Dasypus bellus
| Dasypus bellus Temporal range: Pleistocene | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Cingulata |
| Family: | Dasypodidae |
| Genus: | Dasypus |
| Species: | †D. bellus (Simpson, 1930) |
| Binomial name | |
| †Dasypus bellus | |
| Synonyms | |
|
†Tatu bellus Simpson, 1930 | |
Dasypus bellus, the beautiful armadillo,[1] is an extinct armadillo species endemic to North America and South America from the Pleistocene, living from 1.8 mya—11,000 years ago, existing for approximately 1.789 million years.[2]
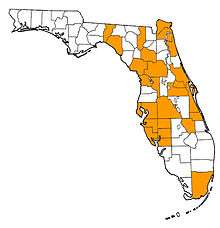
Slightly larger than its living relative, the nine-banded armadillo,[1] its fossils are known from Bolivia, Argentina, and Brazil to Florida. Records extend west to New Mexico and north to Iowa and Indiana.[3]
Anatomy
Appearance
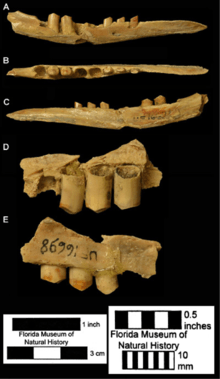
D. bellus had small, simple, peg like teeth similar to D. novemcinctus. This armadillo had a height 3.3 feet (1m). The anterior teeth had a single, slanted wear surface. The more latter teeth likely had two flat wear surfaces that meet at a shallow angle. The diet is believed to be similar to the modern species.
Body Size
The beautiful armadillo was large approximately 1.2 m long . It was about twice the size of the nine-banded armadillo. The osteoderms of the shell and the limb bones of D. bellus are about two to two and a half times the extent of those of the living modern nine-banded armadillo D. novemcinctus. The small D. bellus overlapped in size with the D.novemcinctus. The body size of D. bellus decreased during the late Pleistocene, suggesting body size was variable.
Location and Environment
Range
Earliest fossils are found in early Pleistocene South America, and would emigrate into southern North America. By the late Pleistocene, D. bellus spread into the southwestern United States. The living animals apparently preferred dry scrub environments.
Relations
DNA
Testing of two D. bellus fossils and modern armadillos has proved the species are not genetically the same. However, one of the D. bellus fossils proved to be a D. novemcinctus. The mistake was due to the high morphological similarities between the two species. It also proved that D. novemcinctus was in Florida much earlier than previously thought.

Fossils
Fossils of D. bellus have been found at many sites in Florida, including caves, sinkholes, river sites, coastal, and lake deposits. The most frequent type of fossil found are isolated osteoderms. The most common types of osteoderms that have been found are the hexagonal elements, which include most of osteoderms covering the shoulder or pectoral regions. Other types of osteoderms include those covering the pelvic region of the carapace or the so-called buckler or immovable osteoderms and the elongate rectangular elements from the movable bands, the imbricating or movable osteoderms.
Modern Decedents
The beautiful armadillo likely shares a closer common lineage with numerous species of large armadillos from the Pleistocene of South America. This includes Propraopus sulcatus and Propraopus grandis. D. kappleri, the great long nosed armadillo, which is the largest living species of armadillo from tropical South America, has the same features of osteoderms as D. bellus. They also share a large, unreduced fifth digit on the manus.
The range of D. novemcinctus, the smaller nine banded armadillo, has broadened out of Mexico and emigrated into much of the former range of Dasypus bellus. The two species are morphologically similar to each other. This had led many to believe that they might be a single, highly adaptable species that has gone through a course of phenotypical changes along with geographical range fluctuations causing from environmental changes. However, as previously stated, DNA research has proved D. bellus and D. novemcinctus to be separate species.
References
Tomak, C.H. (1982). "Dasypus bellus and Other Extinct Mammals From the Prairie-Creek Site". Journal of Mammalogy. 63 (1): 158–160. doi:10.2307/1380686. Web of Science.
Slaughter, B.H. (1959). "The First Noted Occurrence of Dasypus bellus in Texas". Field And Lab. 27 (2): 77–80. Web of Science.
Stangl, FB (2010). "A Case of Tail Mutation in A North Texas Specimen of the Pleistocene Dasypus bellus (Xenarthra: Dasypodidae)". Texas Journal of Science. 62 (1): 67–72. Web of Science. Web. 27 Oct. 2015
Shapiro, B; Graham, RW; Letts, B (2015). "A Revised Evolutionary History of Armadillos (Dasypus) in North America Based on Ancient Mitochondrial DNA". Boreas. 44 (1): 14–23. doi:10.1111/bor.12094. Web of Science.
Hulbert, Richard. “Dasypus bellus.” Florida Museum of Natural History. n. p. 11 March 2015. Web. 27 Oct. 2015
"Dasypus bellus Extinct Armadillo Fossil Facts and Photos." Fossil-Treasures-of-Florida. Web. 27 Oct. 2015.
Letts, Brandon, Shapiro, Beth. “The Recovery of Ancient DNA from Dasypus bellus Provides New Possibilities for Investigating Late Pleistocene Mammal Response to Climate Change.” Geophysical Research Abstracts. EGU General Assembly. 2010. Web. 27 Oct. 2015
Auffenberg, W (1958). "A Note on an unusually complete specimen of Dasypus bellus (Simpson from Florida)". Quarterly Journal of the Florida Academy of Sciences. 20: 233–237.
- 1 2 Illinois State Museum
- ↑ "The Paleobiology Database query for Dasypus bellus". Retrieved 2007-11-03.
- ↑ "FaunMap query for Dasypus bellus". Retrieved 2007-11-03.