Consolidated TBY Sea Wolf
| TBY Sea Wolf | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Role | Torpedo bomber |
| Manufacturer | Consolidated Aircraft |
| Designer | Vought |
| First flight | 22 December 1941 |
| Introduction | 1944 |
| Status | Retired |
| Primary user | United States Navy |
| Number built | 180 |
|
| |
The Consolidated TBY Sea Wolf was a United States Navy torpedo bomber of World War II. A competitor and contemporary to the very similar Grumman TBF Avenger, the Sea Wolf was subject to substantial delays and never saw combat; only 180 of the type were built before cancellation after VJ Day.
Design and development

The original design was not by Consolidated Aircraft, but rather by Vought, who designed the then XTBU-1 Sea Wolf to a 1939 US Navy requirement. The first prototype flew two weeks after Pearl Harbor. Its performance was deemed superior to the Avenger and the Navy placed an order for 1,000 examples.[1]
Several unfortunate incidents intervened; the prototype was damaged in a rough arrested landing trial, and when repaired a month later was again damaged in a collision with a training aircraft. Once repaired again, the prototype was accepted by the Navy. However, by this time Vought was heavily overcommitted to other contracts, especially for the F4U Corsair fighter, and had no production capacity. It was arranged that Consolidated-Vultee would produce the aircraft (as the TBY), but this had to wait until the new production facility in Allentown, Pennsylvania was complete, which took until late 1943.
Operational history
The production TBYs were radar-equipped, with a radome under the right-hand wing. The first aircraft flew on 20 August 1944. By this time though, the Avenger equipped every torpedo squadron in the Navy, and there was no need for the Sea Wolf; in addition, numerous small problems delayed entry into service. Orders were cancelled after production started, and the 180 built were used for training.[2]
Specifications (TBY Sea Wolf)

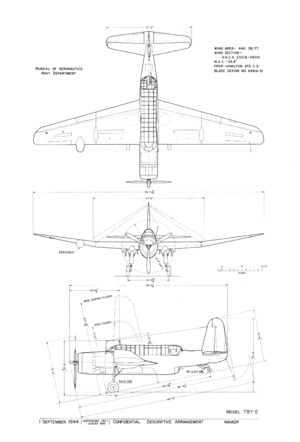
General characteristics
- Crew: three
- Length: 39 ft 2 in (11.95 m)
- Wingspan: 56 ft 11 in (17.35 m)
- Height: 15 ft 6 in (4.72 m)
- Wing area: 440 ft² (40.88 m²)
- Empty weight: 11,366 lb (5,142 kg)
- Max. takeoff weight: 18,448 lb (8,386 kg)
- Powerplant: 1 × Pratt & Whitney R-2800-6 Double Wasp radial engine, 2,000 hp (1,491 kW)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 306 mph (492 km/h)
- Range: 1,500 mi (2,414 km)
- Service ceiling: 27,200 ft (8,290 m)
Armament
- 1 × .50 in (12.7 mm) M2 Browning machine gun in cowling
- 2 × .50 in machine gun in the wings
- 1 × .50 in machine gun in dorsal turret
- 1 × .30 in (7.62 mm) M1919 Browning machine gun in ventral mount
- Up to 2,000 lb (910 kg) of bombs or one torpedo
See also
- Aircraft of comparable role, configuration and era
- Related lists
References
- Notes
- ↑ Hansen, Dave. "Vought TBU / Consolidated TBY Sea Wolf." daveswarbirds.com. Retrieved: 29 September 2010.
- ↑ Chant, Chris (2007). Aircraft of World War II: 300 of the World's Greatest Aircraft. Grange Books.
- Bibliography
- Ginter, Steve, Bill Chana and Phil Prophett. Vought XTBU-1 & TBY-2 Sea Wolf (Naval Fighters number Thirty-Three). Simi Valley, CA: Ginter Books, 1995 . ISBN 0-942612-33-7.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Consolidated TBY Sea Wolf. |
- TBY Seawolf at Brown Shoe Navy
- TBY Seawolf at Dave's Warbirds
- AirToAirCombat.Com: Vought TBU-1 Sea Wolf