Operation Anthropoid
| Operation Anthropoid | |
|---|---|
 Heydrich's Mercedes 320 Convertible B after the attack, showing the tank grenade damage | |
| Operational scope | Assassination |
| Location | Prague, Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia (today Czech Republic) |
| Planned | December 1941–May 1942 |
| Planned by | Special Operations Executive |
| Target | Reinhard Heydrich |
| Date | 27 May 1942 |
| Executed by | Jozef Gabčík Jan Kubiš |
| Outcome | Heydrich dies from his wounds, 4 June; Nazis order reprisals
|
Operation Anthropoid was the code name for the assassination of Schutzstaffel (SS)-Obergruppenführer and General der Polizei Reinhard Heydrich, head of the Reichssicherheitshauptamt (Reich Main Security Office, RSHA), the combined security services of Nazi Germany, and acting Reichsprotektor of the Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia.[1] The operation was carried out in Prague on 27 May 1942 after having been prepared by the British Special Operations Executive with the approval of the Czechoslovak government-in-exile. Wounded in the attack, Heydrich died of his injuries on 4 June 1942. His death led to a wave of merciless reprisals by German SS troops, including the destruction of villages and the killing of civilians. Anthropoid was the only successful assassination of a senior Nazi leader during World War II.
Heydrich was one of the most powerful men in Nazi Germany and an important figure in the rise of Adolf Hitler; as a Nazi potentate, he was given overall charge of the so-called Final Solution (Holocaust) of the Jews in Europe. Despite the risks, the Czechoslovaks decided to undertake the operation to help confer legitimacy on Edvard Beneš's government-in-exile in London, as well as for retribution against Heydrich's harsh rule.[2]
Background

Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia
Heydrich had been the chief of the RSHA since September 1939 and was appointed acting Protector of Bohemia and Moravia after replacing Konstantin von Neurath in September 1941. Hitler agreed with Reichsführer-SS Heinrich Himmler and Heydrich that von Neurath's relatively lenient approach to the Czechs promoted anti-German sentiment, and encouraged anti-German resistance by strikes and sabotage.[3] [4]
Heydrich came to Prague to "strengthen policy, carry out countermeasures against resistance", and keep up production quotas of Czech motors and arms that were "extremely important to the German war effort".[4] During his role as de facto dictator of Bohemia and Moravia, Heydrich often drove with his chauffeur in a car with an open roof. This was a show of his confidence in the occupation forces and in the effectiveness of his government.[5] Due to his brutal efficiency, Heydrich was nicknamed the Butcher of Prague, the Blond Beast, and the Hangman.[6]
Strategic context

By late 1941, Hitler controlled almost all of continental Europe, and German forces were approaching Moscow.[7] The Allies deemed Soviet capitulation likely. The exiled government of Czechoslovakia under President Edvard Beneš was under pressure from British intelligence, as there had been very little visible resistance since the occupation of the Sudeten regions of the country in 1938. (Occupation of the whole country began in 1939.) The takeover of these regions was enforced by the Munich Agreement, and the subsequent terror of the German Reich broke the will of the Czechs for a period.
The resistance was active from the very beginning of occupation in several other countries defeated in open warfare (e.g., Poland, Yugoslavia, and Greece), but the subjugated Czech lands remained relatively calm and produced significant amounts of materiel for the Third Reich. The exiled government felt that it had to do something that would inspire the Czechoslovaks as well as show the world that the Czechs and Slovaks were allies. Reinhard Heydrich was chosen over Karl Hermann Frank as an assassination target due to his status as the acting Protector of Bohemia and Moravia as well as his reputation for terrorizing local citizens. The operation was also intended to demonstrate to senior Nazis that they were not beyond the reach of allied forces and the resistance groups they supported.[2]
Operation
Planning
The operation was given the codename Anthropoid, Greek for "having the form of a human", a term usually used in zoology. Preparation began on 20 October 1941 with the British Special Operations Executive (SOE). Warrant Officer Jozef Gabčík (Slovak) and Staff Sergeant Karel Svoboda (Czech) were chosen to carry out the operation on 28 October 1941 (Czechoslovakia's Independence Day).[2] Svoboda was replaced with Jan Kubiš (Czech) after a head injury during training, causing delays in the mission as Kubiš had not completed training, nor had the necessary false documents been prepared for him.[8]
Insertion
Jozef Gabčík and Jan Kubiš were airlifted along with seven soldiers from Czechoslovakia's army-in-exile in the United Kingdom and two other groups named Silver A and Silver B (who had different missions) by a Royal Air Force Halifax of No. 138 Squadron into Czechoslovakia at 22:00 on 28 December 1941. Gabčík and Kubiš landed near Nehvizdy east of Prague. The plan was to land near Pilsen, but the pilots had navigation problems.[9] The soldiers then moved to Pilsen to contact their allies, and from there on to Prague, where the attack was planned.
