Based on the ship shapes, the ship may be launched, using air bags, by either end launching type or side launching type
End launching type
There are three ways to arrange air bags when using the end launching type. They are (1) linear arrangement (see Figure A.1), (2) staggered arrangement (see Figure A.2), and (3) two-lines arrangement (see Figure A.3). As for which arrangement to use, it will depend on the ship’s width and the length of the air bags.
When the ship’s width is not greater than the effective length of the air bags,
the linear arrangement shall be selected

When the ship’s width is greater than the effective length of an air bag and less than the effective length of two air bags, the staggered arrangement shall be selected.

When the ship’s width is greater than the combined effective length of two air bags,or for special ship such as catamaran HSC or split hopper barge, the two lines arrangement shall be selected.The distance between the near ends of two air bags is greater than 0,2 m.

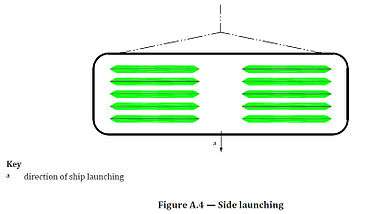
Side launching type
For small flat-bottom ships, side launching method may be utilized (see Figure A.4)
Air bags quantity
Air bags shall meet the requirements of ISO 14409[3]>
According to the weight of the ship being launched, the quantity of the air bags needed for this operation shall be calculated in accordance with Formula (1):
.jpg)
where
N is the quantity of air bags used for ship launching;
K1 is a coefficient, in general, K1 ≥ 1,2;
Q is the weight of the ship (ton);
g is acceleration of gravity (m/s2), g = 9,8;
Cb is the block coefficient of the ship being launched;
R is the allowable unit bearing capacity of the air bags (kN/m);
Ld is the contact length between the bottom of the ship and the body of the air bag at the midship section (m).
For ship shifting, 2 to 4 additional air bags shall be made ready and available.
The centre to centre distance between two neighbouring air bags shall be less than or equals to that found in Formula (2) and equals to or be greater than that found in Formula (3).
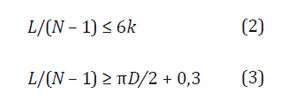
where
L is the actual length of the ship bottom that can make contact with the air bags (m);
N is the quantity of air bags used for ship launching;
k is a coefficient, k = 1 for steel ships, k = 0,8 for wooden, aluminium and glass-fibre-reinforced ships;
D is the nominal diameter of air bags (m).
Slipway
The gradient and the length of the slipway shall be determined according to the size of the ship and the hydrological condition of the area water.
The bearing capacity of the slipway shall be at least twice as strong as the working pressure of air bags.
For ships of more than 3 000 tons of length, more than 120m,the slipway shall be constructed with reinforced concrete and the height difference between the right and left sides shall be less than 20 mm. For ships of more than 1 000 tons but less than or equal to 3 000 tons in weight, or more than 90 m but less than or equal to 120 m in length, the slipway shall be constructed with cement concrete and the height difference between the right and left sides shall be less than 50 mm. For ships of not more than 1 000 tons in weight or not more than 90 m in length, the slipway may be an earthen slope and shall be compacted even by rollers. The height difference between the right and left sides shall be less than 80 mm.
The main slipway shall enable the ship to glide automatically when the ship is off the tow. The auxiliary slipway shall be determined according to the ship type, the water level at time of launching, the diameter of the air bags, and the safety requirements.
Towing arrangement
A windlass shall be used to control the movement of the ship. Tow system that comprises windlass, steel wire rope and pulley set shall be securely fastened to the ground anchor in front of the berth.
In general, a slow windlass shall be selected for ship launching. The veering speed of the windlass shall be 9 m/min to 13 m/min.
The forces of the windlass and the steel wire rope should be calculated carefully by technicians of ship yards or air bags company.
See also
References
- ↑ ISO 17682-2013 Ships and marine technology — Methodology for ship launching utilizing air bags
- ↑ "荣成神飞船舶6200吨成品油轮-SF601下水".
- ↑ ISO14409-Ships and marine technology of Ship launching air bags