Analogue modelling (geology)
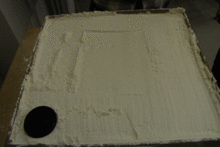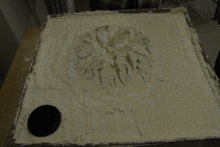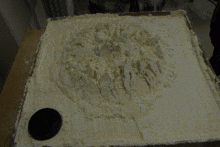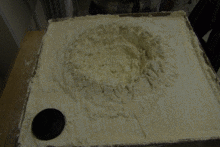
Analogue modelling is used in geology to understand geological processes such as faulting and the emplacement of igneous intrusions, using various materials such as sand, clay, silicone and paraffin wax. These models may be precisely scaled to allow processes that take significant time on a geological timescale to be studied in the laboratory. Analogue models have been used since at least 1812, when James Hall squeezed layers of clay to produce folds similar to those that he had studied at outcrop.[1]
Scaling
In 1937 King Hubbert described the key principles for scaling analogue models. He defined three types of similarity between models and the natural world: geometric, kinematic and dynamic. To be geometrically similar, lengths in the model and natural example must be proportional and angles must be equal. To be kinematically similar, they must be geometrically similar and the time needed for changes to occur must be proportional. Dynamic similarity additionally requires that the various forces acting on a point in the model are proportional to those at a corresponding point in nature [2]

References
- ↑ Ranalli G. (2001). "Experimental tectonics: from Sir James Hall to the present". Journal of Geodynamics. 32 (1-2): 65–76. doi:10.1016/S0264-3707(01)00023-0.
- ↑ Koyi (1997). "Analogue modelling: from a qualitative to a quantitative technique—a historical outline". Journal of Petroleum Geology. 20 (2): 223–238. doi:10.1111/j.1747-5457.1997.tb00774.x.