In Prague, they contacted several families and anti-Nazi organisations who helped them during the preparations for the assassination.[10] Gabčík and Kubiš initially planned to kill Heydrich on a train, but after examination of the practicalities, they realised this was not going to be possible. The second plan was to kill him on the road in the forest on the way from Heydrich's home to Prague. They planned to pull a cable across the road that would stop Heydrich's car but, after waiting several hours, their commander, Lt. Adolf Opálka (from the group Out Distance), came to bring them back to Prague. The third plan was to kill Heydrich in Prague.
The attack in Prague


On 27 May 1942 at 10:30, Heydrich proceeded on his daily commute from his home in Panenské Břežany to Prague Castle. Gabčík and Kubiš waited at the tram stop at a tight curve near Bulovka Hospital in Prague 8-Libeň. The spot was chosen because the curve would force the car to slow down. Josef Valčík (from group Silver A) was positioned about 100 metres (109 yards) north of Gabčík and Kubiš as lookout for the approaching car.
Heydrich's green, open-topped Mercedes 320 Convertible B reached the curve two minutes later. Gabčík stepped in front of the vehicle and tried to open fire with his Sten submachine gun, but it jammed. Heydrich ordered his driver, SS-Oberscharführer Klein, to stop the car, then stood up to shoot Gabčík with his Luger pistol. Kubiš threw a modified anti-tank grenade[12] (concealed in a briefcase) at the vehicle and its fragments ripped through the car's right rear bumper, embedding shrapnel and fibres from the upholstery in Heydrich's body upon detonation, even though the grenade failed to enter the car. The grenade also injured Kubiš.[13]
Following the explosion, Gabčík and Kubiš fired at Heydrich with their Colt M1903 pistols but failed to hit him, as they were shocked by the explosion as well.[14] Heydrich staggered out of the car, apparently unaware of his shrapnel injuries, returned fire, and tried to chase Gabčík, but he soon collapsed. Klein returned from his abortive attempt to chase Kubiš, who fled the scene by bicycle. Now bleeding profusely, Heydrich ordered Klein to chase Gabčík on foot, saying "Get that bastard!".[15] Klein chased him into a butcher shop, where Gabčík shot him twice with his pistol, severely wounding him in the leg, and then escaped to a local safe house via tram.[16][17] Gabčík and Kubiš were initially convinced the attack had failed.
Medical treatment and death
A Czech woman and an off-duty policeman went to Heydrich's aid and flagged down a delivery van. Heydrich was first placed in the driver's cab, but complained that the truck's movement was causing him pain. He was then transferred to the back of the truck, placed on his stomach, and taken to the emergency room at Bulovka Hospital.[18] He had suffered severe injuries to his left side, with major diaphragm, spleen, and lung damage as well as a fractured rib. A Dr. Slanina packed the chest wound, while Dr. Walter Diek (the Sudeten German chief of surgery at the hospital) tried unsuccessfully to remove the splinters.
Professor Hollbaum (a Silesian German who was chairman of surgery at Charles University in Prague) operated on Heydrich with Drs. Diek and Slanina's assistance.[18] The surgeons reinflated the collapsed left lung, removed the tip of the fractured eleventh rib, sutured the torn diaphragm, inserted several catheters, and removed the spleen, which contained a grenade fragment and upholstery material.[19] Heydrich's direct superior Himmler sent his personal physician Karl Gebhardt, who arrived that evening. After 29 May, Heydrich was entirely in the care of SS physicians. Postoperative care included administration of large amounts of morphine.
