Brassy trevally
| Brassy trevally | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Actinopterygii |
| Order: | Perciformes |
| Suborder: | Percoidei |
| Superfamily: | Percoidea |
| Family: | Carangidae |
| Genus: | Caranx |
| Species: | C. papuensis |
| Binomial name | |
| Caranx papuensis Alleyne & W. J. Macleay, 1877 | |
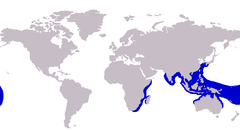 | |
| Approximate range of the brassy trevally | |
| Synonyms | |
The brassy trevally, Caranx papuensis (also known as the brassy kingfish, Papuan trevally, tea-leaf trevally and green back trevally) is a species of large marine fish classified in the jack family, Carangidae. The brassy trevally is distributed throughout the tropical waters of the Indian and West Pacific Oceans, ranging from South Africa in the west to the Marquesas Islands in the east, including Australia to the south and Japan in the north. The brassy trevally is best distinguished by its colouration, having small black spots scattered above and below its lateral line, with a narrow white outside edge to its lower caudal fin. The species grows to a known maximum length of 88 cm and a weight of at least 6.4 kg. It predominantly inhabits both coastal and offshore reefs, as well as inshore lagoons, bays and even estuarine waters as a juvenile. It is a predatory species, moving either individually or small schools, where it takes small fish and occasionally squid and crustaceans. Nothing is known of its reproductive cycle. The brassy trevally is not of great importance to commercial fisheries, but is taken in many netting and hook and line operations throughout its range. It is valued as a gamefish by anglers and spearfishermen, and is considered an excellent table fish.
Taxonomy and naming
The brassy trevally is classified within the genus Caranx, one of a number of groups known as the jacks or trevallies. Caranx itself is part of the larger jack and horse mackerel family Carangidae, a group of percoid fishes in the order Perciformes.[1]
The species was first scientifically described by the Australian zoologists Haynes Gibbs Alleyne and William John Macleay in 1877 based on a specimen collected from Hall Sound off Papua New Guinea which was designated to be the holotype.[2] They named the species Caranx papuensis, with the specific epithet taking its name from Papua New Guinea where the holotype was taken.[3] They referred the species to the genus Caranx, where it has remained. The species was independently redescribed twice; the first by Samuel Garman, who applied the name Caranx regularis and then by J.L.B. Smith with the name Caranx celetus.[4] The species was apparently widely confused with the now dubious Caranx sansun,[5] a move which resulted in Smith trying to resolve the taxon by renaming the species that had been identified as C. sansun,[6] which led to several now defunct junior synonyms.
The species is commonly referred to as the 'brassy trevally', 'tea-leaf trevally' or 'green back trevally' in reference to its colouration, while 'Papuan trevally' is used in reference to the specific epithet.[4]
Description

The brassy trevally is a large species of fish, growing to a known maximum of 88 cm in length and 6.4 kg in weight.[4] It is often confused with the giant trevally, Caranx ignobilis, but is best distinguished by its lighter dorsal colouring and abundant black spots. It is similar in general appearance to most jacks in the genus, having a compressed, oblong body, with the dorsal profile more convex than the ventral profile, particularly anteriorly.[7] The dorsal fin is in two distinct parts; the first consisting of 8 spine and the second of 1 spine and 21 to 23 soft rays. The anal fin consists of 2 anteriorly detached spines followed by 1 spine and 16 to 19 soft rays,[8] while the pelvic fins have 1 spine followed by 19 to 20 soft rays. The lateral line is moderately arched anteriorly, with 53 to 61 scales in this section, while the straight section contains 0 to 3 scales and 31 to 39 strong scutes. The breast is naked ventrally with the exception of a small patch of scales before the pelvic fin.[9] The species has weakly developed adipose eyelids, while its dentition consists of an outer row of widely spaced canines and an inner band of villiform teeth in the upper jaw with a row of widely spaced conical teeth on the lower jaw. The brassy trevally has 26 to 30 gill rakers and 24 vertebrae.[7]
