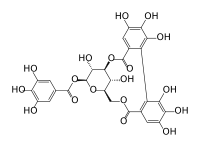
Corilagin
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
[3,5-dihydroxy-2-(3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoyl)oxy-6-[(3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoyl)oxymethyl]oxan-4-yl] 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoate | |
| Other names | |
| Identifiers | |
| 23094-69-1 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image Interactive image |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL449392 |
| ChemSpider | 4265734 |
| PubChem | 73568 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C27H22O18 | |
| Molar mass | 634.45 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Corilagin is an ellagitannin. Corilagin was first isolated in 1951 from Dividivi extract and from Caesalpinia coriaria,[1][2] hence the name of the molecule. It can also be found in Alchornea glandulosa and in the leaves of Punica granatum (pomegranate).[3]
It is a weak carbonic anhydrase inhibitor.[4]
References
- ↑ Schmidt, O. T. .; Lademann, R. (1951). "Corilagin, ein weiterer kristallisierter Gerbstoff aus Dividivi. X. Mitteilung über natürliche Gerbstoffe". Justus Liebigs Annalen der Chemie. 571 (3): 232. doi:10.1002/jlac.19515710305.
- ↑ Schmidt, O. T.; Schmidt, D. M. (1952). "Die Umwandlung von Chebulagsäure in Corilagin XIV. Mitteilung über natürliche Gerbstoffe". Justus Liebigs Annalen der Chemie. 578: 25. doi:10.1002/jlac.19525780105.
- ↑ Tanaka, T.; Nonaka, G. I.; Nishioka, I. (1985). "Punicafolin, an ellagitannin from the leaves of Punica granatum". Phytochemistry. 24 (9): 2075. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(00)83125-8.
- ↑ Satomi, H.; Umemura, K.; Ueno, A.; Hatano, T.; Okuda, T.; Noro, T. (1993). "Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors from the pericarps of Punica granatum L". Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin. 16 (8): 787–790. doi:10.1248/bpb.16.787. PMID 8220326.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/1/2015. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.