There are contradictory accounts concerning whether sulfanilamides were given, but Gebhardt testified at his 1947 war crimes trial that they were not.[19] The patient developed a high fever of 38–39 °C (100.4–102.2 °F) and wound drainage. After seven days, his condition appeared to be improving, when he collapsed while sitting up eating a noon meal and went into shock. He spent most of his remaining hours in a coma and died around 04:30 the next morning.[19] Himmler's physicians officially described the cause of death as septicemia.[20]
One of the theories was that some of the horsehair used in the upholstery of Heydrich's car was forced into his body by the blast of the grenade, causing a systemic infection.[21] It has also been suggested that he died of a massive pulmonary embolism. In support of the latter possibility, particles of fat and blood clots were found at autopsy in the right ventricle and pulmonary artery, and severe edema was noted in the upper lobes of the lungs, while the lower lobes were collapsed.[19]
Botulinum poisoning theory
The authors of A Higher Form of Killing claim that Heydrich died from botulism (botulinum poisoning).[22] According to this theory, the No. 73 anti-tank hand grenade used in the attack had been modified to contain botulinum toxin. This story originates from comments made by Paul Fildes, a Porton Down botulism researcher. The authors say that there is only circumstantial evidence to support this allegation[19][23] (the records of the SOE for the period have remained sealed), and few medical records of Heydrich's condition and treatment have been preserved.[19]
The general evidence cited to support the theory includes the modifications made to the No. 73 grenade: the bottom two thirds of this British weapon had been removed, and the open end and sides wrapped up with adhesive tape. The modification of the weapon could indicate an attached toxic or biological payload. Heydrich received excellent medical care by the standards of the time. His autopsy showed none of the usual signs of septicemia, although infection of the wound and areas surrounding the lungs and heart was reported.[19] A German wartime report on the incident stated, "Death occurred as a consequence of lesions in the vital parenchymatous organs caused by bacteria and possibly by poisons carried into them by bomb splinters".
Heydrich's condition while hospitalized was not documented in detail, but he was not noted to have developed any of the distinctive symptoms associated with botulism (which have a gradual, progressive onset, invariably including paralysis, with death generally resulting from respiratory failure). Two others were also wounded by fragments of the same grenade—Kubiš, the Czech soldier who threw the grenade, and a bystander—but neither was reported to have shown any sign of poisoning.[19][24]
The botulinum toxin theory has not found widespread acceptance among scholars for the above reasons. In addition, Fildes had a reputation for "extravagant boasts", the grenade modifications could have been aimed at making the 2 kg weapon lighter, and the toxin would have been unlikely to survive the flight and five months of mid-European winter.[19] Two of the six original modified grenades are kept by the Military History Institute in Prague.[25]
Consequences
Reprisals

Hitler ordered an investigation and reprisals on the very day of the assassination attempt, suggesting that Himmler send SS General Erich von dem Bach-Zelewski to Prague. According to Karl Hermann Frank's postwar testimony, Hitler knew Zelewski to be even harsher than Heydrich.[27] Hitler favored killing 10,000 politically unreliable Czechs but, after he consulted Himmler, the idea was dropped because Czech territory was an important industrial zone for the German military, and indiscriminate killing could reduce the productivity of the region.[28]
The Nazi retaliation ordered by Himmler was brutal, nonetheless. More than 13,000 were arrested, including Jan Kubiš' girlfriend Anna Malinová, who subsequently died in the Mauthausen-Gusen concentration camp. First Lieutenant Adolf Opálka's aunt Marie Opálková was executed in the Mauthausen camp on 24 October 1942;[29] his father Viktor Jarolím was also killed.[30] According to one estimate, 5,000 were killed in reprisals.[31]
Intelligence falsely linked the assassins to the village of Lidice. A Gestapo report identified Lidice as the assailants' suspected hiding place, since several Czech army officers exiled in England at the time were known to have come from there.[32] The village of Lidice was destroyed on 9 June 1942; 199 men were executed, 195 women were immediately deported to Ravensbrück concentration camp, and 95 children taken prisoner. Of the children, 81 were later killed in gas vans at the Chełmno extermination camp, while eight others were taken for adoption by German families. Another Czech village, Ležáky, was also destroyed because a radio transmitter belonging to the Silver A team was found there. All adults were murdered in the village of Ležáky, men and women alike. Both towns were burned, and the ruins of Lidice leveled.[33][34]
The Czech government-in-exile either did not foresee the possibility that the Germans would apply the principle of "collective responsibility" on this scale in avenging Heydrich's assassination, or else they deemed it an acceptable price to pay for eliminating Heydrich and provoking reprisals, that would reduce Czech acquiescence to the German administration. Winston Churchill was infuriated enough to suggest leveling three German villages for every Czech village that the Nazis destroyed. A similar assassination attempt was planned but not approved two years after Heydrich's death, this time targeting Hitler in Operation Foxley.