As its name suggests, the brassy trevally is a brassy to yellow greenish colour dorsally, becoming silvery white on the underside. Juveniles generally lack the brassy tinge, being silver all over.[9] The species head and body above the lateral line is scattered with small black spots, with few spots occasionally much lower near the pectoral fins. These spots become more numerous with age. The species also has a conspicuous pale silvery-white spot with black margins shoulder near the upper opercle. The fins are yellow to dusky with the exception of the caudal fin which has a dusky upper lobe and a dusky to yellow lower lobe and distinctive narrow white band on the trailing edge.[7][8]
Distribution and habitat

The brassy trevally is widespread throughout the tropical and subtropical waters of the Indian and West Pacific Oceans. Its range extends from South Africa and Madagascar north along the east African coast, but no records of the species are known from the Red Sea or Persian Gulf. Records resume from India eastward throughout South East Asia, the Indonesian Archipelago and numerous Indian Ocean and east Pacific island groups. The species is known from as far south as Sydney, Australia[10] and as far north as the Ryukyu Islands of Japan. Its range extends eastward to the Marquesas Islands in the central Pacific.[4][7]
The brassy trevally inhabits both inshore and offshore environments, predominantly inhabiting the seaward side of reef complexes or deep water pinnacles as an adult.[11] Other habitats the species is known from include rock outcrops in sandy bays and lagoons,[12] while juveniles are often found in tidal mangrove lined creeks in turbid waters.[13] Juveniles are also found in estuaries throughout their range, occasionally extending to the upper reaches of rivers.[14][15][16]
Biology and fishery
The brassy trevally is a predatory fish, traveling either individually or in small schools, where it hunts down a variety of prey including small fish, squid, prawns and crabs.[11] Studies on the species in Natal estuaries found juveniles take predominantly crustaceans as prey, switching to teleosts as they mature.[14] Other aspects of the species biology are poorly understood, including reproduction and movements, although catch data indicates higher numbers occur in South Africa in summer.[11]
As other fish, the brassy trevally is the host of various parasites. Internal parasites include the bucephalid digenean Prosorhynchoides lamprelli in the intestine[17] and external parasites include the protomicrocotylid monogenean Lethacotyle vera on the gills.[18]
The brassy trevally is not of high importance to commercial fisheries, often finding its way to market as bycatch in various netting and hook and line fisheries.[7] Catch statistics are not kept for the species. The species is of some importance to recreational fishermen, and is considered a good gamefish and is often taken by various fish baits as well as lures and flies.[19] Despite this, it is rarely targeted by anglers, who overlook it for larger relatives such as giant trevally and bluefin trevally,[20] with the species often being an incidental catch, and rarely kept.[21] The species is also commonly taken by spearfishermen. Brassy trevally is considered to be an excellent table fish.[11] The species has been held in large saltwater aquaria, with studies at the Reunion Island Aquarium reporting the species adjusts to aquarium life, but needs a large tank.[22]
References
- ↑ "Caranx papuensis". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved 14 April 2009.
- ↑ Hosese, D.F.; Bray, D.J.; Paxton, J.R.; Alen, G.R. (2007). Zoological Catalogue of Australia Vol. 35 (2) Fishes. Sydney: CSIRO. p. 1150. ISBN 978-0-643-09334-8.
- ↑ Alleyne, Haynes G.; William J. Macleay (1877). "The Ichthyology of the Chevert Expedition". Proceedings of the Linnean Society of New South Wales. 1 (3–4): 261–281. ISSN 0370-047X.
- 1 2 3 4 Froese, Rainer and Pauly, Daniel, eds. (2009). "Caranx papuensis" in FishBase. April 2009 version.
- ↑ Fricke, R. (1999). Fishes of the Mascarene Islands (Réunion, Mauritius, Rodriguez): an annotated checklist, with descriptions of new species. Koeltz Scientific Books. p. 759. ISBN 978-3-87429-411-9.
- ↑ Smith, J.L.B. (1968). "Studies in carangid fishes No. 4. The identity of Scomber sansun Forsskal, 1775". Occasional Papers of the Department of Ichthyology, Rhodes University. 15: 173–184. ISSN 0075-207X.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Smith-Vaniz, W. (1999). "Carangidae". In Carpenter, K.E.; Niem, V.H. The living marine resources of the Western Central Pacific Vol 4. Bony fishes part 2 (Mugilidae to Carangidae) (PDF). FAO species identification guide for fishery purposes. Rome: FAO. pp. 2659–2757. ISBN 92-5-104301-9.
