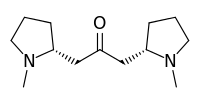
Cuscohygrine
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1-[(2R)-1-Methyl-2-pyrrolidinyl]-3-[(2S)-1-methyl-2-pyrrolidinyl]acetone | |
| Identifiers | |
| 454-14-8 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 21864896 |
| KEGG | C06521 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H24N2O | |
| Molar mass | 224.35 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 40–41 °C (104–106 °F; 313–314 K) (trihydrate) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Cuscohygrine is a pyrrolidine alkaloid found in coca. It can also be extracted from plants of the family Solanaceae as well, including Atropa belladonna (deadly nightshade), Datura inoxia and Datura stramonium (jimson weed). Cuscohygrine usually occurs along with other, more potent alkaloids such as atropine or cocaine.
Cuscohygrine, along with the related metabolite hygrine, was first isolated by Carl Liebermann in 1889 as an alkaloid accompanying cocaine in coca leaves (also known as Cusco-leaves).
Cuscohygrine is an oil that can be distilled without decomposition only in vacuum. It is soluble in water. It also forms a crystalline trihydrate which melts at 40–41 °C.
See also
References
- "USDA, ARS, National Genetic Resources Program. Phytochemical and Ethnobotanical Databases.[Online Database] National Germplasm Resources Laboratory, Beltsville, Maryland.". Retrieved July 14, 2005.
- Dr. Ame Pictet (1904). The Vegetable Alkaloids. With particular reference to their chemical constitution. London: Chapman & Hall.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 2/7/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.