Operation Anthropoid was the only successful government-organized assassination of a top-ranking Nazi. The Polish underground killed two senior SS officers in the General government (see Operation Kutschera and Operation Bürkl). Also, General-Kommissar of Belarus Wilhelm Kube was killed in Operation Blowup by Soviet partisan Yelena Mazanik, a Belarusian woman who had managed to find employment in his household in order to assassinate him.[35]
Investigation and manhunt
In the days following Lidice, no leads were found for those responsible for Heydrich's death, despite the Nazis' zealous impatience to find them. During that time, a deadline was publicly issued to the military and the people of Czechoslovakia for the assassins to be apprehended by 18 June 1942. If they were not caught by then, the Germans threatened to spill far more blood as a consequence, believing that this threat would be enough to force a potential informant to sell out the culprits. Many civilians were indeed weary and fearful of further retaliations, making it increasingly difficult to hide information much longer. The assailants initially hid with two Prague families and later took refuge in Karel Boromejsky Church, an Eastern Orthodox church dedicated to Sts. Cyril and Methodius in Prague. The Germans were unable to locate the attackers until Karel Čurda of the "Out Distance" sabotage group was arrested and questioned by the Gestapo and gave them the names of the team's local contacts for the bounty of one million Reichsmarks.[36]
Čurda betrayed several safe houses provided by the Jindra group, including that of the Moravec family in Žižkov. At 05:00 on 17 June, the Moravec flat was raided. The family was made to stand in the hallway while the Gestapo searched their flat. Mrs. Marie Moravec was allowed to go to the toilet, where she bit into a cyanide capsule and killed herself. Mr. Alois Moravec was unaware of his family's involvement with the resistance; he was taken to the Petschek Palace together with his 17-year-old son Ata, who was tortured throughout the day but refused to talk. The youth was stupefied with brandy, shown his mother's severed head in a fish tank, and warned that, if he did not reveal the information that they were looking for, his father would be next.[37] Ata's strong willpower finally snapped, and he told the Gestapo what they wanted to know. Vlastimil "Ata" Moravec was executed by the Nazis in Mauthausen on 24 October 1942, the same day as his father, his fiancée, her mother and her brother were executed.[38]
Waffen-SS troops laid siege to the church the following day, but they were unable to take the paratroopers alive, despite the best efforts of 750 SS soldiers under the command of SS-Gruppenführer Karl Fischer von Treuenfeld. Kubiš, Adolf Opálka, and Jaroslav Svarc were killed in the prayer loft after a two-hour gun battle. (Kubiš was said to have survived the battle, but he died shortly after from his injuries.)[39] Gabčík, Josef Valcik, Josef Bublik, and Jan Hruby committed suicide in the crypt after repeated SS attacks, attempts to smoke them out with tear gas, and Prague fire brigade trucks brought in to try to flood the crypt.[40] The German SS and police suffered casualties, as well, with 14 SS allegedly killed and 21 wounded, according to one report,[41][42] although the official SS report about the fight mentioned only five wounded SS soldiers.[43] The men in the church had only small-caliber pistols, while the attackers had machine guns, submachine guns, and hand grenades. After the battle, Čurda confirmed the identity of the dead Czech resistance fighters, including Kubiš and Gabčík.
