Death (Tarot card)

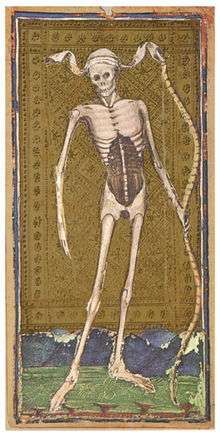
Death (XIII) is the thirteenth trump or Major Arcana card in most traditional Tarot decks. It is used in Tarot, tarock and tarocchi games as well as in divination.
Description
Some decks, such as the Tarot of Marseilles and Visconti Sforza Tarot omit the name from the card, calling this card simply The Card with No Name, thus giving this card a broader and less frightening meaning.
Meaning in Divination
This card simply signifies, in any subject you're inquiring about, "giving up all that is superficial and concentrating on what is basic, fundamental and truly important" in the specific matter you're asking about.
The Death card usually depicts a skeleton, sometimes riding a horse but more often wielding a sickle. Surrounding it are dead and dying people from all classes, including kings, bishops and commoners. The Rider-Waite tarot deck depicts the skeleton carrying a black standard emblazoned with a white flower along with the Crashing Towers from The Moon raising with The Sun setting behind them in the background.
The number 13 card shows positive meaning in reverse reading.
Interpretation
According to Eden Gray and other authors on the subject, it is unlikely that this card actually represents a physical death. Typically it implies an end, possibly of a relationship or interest, and therefore implies an increased sense of self-awareness—not to be confused with self-consciousness or any kind of self-diminishment.[1][2]
Other versions
- In the Mythic Tarot deck, Death is depicted by Hades.
In popular culture
- Death is the name of a boss in The House of the Dead III, depicted as a hulking security guard zombie with a club covered in human skulls. All bosses in The House of the Dead games are named for tarot cards of the Major Arcana. During the prologue of the game, Death attacks player characters Thoman Rogan and Dan Taylor, incapacitating them for the remainder of the game.
- Death 13 is the name of the Mannish Boy's Stand in JoJo's Bizarre Adventure, appearing as a grim reaper with a clown's face that drags its victims in its nightmares, when they go to sleep near to his user. Most of the other Stands in Part III Stardust Crusaders are also named after Tarot Cards.
- In the 1973 James Bond film Live and Let Die, Solitaire is presented with a Death Tarot card by the villain Dr. Kananga after he learns she has betrayed him, essentially sentencing her to her execution.
- In the 1996 video game Titanic: Adventure Out of Time, the player can win a Death Tarot card in a game of Blackjack. The death card serves as a free pass to the lifeboats.
- In the Virtua Fighter series, Death is the name of one of the six branches of Judgment Six, the antagonistic sponsors of the fighting game series' tournaments. This particular branch manufactures atomic, biological, and chemical weapons.
- In the SNES video game Ogre Battle: The March of the Black Queen, the Death Tarot card depicts a black-winged Grim Reaper skeleton wearing a tattered orange robe, holding a huge scythe and stepping forward. On drawing the card after liberation of one of the towns, it decreases the Reputation Meter by 2 points, and summons said Grim Reaper skeleton to wipe out weak enemy units, sending all the experience points from slain units to the main character when used in battle.[3]
- Metalcore band Sworn In's debut album is called The Death Card.
- In the 2013 film Now You See Me, this card is in the possession of Jack Wilder upon his recruitment.
- Along with other Major Arcana, Death is a character in Data East's puzzle video game series, Magical Drop.
- In Tokyo Ghoul The tarot card is in Juuzou Suzuya's hair. It is also present on his quinque, a weapon made from the body parts of ghouls.
- The Death card, along with the other Tarot cards of the Major Arcana, appears in the 2011 video game, The Binding of Isaac, and its 2014 remake, The Binding of Isaac: Rebirth, where they act as consumable items with varying effects. Death deals damage to all nearby enemies.
- In X/1999, a manga by CLAMP, the Tarot set Death is Seishirou Sakurazuka.
References
- ↑ Gray, Eden. The Complete Guide to the Tarot.
- ↑ Bunning, Joan. Learning the Tarot.
- ↑ "Ogre Battle - Tarot Cards". fantasyanime.com.
Further reading
- A. E. Waite's 1910 Pictorial Key to the Tarot
- Sir James Frazer The Golden Bough
- Hajo Banzhaf, Tarot and the Journey of the Hero (2000)
- Most works by Joseph Campbell
- The Book of Thoth (Crowley) by Aleister Crowley
- G. Ronald Murphy, S.J., The Owl, The Raven, and The Dove: Religious Meaning of the Grimm's Magic Fairy Tales (2000)
- Riane Eisler, The Chalice and the Blade (1987)
- Mary Greer, The Women of the Golden Dawn (1994)
- Merlin Stone, When God Was A Woman (1976)
- Robert Graves, Greek Mythology (1955)
- Joan Bunning, Learning the Tarot
- Juliette Wood, Folklore 109 (1998):15–24, The Celtic Tarot and the Secret Tradition: A Study in Modern Legend Making (1998)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Death (Tarot). |