Bifurcated ligament
| Bifurcated ligament | |
|---|---|
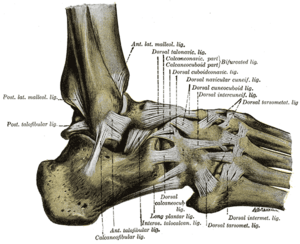 The ligaments of the foot from the lateral aspect (bifurcated ligament labeled at upper right) | |
 Talocalcaneal and talocalcaneonavicular articulations exposed from above by removing the talus (bifurcated ligament labeled at upper right) | |
| Details | |
| From | Calcaneus |
| To | cuboid and navicular bone |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Ligamentum bifurcatum |
| TA | A03.6.10.511 |
| FMA | 44216 |
The bifurcated ligament (internal calcaneocuboid, interosseous ligament or bifurcate ligament) is a strong band, attached behind to the deep hollow on the upper surface of the calcaneus and dividing in front in a Y-shaped manner into a calcaneocuboid and a calcaneonavicular part.
- The calcaneocuboid ligament (ligamentum calcaneocuboideum) is fixed to the medial side of the cuboid and forms one of the principal bonds between the first and second rows of the tarsal bones.
- The calcaneonavicular ligament (ligamentum calcaneonaviculare) is attached to the lateral side of the navicular.
It is commonly injured in "sprain-type" inversion injuries producing an avulsion fracture at the anterolateral process of the calcaneus.[1]
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ↑ David A. Porter (2008). Baxter, Donald E.; Porter, David A.; Schon, Lew, eds. Baxter's The Foot and Ankle in Sport (2nd (illustrated) ed.). Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 297. ISBN 9780323023580.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/5/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.