Bishop Gorazd took the blame for the actions in the church, in an attempt to minimize the reprisals among his flock, and even wrote letters to the Nazi authorities, who arrested him on 27 June 1942 and tortured him. On 4 September 1942, the bishop, the church's priests, and senior lay leaders were taken to Kobylisy Shooting Range in a northern suburb of Prague and shot by Nazi firing squads. For his actions, Bishop Gorazd was later glorified as a martyr by the Eastern Orthodox Church.
Political consequence and aftermath
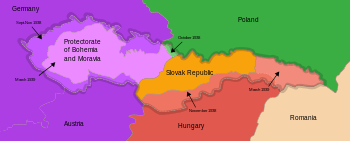
The assassination of Heydrich was one of the most significant moments of the resistance in Czechoslovakia. The act had such an impact that it led to the immediate dissolution of the Munich Agreement (called the "Munich diktat" by the Czechs) signed by Great Britain, France, and Germany's ally Italy. Britain and France agreed that, after the Nazis were defeated, the annexed territory (Sudetenland) would be restored to Czechoslovakia.
Two large funeral ceremonies were performed for Heydrich as one of the most important Nazi leaders: first in Prague, where the way to Prague Castle was lined by thousands of SS men with torches, and then in Berlin attended by all leading Nazi figures, including Hitler, who placed the German Order and Blood Order medals on the funeral pillow.[44]
The betrayer Karel Čurda was hanged for high treason in 1947, after attempting suicide.[45][46]
Memorials


The National Memorial to the Heroes of the Heydrich Terror is beneath the Orthodox Cathedral of Saints Cyril and Methodius in Prague.
The Slovak National Museum opened an exhibition in May 2007 to commemorate the heroes of the Czech and Slovak resistance, presenting one of the most important resistance actions in the whole of German-occupied Europe. There is a small fountain commemorating the bravery of the troops located in the Jephson Gardens, Leamington Spa, Warwickshire (one of the places where the Czech Free Army were based).
The Anthropoid Operation Memorial, 2009, Prague, authors: sculptor David Mojescik and sculptor Michal Smeral; architects: M. Tumova and J. Gulbis.

There is also a memorial in Arisaig, Scotland to the Czechoslovakian members of SOE who trained in that area, with a list of those killed and the missions in which they took part.[47]
Portrayals in literature and popular culture
Operation Anthropoid is the basis for the films Hangmen Also Die and Hitler's Madman (1943); Atentát (1964), Operation Daybreak (1975), Bullet for Heydrich (2013),[48] Anthropoid (2016), and HHhH.[49]
It is also the subject of several books, including:
- Seven Men at Daybreak (1960) by Alan Burgess
- The Killing of SS-Obergruppenführer Reinhard Heydrich (1998) by Callum MacDonald
- the novel The Visible World (2008) by Mark Slouka
- The Mirror Caught the Sun: Operation Anthropoid 1942 (2009) by John Martin
- the novel HHhH (2010) by Laurent Binet, winner of that year's Prix Goncourt du premier roman
- the novel Resistance (2012) by Gerald Brennan
- the novel Mendelssohn Is on the Roof by Jiří Weil
- the novel No Known Graves by Maureen Jennings
- the novel Hunting the Predator (2007) by Jiří Šulc (originally published in Czech as cs:Dva proti Říši), winner of that year's Book Club Literary Prize
- Operation daybreak, a 1975 movie.
- Anthropoid 2016, movie starring Cillian Murphy
The short story "The Assassination of Reinhard Heydrich" by Jim Shepard gives a fictionalized account of Operation Anthropoid from Kubiš's point of view.
The operation is the subject of the song "A Lovely Day Tomorrow" by the English band British Sea Power. The song was released as an EP containing Czech and English versions in collaboration with the Czech band The Ecstasy of Saint Theresa (band)
It is also the subject of the song "Anthropoid" from the album VII: Sturm und Drang by Richmond, Virginia–based groove metal band Lamb of God.
