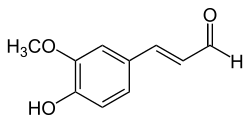
Coniferyl aldehyde
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC names
(Z)-3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-enal (E)-3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-enal | |
| Other names
Coniferaldehyde cis-coniferyl aldehyde trans-coniferyl aldehyde | |
| Identifiers | |
| 458-36-6 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:16547 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL242529 |
| ChemSpider | 4444167 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.618 |
| PubChem | 5352904 5280536 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H10O3 | |
| Molar mass | 178.18 g/mol |
| Density | 1.186 g/mL |
| Melting point | 80 °C (176 °F; 353 K) |
| Boiling point | 338.8 °C (641.8 °F; 612.0 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Coniferyl aldehyde is a low molecular weight phenolic compound susceptible to be extracted from cork stoppers into wine.[1]
Metabolism
Coniferyl-alcohol dehydrogenase uses coniferyl alcohol and NADP+ to produce coniferyl aldehyde, NADPH, and H+.
Coniferyl-aldehyde dehydrogenase uses coniferyl aldehyde, H2O, NAD+, and NADP+ to produce ferulate, NADH, NADPH, and H+.
Dihydroflavonol 4-reductase uses sinapaldehyde or coniferyl aldehyde or coumaraldehyde and NADPH to produce sinapyl alcohol or coniferyl alcohol or coumaryl alcohol respectively and NADP+.
See also
References
- ↑ Polyphenolic Composition of Quercus suber Cork from Different Spanish Provenances. Elvira Conde, Estrella Cadahía, María Concepción García-Vallejo and Brígida Fernández de Simón, J. Agric. Food Chem., 1998, 46 (8), pp 3166–3171 doi:10.1021/jf970863k
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/1/2015. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.