Point system (driving)
A penalty point or demerit point system is one in which a driver's licensing authority, police force, or other organization issues cumulative demerits, or points to drivers on conviction for road traffic offenses. Points may either be added or subtracted, depending on the particular system in use. A major offense may lead to more than the maximum allowed points being issued. Points are typically applied after driving offenses are committed, and cancelled a defined time, typically a few years, afterwards, or after other conditions are met; if the total exceeds a specified limit the offender may be disqualified from driving for a time, or the driving license may be revoked. Fines and other penalties may be applied additionally, either for an offense or after a certain number of points have been accumulated.
The primary purpose of such point systems is to identify, deter, and penalize repeat offenders of traffic laws, while streamlining the legal process. Germany introduced a demerit point system, in 1974, and one was introduced in New York at about that time.
Description
- This article discusses point systems in the abstract; for details about any point system in place in your area, consult your local police department, or other drivers' licensing authority. This description treats points as demerits; in some jurisdictions, points may instead be measures of merit which are subtracted when a traffic offense is committed.
In jurisdictions which use a point system, the police or licensing authorities (as specified by law) maintain, for each driver, a driving score—typically an integer number specified in points. Traffic offenses, such as speeding or disobeying traffic signals, are each assigned a certain number of points, and when a driver is determined to be guilty of a particular offense (by whatever means appropriate in the region's legal system), the corresponding number of points are added to the driver's total. When the driver's total exceeds a certain threshold, the driver may face additional penalties, be required to attend safety classes or driver training, be subject to re-examination, or lose his/her driving privileges.
The threshold(s) to determine additional penalties may vary based on the driver's experience level, prior driving record, age, educational level attained, and other factors. In particular, it is common to set a lower threshold for young, inexperienced motorists.
In some jurisdictions, points can also be added if the driver is found to be significantly at fault in a traffic accident. Points can be removed from a driver's score by the simple passage of time, by a period of time with no violations or accidents, or by the driver's completion of additional drivers' training or traffic safety training.
Major traffic offenses, such as hit and run or drunk driving may or may not be handled within the point system. Such offenses often carry a mandatory suspension of driving privileges, and may incur penalties such as imprisonment.
Requirements of point systems
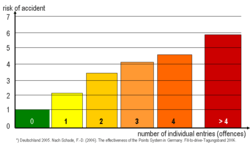
- A close relation of points and accident risk (validity)
- Comprehensibility for a good acceptance
- A high level of transparency for concerned persons
- Regulated reduction of points by effective psychological help
- Higher caution by the drivers.
Jurisdictions that use a point system
Australia
Traffic laws are the responsibility of the State and Territory Governments. Demerit points are used in all states and territories, and road authorities share information about interstate offenses.
In all states, drivers holding a full, unrestricted license will be disqualified from driving after accumulating 12 demerit points or more within a three-year period, except in New South Wales, where drivers are allowed 13 points in a three-year period. Those who can prove they are professional drivers are allowed an additional point. The minimum suspension period is three months, plus one further month for every extra four demerit points beyond the license's limit, with a cap in most states of five months (for 8 points or more over the suspension trigger; e.g. 20 points or more on a full license). An alternative to initially accepting the suspension, a driver can apply for a "good behavior" period of 12 months. In most states, drivers under a good behavior period who accumulate one or two further points (except Victoria does not allow any further offenses) have their license suspended for double the original period.
Most states also provide for immediate suspension of a license, instead of or in addition to demerit points, in certain extreme circumstances. These generally include offenses for driving under the influence of alcohol or other drugs, or for greatly excessive speed.
New South Wales
Provisional licence holders are allowed different numbers of demerit points over the lifetime of their licence, depending on their licence class, before being suspended from driving for three months. Holders of a P1 licence, which lasts 12–18 months (but can be renewed), are suspended after accumulating 4 points, while P2 licence holders are suspended after 7 points in a 24- to 30-month period (but can be renewed). Speeding offences for provisional licence holders are set to a minimum of four points, meaning that P1 holders will be suspended after one speeding offence of any speed.
During holiday periods, double demerit points apply for speeding, seatbelt and helmet-related offences. Offences in school zones attract more demerit points than in other areas. Automatic suspensions apply for all drink- and drug-driving offences, as well as speeding by more than 30 km/h.
Victoria
Victoria introduced a demerit points suspension scheme in 1970. Learner and probationary drivers are sent a combined option-suspension notice for accumulating 5 points or more over any 12-month period. An option notice allows for either a 12-month bond or a three-month minimum suspension. If a driver breaches the bond by incurring one demerit point in the 12-month period, their licence is suspended for a minimum of six months. A limit of 12 points in any three-year period with the same option applies for full licence holders. The list of traffic offences and their respective points is in schedule 3 of the Road Safety (Drivers) Regulations 2009.
In Victoria, drunk-driving offences only result in immediate licence cancellation for unrestricted drivers with a blood alcohol concentration of 0.05 or higher. Readings lower than this have the option of a 10-point penalty being imposed of being taken immediately to court; this option still results in a minimum four-month suspension for novice drivers. Automatic suspensions apply for higher level charges, and re-licensing may require an order to install an interlocking device onto the vehicle. Automatic suspension periods of at least 1 month also apply for speeding by greater than 25 km/h over the speed limit, or any speed greater than 130 km/h.[1]
South Australia
In South Australia, if a traffic offence is committed against the Road Traffic Act 1961 or the Australian Road Rules 1999, demerit points may be incurred against a driver’s licence. The number of points incurred depends on the offence and how likely it is to cause a crash. If 12 or more demerit points are accumulated in any three-year period, a driver will be disqualified from holding or obtaining a driver’s licence or permit. Each three-year period is calculated based on the dates the offences were committed.
If a driver accumulates:
- 12 to 15 points, a driver loses his permission to drive for three months.
- 16 to 20 points, a driver loses his permission to drive for four months.
- 20 points or more, a driver loses his permission to drive for five months.
Demerit points are incurred whether the offence is committed in South Australia or interstate. [2]
Northern Territory
A demerit points scheme was introduced into the Northern Territory on 1 September 2007. Offences that accrue points include speeding, failing to obey a red traffic light or level crossing signal, failing to wear a seatbelt, drink driving, using a mobile phone, failure to display L or P plates, street racing, burnouts and causing damage.[3]
Learner and provisional drivers are subject to suspension for accumulating 5 points or more over a 12-month period. The three-year limit of 12 points still applies.
Queensland
In Queensland provisional or learner drivers are entitled to accumulate 4 demerit points, and open licence holders 12 demerit points, without it affecting their licence. A driver who exceeds their demerit point threshold may elect to lose their licence for a period of 3 months or elect a good driving behaviour period which allows them to incur only one demerit point offences without it affecting their licence. If whilst on the good driving behaviour period a driver incurs more than one demerit point then they will lose their licence for a minimum of 6 months unless a Magistrates Court grants a special hardship licence [4]
Europe
Bulgaria
Bulgaria has implemented a penalty point system with a total of 34 points, introduced in 1999.[5]
Denmark
Denmark has a penalty point system that penalizes drivers with a klip ("cut/stamp")[6] for certain traffic violations. The term klip refers to a klippekort ("punch card ticket").[7] If a driver with a non-probationary license accumulates three penalty points, then police conditionally suspend the driver's license. To get a new license, suspended drivers must pass both written and practical drivers examinations. Drivers who have been suspended and first-time drivers must avoid collecting two penalty points for a three-year probationary period; if the driver has not accumulated any penalty points, then the driver is allowed an extra penalty point so they can have three maximum. Penalty points are deleted from the police database three years after they were assessed. Police can also unconditionally ban people from driving.
United Kingdom
England and Wales
In England and Wales, penalty points are given by courts for some of the traffic offences listed in Schedule 2 of the Road Traffic Offenders Act 1988. Where points are given, the minimum is 2 points for some lesser offences and the maximum 11 points for the most serious offences; some incidents can result in points being given for multiple offences or for multiple occurrences of the same offence (typically for having more than one defective tyre); the majority of applicable offences attract 3 or more penalty points. The giving of penalty points is obligatory for most applicable offences, but the number of points, and the giving of points for some of several offences, can be discretionary . Points remain on the driver's record, and an endorsement is made upon the driver's licence, for four years from conviction (eleven years for drink- and drug-related convictions). Twelve points on the licence within three years make the driver liable to disqualification; however this is not automatic, but must be decided by a law court.[8]
Since the introduction of the Road Traffic (New Drivers) Act 1995, if a person in the two years after passing their first practical test accumulates six penalty points, their licence is revoked by the DVLA, and the driver has to reapply and pay for the provisional licence, drive as a learner, and pay for and take the theory and practical tests before receiving a full licence again. In the case of egregious offences, the court may order the driver to pass an extended driving test before the licence is returned, even beyond the two-year probation period.[9]
Since 11 October 2004 there has been mutual recognition of driver disqualification arising from the penalty points given in England and Wales (and/or Scotland) with Northern Ireland; before that date disqualification in England and Wales would only have extended to Scotland by virtue of the driver registration system covering only Great Britain.
Northern Ireland
The driver registration system is separate from that of Great Britain with different laws covering penalty points and the offences to which they apply. In other respects the application of the system is similar to that in England and Wales. Offences to which penalty points apply are indicated in Schedule 1 of the Road Traffic Offenders (Northern Ireland) Order 1996.
Scotland
Road traffic laws are mostly shared with, or similar to those of, England and Wales, although Scotland is a separate jurisdiction. The driver registration system currently covers all of Great Britain and the Road Traffic Offenders Act 1988 currently governs the penalty points system in Scotland. The main differences in the penalty points provisions of the 1988 Act are the theft and homicide offences attracting penalty points indicated in Schedule 2 Part II ("Other Offences") which are not common between Scots Law and English Law.
Germany
Since May 14, 2014 Germany uses a new point system, this section describes the old one.
Points rating:
- Criminal acts in traffic are rated by 5 - 7 points depending on type and severity.
- Traffic offences are rated by 1 - 4 points.
- The person concerned may obtain information on his or her points at any time free of charge.
Measures:
The driving license authorities of the federal states are responsible for enforcing the penalty points system called Punkte in Flensburg (eng. Points in Flensburg - as Flensburg is the seat of the administrator of the system, the Kraftfahrt-Bundesamt). The system provides for the following graded measures. Points rebate is only possible by voluntary measures once within 5 years. It is not possible to accumulate positive points. The date of issue of the participation certificate is decisive for the number of points and the calculation of the five-year period.
Points Description Deduction 4 to 8 Voluntary attendance at a constructive seminar 4 points 9 to 13 A caution is issued with a reference to voluntary attendance at a constructive seminar. After voluntary attendance: 2 points 14 to 17 Mandatory attendance at a constructive seminar, if the person concerned has not attended a constructive seminar within the last 5 years. After mandatory attendance at the seminar a second written caution is issued with a reference to voluntary participation in a traffic psychologist‘s counselling. After voluntary participation: 2 points 18 and more Driving permit is withdrawn. To regain the permit, a certificate of MPA is necessary.
Cancellation of entries/Cancellation of points
When the entry is taken off, the points are also deleted. The entries are always taken off the records once the fixed periods laid down in the traffic law (§ 29 StVG) have expired. The entry of a decision concerning an offence cannot be deleted as long as the person concerned is stored in the Central Register of Driving Permits as the holder of a beginner driver’s license (FaP).
Start of cancellation period
The period of time begins for sentences passed by courts with the day of the first verdict. When a driving permit has been denied or withdrawn or a driving ban has been imposed or if the permit has been renounced, the cancellation period does not begin until the driving permit is issued or re-issued, at the latest 5 years after the decision or the renunciation.
After attendance at a constructive seminar or a traffic psychologist's counselling, the suspension period begins on the day the certificate of attendance is issued. If a driving permit is revoked, the period begins on the day the notification is received at the responsible authority.
Extension period
Records are deleted when the cancellation period plus an extension period of one year has elapsed, provided no other decisions hamper cancellation. Cancellation occurs automatically without an application having to be made. No notification of cancellation is sent out. Deleted entries are completely destroyed, therefore no information can be given on them at a later date.
Years Cancellation periods 2 For decisions on traffic offences 5 For decisions on criminal acts with the exception of DUI. Also excepted are decisions whereby a driving permit has been withdrawn or a driving ban has been imposed. 10 In all other cases (e. g. exceptions to the 5-year period, renunciation of driving permit, denial of driving permit).
Ireland
In the Republic of Ireland, twelve points accrued results in six months' disqualification.[10] 38 regulatory offences notified by post incur 1-2 point penalties on payment of a fine.[11] 10 more serious offences require a mandatory court appearance and incur 3-5 point penalties.[11] The most serious offences are outside the penalty point system and incur automatic driving bans, and in some cases imprisonment.[12]
Italy
In Italy the driver has 20 points by default, and receives a bonus of 2 points for every 2 years of correct behavior, with a maximum of 30 points.
Each traffic violation incurs a specific point penalty (for example, ignoring a traffic light involves a penalty of 6 points). If the driver loses all points, the driving license is revoked.
In case of the second alcohol abuse in 2 years, the driving license will be revoked.
A suspension is effective from when the driver is personally served with the suspension notice and they must surrender their driving license to the person giving them the notice.
Netherlands
Since March 30, 2002, The Netherlands has a point system for starting drivers (5 years starting from the moment you first passed a driving test). A driver reaching 2 points in 5 years will lose the driving licence and has to pass a driving test again in order to be regain the licence. On October 1, 2014 this limit was lowered from 3 to 2 points. Drivers can get a point for:
- Dangerous behaviour in traffic,
- Causing an accident resulting in death or injury
- Tailgating
- Exceeding the speedlimit with more than 40 km/h (motorways), or 30 km/h (all other roads)
- Any violation of the law which resulted in injury or damage
Some of these violations could also directly result in loss of the licence, however when a driver has 2 points the licence is automatically revoked and a driving test has to be passed again, whereas normally the violation would only result in the licence being suspended for several months. However, in Dutch media the effectiveness as been doubted, it was said that points were being given but not always correctly registered.
Norway
The system is called "prikkbelastning" with prikk(er) meaning dot(s). Dots are assessed to a driver's license for traffic violations which do not by themselves result in immediate revocation of the license.
After July 1, 2011, the normal penalty for most traffic violations, such as failing to yield or failing to stop at red lights, is three dots in addition to the fine. Speeding violations of between 10 and 15 km/h (where the speed limit is 60 km/h or less), or between 15 and 20 km/h (where the speed limit is 70 km/h or more) result in two dots, for speeding violations below this no dots are assessed. Young drivers between 18-20 are penalized with twice the number of dots.[13]
A driver reaching 8 dots in three years loses his or her driving license for 6 months. Each dot is deleted when three years have passed since the violation took place. When the driving privileges are restored after the six-month ban, the dots which caused the suspension are deleted.[14]
North America
Canada

Alberta
When a driver accumulates 15 or more points within a two-year period, their licence is automatically suspended for one month.[15]
Ontario
Ontario uses a 15-point system where points are "added" to a driver's record following a conviction, though Ontario's point system is unrelated to safe driving behaviour (a lone driver using a high-occupancy vehicle lane in Ontario will earn three demerit points).[16]
United States
The point system is applied in different ways, or not at all, in different states. If a red light running traffic violation is captured by red light camera, no points are assessed.[17] Aspects of a motorist's driving record (including points) may be reported to insurance companies, who may use them in determining what rate to charge the motorist, and whether to renew or cancel an insurance policy.
Arizona
Arizona uses a point system where your license will be suspended if 8 points are accumulated in one year. Offenses that lead to this are the following:
- DUI (blood alcohol concentration (BAC of 0.08% or higher): 8 points
- Extreme DUI: 8 points
- Reckless driving: 8 points
- Aggressive driving: 8 points
- Leaving the scene of an accident: 6 points
- Running a stop sign or traffic signal or failing to yield, accident causing death: 6 points
- Running a stop sign or traffic signal or failing to yield, accident causing serious injury: 4 points
- Speeding: 3 points
- Driving or parking over area where one or more lanes diverge to go in different directions (gore area): 3 points
- All other driving violations: 2 points
There are other offenses that can count toward this (e.g. HOV lane misuse is a 3-point offense)
California
Drivers who accumulate tickets for moving violations may be considered negligent operators and can lose their right to drive. Major offenses, such as hit and run, reckless driving, and driving under the influence, earn 2 points and remain on record for 13 years. Less serious offenses earn 1 point which remain for 39 months (3 years, 3 months).[19]
A driver is considered negligent if they accumulate:
- 4 points in 12 months, or
- 6 points in 24 months, or
- 8 points in 36 months
Suspension or Revocation by Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV)
Negligent drivers can be put on probation for one year (including a six-month suspension) or lose their privilege to drive. At the end of the suspension or revocation period, drivers need to re-apply for a license to drive.
DMV will revoke a license after conviction for hit-and-run or reckless driving.
Suspension by Judge
A judge may suspend license following conviction for:
- Breaking speed laws or reckless driving.
- Driving under the influence of alcohol or drugs.
- Hit-and-run driving.
- Engaging in lewd conduct and prostitution in a vehicle within 1000 feet (300 m) of a residence.
- Assaulting a driver, passenger, bicyclist, or pedestrian when the offense occurs on a highway (road rage).
- Failure to stop as required at a railway grade crossing.
- Felony or misdemeanor offense of recklessly fleeing a law enforcement officer.
When a driver is cited for a traffic violation, the judge may offer the driver the opportunity to attend a Traffic Violator School, this would include any online traffic school if the court allows. Drivers may participate once in any 18-month period to have a citation dismissed from their driving record this way. Upon dismissal of the citation, all record of the citation is removed and no points are accumulated.
Regardless of the number of points accumulated, many serious offenses involving a vehicle are punishable by heavy fines or imprisonment.
Colorado
Colorado uses an accumulating point system according to the Colorado Division of Motor Vehicles Point Schedule.[20] Suspension of driving privileges can result from as few as 6 points in 12 months by a driver under 18 years old. Points remain on the driver's motor vehicle record for 7 years. Some motor vehicle offenses carry 12 points per incident, which could result in immediate suspension of the drivers license. Multiple traffic violation convictions can also result in a suspension of the drivers license if a sufficient number of points are accumulated during a 12- or 24-month period.[21]
Florida
Florida uses a point system similar to that of Colorado. The Florida Department of Highway Safety and Motor Vehicles is the department responsible for the issuance of Driver's Licenses in the state and will also track points issued to drivers who are licensed within the state. The following are point values assigned for the following infractions.
Speeding
- 14 mph or less over the speed limit = 3 points
- 15 mph or more over the speed limit = 4 points
- Speeding which results in a crash = 6 points (enacted to curtail street drag racing)
Speeding Fines are doubled when the infraction occurs within an active school zone or a construction zone.
Moving Violations
- Moving violation (includes driving during restricted hours and parking on a highway outside the limits of a municipality) = 3 points
- Moving violation resulting in a crash = 4 points
- Failing to stop at a traffic signal = 4 points
- Passing a stopped school bus = 4 points
- Reckless driving = 4 points
- Leaving the scene of a crash resulting in property damage of more than US$50 = 6 points
- Improper lane change = 3 points
- Violation of a traffic control sign/device = 4 points
- Open container as an operator = 3 points
- Child restraint violation = 3 points
- Littering = 3 points
- Violation of curfew = 3 points (a licensed driver who is under the age of 17 may not operate a motor vehicle between 11:00 p.m. and 6:00 a.m., unless accompanied by a driver who is 21 years of age or older and holds a valid driver license, or the operator is driving to or from work. A licensed driver who is 17 years of age may not operate a motor vehicle between 1:00 a.m. and 5:00 a.m., unless accompanied by a driver who is 21 years of age or older and holds a valid driver license, or the operator is driving to and from work.)
Any person who collects a certain amount of points within a given time frame will have their license automatically revoked by the state for the length of time listed.
- 12 points earned within 12 months results in a 30-day suspension.
- 18 points earned within 18 months results in a 3-month suspension.
- 24 points earned within 36 months results in a 12-month suspension.
Any driver under the age of 18 who accumulates six or more points within a 12-month period is automatically restricted for one year to driving for business purposes only. If additional points are accumulated the restriction is extended for 90 days for every additional point received.
If a driver license was suspended in the state of Florida for points or as a habitual (but not DUI) traffic offender, or by court order, the holder must complete an advanced driver improvement course before driving privileges are reinstated.
Points issued against a driver's license in Florida remain on the license for at least 10 years.
The State of Florida issues its citizens points against their driver's license for infractions occurring anywhere in the United States.
New York
New York Statutes has a point system; after 11 points or 3 speeding tickets in 18 months, a driver's privileges are subject to suspension, with the possibility of requesting a review hearing. Points are counted from the date of the incident (usually the date of the ticket) rather than the date of conviction. For out-of-state offenses, New York State Department of Motor Vehicles does not record point violations, with the exception of violations from Quebec and Ontario.[22]
North Carolina
North Carolina operates two parallel point systems: one for DMV license suspension purposes and one for insurance purposes.
The DMV point system assigns 2 to 4 points upon conviction or an admission of guilt for most moving violations; non-moving violations carry no points. A driver's license is suspended for 60 days on the first suspension if twelve points are assessed against the license within a three-year period. Serious offenses, such as DWI and excessive speeding (more than 15 mph over the limit at a travelled speed of greater than 55 mph), result in an immediate suspension on conviction. Points are not assessed for up to two granted Prayers for Judgment Continued (PJC) within a five-year period, though some serious offenses (such as DUI, passing a stopped school bus, and speeding in excess of 25 mph over the posted speed limit) are ineligible for a PJC.
The insurance point system assigns points differently, assigning points to incidences of at-fault accidents and moving violations. Rather than using the points for a license suspension, the points lead to insurance surcharges of approximately 25-35% per point assessed. Notably, points are assessed for insurance purposes even if the license is suspended. Only points within the three years preceding the policy purchase date are considered, and a single PJC per household within the three-year period does not result in points assigned.
Incidents from out-of-state are treated as though they occurred in North Carolina for point assessment purposes.
Texas
In Texas most moving violations are worth two points, but three points are assessed in the case that an accident was caused. A license cannot be suspended as a result of point accumulation, however; instead, after six points have been accumulated, the driver must pay a "Driver Responsibility Surcharge" of $100 plus $25 per additional point each year that the license has six or more points recorded. Other convictions carry penalties that remain on the license for three years after conviction, such as a DWI conviction ($1000–$2000), driving without a license ($100), or driving without insurance ($250). The license is suspended if the surcharges are not paid.
Points clear from the license after three years, but the actual convictions clear from the record after five years, except for DWI convictions, which never expire.
Massachusetts
In Massachusetts point system is known as Safe Driver Insurance Plan (SDIP).[23] This encourages safe driving with lower premiums for drivers who do not cause accidents or commit traffic violations, and by ensuring that high-risk drivers pay a greater share of insurance costs. The points are accumulated over a six-year period, and reduced for sustained periods of safe driving.
Ohio
The State of Ohio institutes the following points system.[24] Any Ohio driver convicted of a traffic violation is assessed a specific number of penalty points according to the type of violation. Should that driver be convicted of a second or subsequent offense within two years after the first violation, the point assessment for the new violation is added to the previous total. The number of penalty points given to a violator are assessed by the court system. Following is a schedule of point assessments for specific violations: Six-Point Violations 1. Homicide by vehicle 2. Operating a vehicle while under the influence of alcohol and/or any drug of abuse 3. Failure to stop and disclose identity at the scene of a collision 4. Willingly fleeing or eluding a law enforcement officer 5. Racing 6. Operating a vehicle without the consent of the owner 7. Using a vehicle in the commission of a felony, or committing any crime punishable as a felony under Ohio motor vehicle laws Four-Point Violations Willful or wanton disregard of the safety of persons or property. Two-Point Violations 1. All moving violations and some speed offenses 2. Operating a motor vehicle in violation of a restriction imposed by the Registrar of the Bureau of Motor Vehicles
A speeding violation may result in four points, two points or no points depending on the speed limit in effect and the number of miles per hour (mph) by which the speed limit was exceeded: • Exceeding any speed limit by 30 mph or more results in four points. • If the speed limit is 55 mph or more, exceeding the limit by more than 10 but less than 30 mph results in two points. • If the speed limit is less than 55 mph, exceeding the limit by more than five but less than 30 mph results in two points. • Exceeding any speed limit in an amount less than stated above results in no points.
A driver who has accumulated six points in a two-year period will receive a letter from the Registrar of Motor Vehicles warning that the law provides the following penalties for drivers accumulating 12 or more points in a two-year period: 1. Driving privileges will be suspended for six months. 2. Proof of financial responsibility (see this chapter) must be filed with the Bureau of Motor Vehicles and maintained for three years to five years. 3. After the suspension is served, a remedial driving course approved by the director of the Ohio Department of Public Safety must be taken. The course must include a minimum of 25 percent of the number of classroom hours devoted to instruction on driver attitude. 4. Pay a reinstatement fee of $40. 5. Must take the complete driver exam
A person who has accumulated at least two but no more than 11 points for traffic violations may earn a two-point credit toward his or her driving record by completing an approved remedial driving course. Senate Bill 123, effective January 1, 2004, permits individuals to enroll in remedial driving classes in order to receive a two-point credit, up to five times in a lifetime, once every three years.
South America
Brazil
In Brazil, all traffic violations incur in a certain number of demerit points, depending on their severity, according to the 1997 Brazilian Traffic Code. If a driver accumulates more than 20 points (5 points for provisional drivers), the driving license is suspended and the driver has to take a traffic education course in order to regain the right (privilege) to drive. However, some infractions incur in immediate license suspension regardless of current point tally, such as drunk driving, engaging in street racing and others. It is also notable that many offenses that only apply to pedestrians also incur in demerit points.
Infraction Points Examples Light 3 points Driving while using a mobile phone Medium 4 points Parking where is not allowed, Stop on a crosswalk or intersection Severe 5 points Not wearing a seatbelt, Failure to signal before turning or changing lanes, Speeding Very Severe 7 points Disrespecting traffic lights, Driving a vehicle without the appropriate license, Excessive Speeding
Demerit points expire a year after the date of the violation.
Other jurisdictions
The following jurisdictions also apply point systems:
- People's Republic of China - see also Road Traffic Safety Law of the People's Republic of China
- Republic of China (Taiwan)
- France
- Hong Kong[25]
- Malaysia - see also KEJARA System
- Morocco
- New Zealand
- Serbia
- Singapore
- Slovenia
See also
References
- ↑ Road Safety Act 1986 (Victoria), Schedule 5.
- ↑ http://www.sa.gov.au/subject/transport,%20travel%20and%20motoring/Motoring/Drivers+and+licences/Driving+offences+and+penalties/Demerit+points
- ↑ "Motor Vehicle Registry Information Bulletin - L30 - Northern Territory Demerit Points Scheme" (PDF). Northern Territory Government. Retrieved 2008-05-10.
- ↑
- ↑ "Country Driving Guides" (PDF). TISPOL. Retrieved 26 May 2016.
- ↑ "Danish and English dictionaries". Small labs. Retrieved 11 July 2012.
- ↑ MobileReference (2007). Travel Denmark Illustrated City Guide, Phrasebook, and Maps. Boston: MobileReference.com. ISBN 9781605011370.
- ↑ "Penalty points (endorsements)". Retrieved 26 May 2016.
- ↑ "The Road Traffic (New Drivers) Act 1995", Directgov
- ↑ "Penalty points for driving offences". Citizens Information Board. 28 May 2012. Retrieved 28 September 2013.
- 1 2 "Table 1. Offences Incurring Penalty Points and Fixed Charge Notices with effect from 3 August 2012" (PDF). Road Safety Authority. 15 August 2012. Retrieved 28 September 2013.
- ↑ "Driving offences". Citizens Information Board. 16 April 2012. Retrieved 28 September 2013.
- ↑ Ommundsen, Mads (15 July 2011). "Nå ryker førerkortet fortere enn du tror" (in Norwegian). Bergens Tidende. Retrieved 16 July 2011.
- ↑ "Forskrift om Prikkbelastning" (in Norwegian). regjeringen.no (Norwegian Ministry of Transport and Communications). Retrieved 2009-09-09.
- ↑ "Demerit Point System for Fully Licenced Drivers". Government of Alberta. Retrieved September 2014. Check date values in:
|access-date=(help) - ↑ "Understanding Demerit Points". Queen's Printer for Ontario. Retrieved September 2014. Check date values in:
|access-date=(help) - ↑ Fatemeh Baratian-Ghorghi; Huaguo Zhou; Wesley Zech (2016). "Red-light running traffic violations: A novel time-based method for determining a fine structure". Transportation Research Part A: policy and Practice. Retrieved 27 October 2016.
- ↑ "Points Assessment". Retrieved 26 May 2016.
- ↑ "What is a Point". Calif DMV. Retrieved 26 Nov 2016.
- ↑ Colorado Division of Motor Vehicles Point Schedule
- ↑ State.co.us
- ↑ "Frequently Asked Questions". New York State Department of Motor Vehicles.
- ↑ Mass DOT Safe Driver Insurance Plan-
- ↑ http://publicsafety.ohio.gov/links/hsy7607.pdf
- ↑ "Driving-offence points system". Transport Departmant, The Government of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region. Retrieved 2015-06-22.
External links
- Penalty Points and Fines, UK site, nice clear information on points for various driving offences.
- Penalty Points in Czech republic, CZ site, information on points for various driving offences.
- Czech Point System for OS Android smart phones and tablets, The application provides information about the point system, which applies to drivers in the Czech Republic.