Gallery
Ss. Cyril and Methodius Cathedral, where the Czechoslovak paratroopers died after being cornered, and the memorial there for those killed by the SS in retaliation for Operation Anthropoid.
 Orthodox church of Saints Cyril and Methodius
Orthodox church of Saints Cyril and Methodius Photo of memorial outside door of the church
Photo of memorial outside door of the church Reward poster for Sgt. Josef Valčík, one of the assassins of Heydrich
Reward poster for Sgt. Josef Valčík, one of the assassins of Heydrich- Sgt. Jan Hrubý died in the fight with German troops in the crypt of the church of Saint Cyril and Methodius
 Memorial in the crypt of the Church of St. Cyril and St. Methodius
Memorial in the crypt of the Church of St. Cyril and St. Methodius
See also
- Czech resistance to Nazi occupation
- Occupation of Czechoslovakia
- Operation Foxley – SOE plot to kill Adolf Hitler in 1944
- Operation Kutschera – Polish assassination of the SS and Police Leader Franz Kutschera in 1944
- Lidice
- List of Nazi Party leaders and officials
- List of rulers of the Protectorate Bohemia and Moravia
Notes
- ↑ McNab 2009, pp. 41, 158-161.
- 1 2 3 Burian 2002, p. 31.
- ↑ Longerich 2012, pp. 469, 470.
- 1 2 Williams 2003, p. 82.
- ↑ Williams 2003, p. 141.
- ↑ Ramen, Fred. Reinhard Heydrich: Hangman of the Third Reich, p 8. ISBN 0-8239-3379-2
- ↑ Shepherd, Ammon (2008). "World War II — Timeline". Retrieved 7 July 2008.
- ↑ Burian 2002, p. 35.
- ↑ Burian 2002, p. 44.
- ↑ Burian 2002, p. pp=48–49.
- ↑ "Proč výsadkář Gabčík nevystřelil? Archiv konečně vydal důkaz". Aktuálně.cz - Víte co se právě děje.
- ↑ Michel, Wolfgang, Britische Spezialwaffen 1939–1945: Ausrüstung für Eliteeinheiten, Geheimdienst und Widerstand, p. 72. ISBN 3-8423-3944-5
- ↑ Williams 2003, pp. 145–147.
- ↑ "Nová tajemství muže, který zabil Reinharda Heydricha". Aktuálně.cz - Víte co se právě děje.
- ↑ Williams 2003, pp. 147, 155.
- ↑ Burgess, Alan, Seven Men At Daybreak, p. 160. ISBN 0-553-23508-7
- ↑ Burian 2002, p. 64.
- 1 2 Williams 2003, p. 155.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Defalque, R. J.; Wright, A. J. (January 2009). "The Puzzling Death of Reinhard Heydrich" (PDF). Bulletin of Anesthesia History. Pittsburgh PA: Anesthesia History Association and Wood-Library Museum of Anesthesiology. 27 (1): 1–7. Retrieved 29 May 2009.
- ↑ Burian 2002, p. 65.
- ↑ MacDonald 1998, pp. 182–183.
- ↑ Harris, Robert; Paxman, Jeremy (1982). A Higher Form of Killing: The Secret History of Chemical and Biological Warfare. London: Chatto & Windus. pp. chapter 4, pp. 70–108. ISBN 978-0-8129-6653-4. OCLC 8261705.
- ↑ Carus, W. Seth (2001). Bioterrorism and Biocrimes: The Illicit Use of Biological Agents Since 1900. The Minerva Group, Inc. p. 89. ISBN 1-4101-0023-5.
- ↑ Middlebrook and Franz (1998). Botulinum toxins (PDF). Office of The Surgeon General, Department of the Army, United States of America.
- ↑ http://aktualne.centrum.cz/domaci/spolecnost/clanek.phtml?id=746282 Grenades in The Military History Institute (acc to Eduard Stehlík).
- ↑ "List of people executed in Mauthausen-Gusen concentration camp". Fronta.cz.
- ↑ Dederichs 2009, pp. 150–151.