- 1 2 Randall, John Ernest; Roger C. Steene; Gerald R. Allen (1997). Fishes of the Great Barrier Reef and Coral Sea. University of Hawaii Press. p. 161. ISBN 0-8248-1895-4.
- 1 2 Lin, Pai-Lei; Shao, Kwang-Tsao (1999). "A Review of the Carangid Fishes (Family Carangidae) From Taiwan with Descriptions of Four New Records". Zoological Studies. 38 (1): 33–68.
- ↑ Hutchins, B.; Swainston, R. (1986). Sea Fishes of Southern Australia: Complete Field Guide for Anglers and Divers. Melbourne: Swainston Publishing. p. 187. ISBN 1-86252-661-3.
- 1 2 3 4 van der Elst, Rudy; Peter Borchert (1994). A Guide to the Common Sea Fishes of Southern Africa. New Holland Publishers. p. 142. ISBN 1-86825-394-5.
- ↑ Kulbicki, M.; N. Guillemot; M. Amand (2005). "Ageneral approach to length-weight relationships for New Caledonian lagoon fishes" (PDF). Cybium. 29 (3): 235–252. Retrieved 2009-05-13.
- ↑ Laroche, J.; E. Baran; Rsoandrasana, N.B. (1997). "Temporal patterns in a fish assemblage of a semiarid mangrove zone in Madagascar". Journal of Fish Biology. 51 (1): 3–20. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8649.1997.tb02509.x. PMID 9236084.
- 1 2 Blaber, S.J.M.; Cyrus, D.P. (1983). "The biology of Carangidae (Teleostei) in Natal estuaries". Journal of Fish Biology. 22 (2): 173–188. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8649.1983.tb04738.x.
- ↑ Blaber, S.J.M.; J.P. Salini; D.T. Brewer (1990). "A Checklist of the Fishes of Albatross Bay and the Embley Estuary, North Eastern Gulf of Carpentaria" (PDF). CSIRO Marine Laboratories Report. Hobart, Tas.: CSIRO Marine. No. 210: 1–23. ISBN 0-643-05032-9. ISSN 0725-4598. Retrieved 2009-03-13.
- ↑ Kuo, S.R.; H.J. Lin; K.T. Shao (1999). "Fish Assemblages in the Mangrove Creeks of Northern and Southern Taiwan". Estuaries. Coastal and Estuarine Research Federation. 22 (4): 1004–1015. doi:10.2307/1353079. ISSN 0160-8347. JSTOR 1353079.
- ↑ Bray, R. A. & Justine, J.-L. 2006: Prosorhynchus maternus sp. n. (Digenea: Bucephalidae) from the Malabar grouper Epinephelus malabaricus (Perciformes: Serranidae) off New Caledonia. Folia Parasitologica, 53, 181-188. doi:10.14411/fp.2006.024
- ↑ Justine J-L, Rahmouni C, Gey D, Schoelinck C, Hoberg EP (2013). "The Monogenean which lost its clamps". PLOS ONE. 8 (11): e79155. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0079155. PMC 3838368
 . PMID 24278118.
. PMID 24278118. - ↑ Hansford-Steele, B. (2004). African Fly-fishing Handbook. Struik. p. 472. ISBN 978-1-86872-882-4.
- ↑ Knaggs, B. (2008). Knaggs, B., ed. "12 Rounds with Trevally". Saltwater Fishing. Silverwater, NSW: Express Publications (58): 72–80.
- ↑ Williamson, P.C.; N.R. Sumner; B.E. Malseed (2006). "A 12-month survey of recreational fishing in the Pilbara region of Western Australia during 1999-2000" (PDF). Fisheries Research Report. Department of Fisheries, Perth, Western Australia. No. 153: 1–64. Retrieved 2009-05-13.
- ↑ Mulochau and, T.; P. Durville (2005). "A review of the movements of fish held in captivity in the Reunion Island Aquarium over a five-year period" (PDF). SPC Live Reef Fish Information Bulletin. 15: 13–18. Retrieved 2009-05-13.