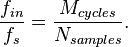Coherent sampling
Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) is a common tool to investigate performance of data converters and other sampled systems. Coherent sampling refers to a certain relationship between input frequency, 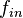 , sampling frequency,
, sampling frequency, 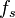 , number of cycles in the sampled set,
, number of cycles in the sampled set, 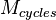 , and number of samples,
, and number of samples, 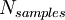 . With coherent sampling one is assured that the signal power in an FFT is contained within one FFT bin, assuming single input frequency.
. With coherent sampling one is assured that the signal power in an FFT is contained within one FFT bin, assuming single input frequency.
The condition for coherent sampling is given by
Where 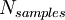 value must be a power of 2 and
value must be a power of 2 and 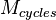 value must be an odd or prime number.
value must be an odd or prime number.
If we have 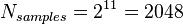 and
and 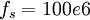 and we want an input frequency close to
and we want an input frequency close to 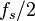 , let's say
, let's say 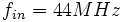 , then
, then 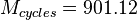 which is close to an integer, so we could round it down to
which is close to an integer, so we could round it down to 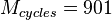 and we would get
and we would get 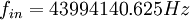 . This is an input frequency that satisfies coherent sampling and makes sure that we get an integer number of cycles.
. This is an input frequency that satisfies coherent sampling and makes sure that we get an integer number of cycles.
This integer number 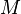 can be chosen to be a Prime number (except for 2). This ensures that the same FFT samples will not be repeated across any input signal cycles of the sampled signal. For example, if N=32 and M=6 (non-prime) then there will be N/M=5.33 samples per cycle of the input frequency, so three cycles of the input will take exactly 16 samples, and so the first 16 samples will be identical to the second 16 samples. Usually, no additional information is gained by repeating with the same sampling points and so generally a non-prime M should not be used.
can be chosen to be a Prime number (except for 2). This ensures that the same FFT samples will not be repeated across any input signal cycles of the sampled signal. For example, if N=32 and M=6 (non-prime) then there will be N/M=5.33 samples per cycle of the input frequency, so three cycles of the input will take exactly 16 samples, and so the first 16 samples will be identical to the second 16 samples. Usually, no additional information is gained by repeating with the same sampling points and so generally a non-prime M should not be used.