- ↑ Dederichs 2009, p. 151.
- ↑ "SPOLEK PRO VOJENSKÁ PIETNÍ MÍSTA, O. S. – VPM okres Znojmo – Rešice". Vets.estranky.cz. Retrieved 12 January 2012.
- ↑ "SPOLEK PRO VOJENSKÁ PIETNÍ MÍSTA, O. S. – VPM okres Znojmo – Vémyslice". Vets.estranky.cz. Retrieved 12 January 2012.
- ↑ "Radio Prague - Heroes or cowards? Czechs in World War II".
- ↑ Dederichs 2009, pp. 151–152.
- ↑ MacDonald 1998, pp. 186, 187.
- ↑ Dederichs 2009, p. 152.
- ↑ Vasiliy Tsvetkov. "A BOMB FOR GAULEITER". De Bello. Retrieved 2012-12-24.
- ↑ "The Assassination of Reinhard Heydrich", The Holocaust Education & Archive Research Team
- ↑ MacDonald 1998, p. 202.
- ↑ "The attentat on SS Obergruppenführer Reinhard Heydrich".
- ↑ MacDonald 1998.
- ↑ Burgess, Alan, Seven Men At Daybreak. ISBN 0-553-23508-7
- ↑ "Last fight of Heydrich's killers - Axis History Forum". Axis History Forum.
- ↑ Cowdery, Ray R. & Vodenka, Peter, Reinhard Heydrich: Assassination. Victory WW2 Publishing Ltd. (1994) Lakeville, MN, USA
- ↑ Karl von Treuenfeld: Report about the employment of Waffen-SS 23 June 1942 (in Czech translation)
- ↑ Williams 2003, p. 223.
- ↑ "Czech Traitors Hanged Today", 1947, The Free Lance-Star
- ↑ "Trial and terror in a by-gone Prague", 2007, The Telegraph
- ↑ Arisaig, Czechoslovakian Special Operations Executive Training Memorial Canmore.
- ↑ "Kulka pro Heydricha (TV film) (2013) | Galerie". CSFD.cz. Retrieved 20 July 2016.
- ↑ FNE Staff. "Fifty Shades Star Jamie Dornan to Play Czech Soldier". FilmNewEurope.com.
References
- Burian, Michal (2002). "Assassination — Operation Arthropoid, 1941–1942" (PDF). Ministry of Defence of the Czech Republic. Retrieved 20 May 2010.
- Dederichs, Mario R. (2009) [2005]. Heydrich: The Face of Evil. Drexel Hill, PA: Casemate. ISBN 978-1-935149-12-5.
- Longerich, Peter (2012). Heinrich Himmler: A Life. Oxford; New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-959232-6.
- MacDonald, Callum (1998) [1989]. The Killing of Reinhard Heydrich: The SS 'Butcher of Prague'. New York: Da Capo Press. ISBN 978-0-306-80860-9.
- McNab, Chris (2009). The SS: 1923–1945. London: Amber Books. ISBN 978-1-906626-48-8.
- Williams, Max (2003). Reinhard Heydrich: The Biography, Volume 2—Enigma. Church Stretton: Ulric Publishing. ISBN 978-0-9537577-6-3.
Further reading
- Wiener, Jan G. (2012) [1969 (Grossman Publishers)]. The Assassination of Heydrich. Gerald Hausman (Epilogue), William L. Shirer (Introduction). New York: Irie Books. ISBN 978-1-61720-372-5. OCLC 247895.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Operation Anthropoid. |
- National Memorial to the Heroes of the Heydrich Terror
- Radio Prague: Czechs in World War II
- Radio Prague: Exhibitions mark 60th anniversary of assassination of Nazi governor Heydrich
- Operation Anthropoid at Everything2
- Czechs in Exile website
- Exhibition on Operation Anthropoid at the Slovak Nation Museum
- The Prague Daily Monitor: Experts find wartime paratroopers' grave
- RCAHMS record for Arisaig memorial
- Highland HER entry for Arisaig memorial
Coordinates: 50°7′4″N 14°27′51″E / 50.11778°N 14.46417°E


.svg.png)