Chromosome 19 (human)
| Chromosome 19 (human) | |
|---|---|
 Pair of human chromosome 19 (after G-banding). One is from mother, one is from father. | |
 Chromosome 19 pair in human male karyogram. | |
| Features | |
| Length (bp) | 58,617,616 bp[1] |
| Number of genes |
2,188 [2] 2,670[3] |
| Type | Autosome |
| Centromere position | Metacentric[4] |
| Identifiers | |
| RefSeq | NC_000019 |
| GenBank | CM000681 |
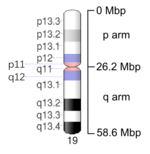
Ideogram of human chromosome 19. Mbp means mega base pair. See locus for other notation.
Chromosome 19 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 19 spans more than 58.6 million base pairs, the building material of DNA.
Identifying genes on each chromosome is an active area of genetic research. Because researchers use different approaches to predict the number of genes on each chromosome, the estimated number of genes varies. Depending on the genome annotation used, chromosome 19 contains 2,188 or 2,670 genes,[2][3] and chromosome 19 thereby has the highest gene density of all the 23 chromosomes.
Genes
The following are some of the genes located on chromosome 19:
- ACSBG2: encoding enzyme Long-chain-fatty-acid—CoA ligase
- ARMC6: encoding protein Armadillo repeat-containing protein 6
- BTBD14B/NACC1: encoding protein Nucleus accumbens-associated protein 1
- ATPase ASNA1: encoding enzyme ATPase ASNA1 also known as arsenical pump-driving ATPase and arsenite-stimulated ATPase
- KLK3: The Prostate-specific antigen (PSA)
- NWD1: NACHT and WD repeat domain containing 1.
- PEX11G: peroxisomal biogenesis factor 11 gamma
- PRX: Periaxin
- SLC5A5: Solute carrier family 5 (sodium iodide symporter), member 5
- STK11: Serine/threonine kinase 11 (Peutz-Jeghers syndrome)
- ZNF649: Transcriptional suppressor
Short arm
- CACNA1A: Calcium channel, voltage-dependent, P/Q type, alpha 1A subunit (Familial hemiplegic migraine Type I). Gene map locus 19p13
- COMP: Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein. Gene map locus 19p13.1
- NOTCH3: Notch homolog 3 (Drosophila): Gene map locus 19p13.1-p13.2
- GCDH: Glutaryl-Coenzyme A dehydrogenase. Gene map locus 19p13.2
- BSG: Basigin (Ok blood group)/Extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer/CD147. Gene map locus 19p13.3
- ICAM4: Landsteiner and Weiner glycoprotein. Gene map locus 19p13.3
- NRTN: Neurturin, associated with Hirschsprung's disease: Gene locus map 19p13.3
- HCL1: Hair Colour 1; Brown hair colour; BRHC. Gene map locus 19p13.1-q13.11 OMIM: 113750
- EYCL1: Eye Colour 1; Eye colour, green/blue; GEY. Gene map locus 19p13.1-q13.11 OMIM: 227240
- KLF2: Krüppel-like factor 2, also known as Lung Krüppel-like factor. Gene map locus 19p13.11 OMIM: 602016
Long arm
- HAMP: Hepcidin antimicrobial peptide. Gene map locus 19q13.12
- BCKDHA: Branched chain keto acid dehydrogenase E1, alpha polypeptide (maple syrup urine disease). Gene map location 19q13.1-q13.2
- APOE: Apolipoprotein E, gene associated with Alzheimer's disease. Gene map locus 19q13.2
- ATP1A3: ATPase. Gene map locus 19q13.31
- DMPK: Dystrophia myotonica-protein kinase. Gene map locus 19q13.32
- A1BG: Plasma glycoprotein, unknown function. Gene map locus 19q13.43
- LRC: The Leukocyte Receptor Complex is a family of immunoreceptors expressed predominantly on monocytes and B cells and at lower levels on dendritic cells and natural killer (NK) cells. The LRC also includes the KIR locus. Gene map locus 19q13.4 OMIM: 604812
- KPTN: Kaptin (actin binding protein) at the tips of stereocilia. Gene map locus 19q13.4[5]
- FUT1: The H locus is located on chromosome 19 at 19q13.3. It contains three exons that span more than 5 kb of genomic DNA, and it encodes a fucosyltransferase that produces the H antigen on RBCs.[6]
- FUT2: The Se locus is located on chromosome 19 at 19q13.3. It contains two exons that span about 25 kb of genomic DNA. The Se locus encodes a specific fucosyltransferase that is expressed in the epithelia of secretory tissues, such as salivary glands, the gastrointestinal tract, and the respiratory tract. The enzyme it encodes catalyzes the production of H antigen.[6]
- MORT (Mortal Obligate RNA Transcript, lincRNA): Gene map locus 19q13.43
Diseases and disorders
The following diseases are some of those related to genes on chromosome 19:[7]
- Alternating hemiplegia of childhood
- Alzheimer's disease
- CADASIL
- Centronuclear myopathy autosomal dominant form
- Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease
- Congenital hypothyroidism
- Congenital hearing loss
- Donohue syndrome
- Familial hemiplegic migraine
- Glutaric acidemia type 1
- Hemochromatosis
- Leber's Congenital Amaurosis[8]
- Maple syrup urine disease
- Multiple epiphyseal dysplasia
- Myotonic dystrophy
- Myotubular myopathy autosomal dominant form
- Marfan Syndrome
- Oligodendroglioma
- Peutz-Jeghers syndrome
- Pseudoachondroplasia
- Spinocerebellar ataxia type-6
- X-linked agammaglobulinemia or Bruton's Disease
- Prolidase deficiency
References
- ↑ "Homo sapiens chromosome 19, GRCh37.p13 Primary Assembly". Nucleotide. National Center for Biotechnology Information. NC_000019.10.
- 1 2 "Homo sapiens (human) Chromosome 19". NCBI Map Viewer. National Center for Biotechnology Information. Retrieved October 17, 2013.
- 1 2 "Homo sapiens: Chromosome summary: Chromosome 19: 1-58,617,616". Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute. Vega Genome Browser 58. Retrieved November 2014. Check date values in:
|access-date=(help) - ↑ "Table 2.3: Human chromosome groups". Human Molecular Genetics (2nd ed.). Garland Science. 1999.
- ↑ Bearer EL, Chen AF, Chen AH, Li Z, Mark HF, Smith RJ, Jackson CL (2000). "2E4/Kaptin (KPTN)—a candidate gene for the hearing loss locus, DFNA4". Ann Hum Genet. 64 (3): 189–196. doi:10.1046/j.1469-1809.2000.6430189.x. PMC 3376086
 . PMID 11409409.
. PMID 11409409. - 1 2 Dean, L. (2005). "Ch. 5: The ABO blood group". Blood Groups and Red Cell Antigens. Bethesda MD: National Center for Biotechnology Information. NBK2261.
- ↑ Gilbert F (1997). "Disease genes and chromosomes: disease maps of the human genome. Chromosome 19". Genet Test. 1 (2): 145–9. doi:10.1089/gte.1997.1.145. PMID 10464639.
- ↑ Moss, K (Spring 2001). "Leber's Congenital Amaurosis". Texas Deafblind Outreach. Texas School for the Blind and Visually Impaired. Archived from the original on November 19, 2013.
- Grimwood J, Gordon LA, Olsen A, Terry A, Schmutz J, Lamerdin J, Hellsten U, Goodstein D, Couronne O, Tran-Gyamfi M, Aerts A, Altherr M, Ashworth L, Bajorek E, Black S, Branscomb E, Caenepeel S, Carrano A, Caoile C, Chan YM, Christensen M, Cleland CA, Copeland A, Dalin E, Dehal P, Denys M, Detter JC, Escobar J, Flowers D, Fotopulos D, Garcia C, Georgescu AM, Glavina T, Gomez M, Gonzales E, Groza M, Hammon N, Hawkins T, Haydu L, Ho I, Huang W, Israni S, Jett J, Kadner K, Kimball H, Kobayashi A, Larionov V, Leem SH, Lopez F, Lou Y, Lowry S, Malfatti S, Martinez D, McCready P, Medina C, Morgan J, Nelson K, Nolan M, Ovcharenko I, Pitluck S, Pollard M, Popkie AP, Predki P, Quan G, Ramirez L, Rash S, Retterer J, Rodriguez A, Rogers S, Salamov A, Salazar A, She X, Smith D, Slezak T, Solovyev V, Thayer N, Tice H, Tsai M, Ustaszewska A, Vo N, Wagner M, Wheeler J, Wu K, Xie G, Yang J, Dubchak I, Furey TS, DeJong P, Dickson M, Gordon D, Eichler EE, Pennacchio LA, Richardson P, Stubbs L, Rokhsar DS, Myers RM, Rubin EM, Lucas SM (2004). "The DNA sequence and biology of human chromosome 19". Nature. 428 (6982): 529–35. doi:10.1038/nature02399. PMID 15057824.
- Human Proteome Project Launch website~ http://www.hupo.org/research/hpp/HPP_legrain_sep_2010.pdf
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Human chromosome 19. |
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 7/29/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.