Bain-marie

A bain-marie (pronounced: [bɛ̃ maʁi]; also known as a water bath or double boiler), a type of heated bath, is a piece of equipment used in science, industry, and cooking to heat materials gently and gradually to fixed temperatures, or to keep materials warm over a period of time. A bain-marie is also used to melt ingredients for cooking.
Description
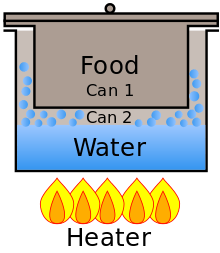
The bain-marie comes in a wide variety of shapes, sizes, and types, but traditionally is a wide, cylindrical, usually metal container made of three or four basic parts: a handle, an outer (or lower) container that holds the working fluid, an inner (or upper), smaller container that fits inside the outer one and which holds the material to be heated or cooked, and sometimes a base underneath. Under the outer container of the bain-marie (or built into its base) is a heat source.
Typically the inner container is immersed about halfway into the working fluid.
The smaller container, filled with the substance to be heated, fits inside the outer container, filled with the working fluid (usually water), and the whole is heated at, or below, the base, causing the temperature of the materials in both containers to rise as needed. The insulating action of the water helps to keep contents of the inner pot from boiling or scorching.
When the working fluid is water and the bain-marie is used at sea level, the maximum temperature of the material in the lower container will not exceed 100 degrees Celsius (212 °F), the boiling point of water at sea level. Using different working fluids (oils, salt solutions, etc.) in the lower container will result in different maximum temperatures.
Alternatives
A contemporary alternative to the traditional, liquid-filled bain-marie is the electric "dry-heat" bain-marie, heated by elements below both pots. The dry-heat form of electric bains-marie often consumes less energy, requires little cleaning, and can be heated more quickly than traditional versions. They can also operate at higher temperatures, and are often much less expensive than their traditional counterparts.
Electric bains-marie can also be wet, using either hot water or vapor, or steam, in the heating process. The open, bath-type bain-marie heats via a small, hot-water tub (or "bath"), and the vapour-type bain-marie heats with scalding-hot steam.
Culinary applications
- Chocolate can be melted in a bain-marie to avoid splitting and caking onto the pot. Special dessert bains-marie have a thermally insulated container and are used as a chocolate fondue.
- Cheesecake is often baked in a bain-marie to prevent the top from cracking in the centre.
- Custard may be cooked in a bain-marie to keep a crust from forming on the outside of the custard before the interior is fully cooked. In the case of the crème brûlée, placing the ramekins in a roasting pan and filling the pan with hot water until it is 1/2 to 2/3 of the way up the sides of the ramekins transfers the heat to the custard gently, which prevents the custard from curdling. The humidity from the steam that rises as the water heats helps keep the top of the custard from becoming too dry.[1]
- Classic warm sauces, such as Hollandaise and beurre blanc, requiring heat to emulsify the mixture but not enough to curdle or "split" the sauce, are often cooked using a bain-marie.
- Some charcuterie such as terrines and pâtés are cooked in an "oven-type" bain-marie.
- Thickening of condensed milk, such as in confection-making, is done easily in a bain-marie.
- Controlled-temperature bains-marie can be used to heat frozen breast milk before feedings.
- Bains-marie can be used in place of chafing dishes for keeping foods warm for long periods of time, where stovetops or hot plates are inconvenient or too powerful.
- A bain-marie can be used to re-liquefy hardened honey by placing a glass jar on top of any improvised platform sitting at the bottom of a pot of gently boiling water.
Other uses
In small scale soap-making, a bain-marie's inherent control over maximum temperature makes it optimal for liquifying melt-and-pour soap bases prior to moulding into bars. It offers the advantage of maintaining the base in a liquid state, or re-liquifying solidified base, with minimal deterioration. Similarly, using a water bath, traditional wood glue can be melted and kept in a stable liquid state over many hours without damaging the volatile saps and resins it incorporates.
History
.tif.jpg)
The name comes from the medieval-Latin term balneum (or balineum) Mariae — literally, Mary's bath — from which the French bain de Marie, or bain-marie, is derived. The device's invention has been popularly attributed to Mary the Jewess, an ancient alchemist. However, the water bath was known many centuries earlier (Hippocrates and Theophrastus).[2]
See also
References
- ↑ "Techniques: Bain Marie". DrGourmet.com. Archived from the original on 4 June 2011. Retrieved 2011-07-20.
- ↑ Edmund Lippmann (1919), Entstehung und Ausbreitung der Alchemie, Springer, p. 50
| Look up bain marie in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |