Diethyl carbonate
"Ethyl carbonate" redirects here. For the monoethyl carbonate group, see Etabonate.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
carbonic ether; ethyl carbonate; Eufin[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
| 105-58-8 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 7478 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.011 |
| PubChem | 7766 |
| UNII | 3UA92692HG |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H10O3 | |
| Molar mass | 118.13 g/mol |
| Appearance | Clear liquid |
| Density | 0.975 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −43 °C (−45 °F; 230 K) |
| Boiling point | 126 to 128 °C (259 to 262 °F; 399 to 401 K) |
| Insoluble | |
| Hazards | |
| EU classification (DSD) |
Flammable (F) |
| R-phrases | R11 |
| S-phrases | S9 S16 S29 S33 |
| Flash point | 33 °C (91 °F; 306 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
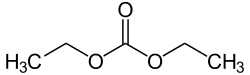
Diethyl carbonate is a carbonate ester of carbonic acid and ethanol with the formula OC(OCH2CH3)2. At room temperature (25 °C) diethyl carbonate is a clear liquid with a low flash point.
Diethyl carbonate is used as a solvent such as in erythromycin intramuscular injections. It can be used as a component of electrolytes in lithium batteries.
Production
It can be made by reacting phosgene with ethanol, producing hydrogen chloride as a byproduct. Because chloroform can react with oxygen to form phosgene, chloroform is stabilized for storage by adding 1 part (by mass) of ethanol to 100 parts (by mass) of chloroform, so that any phosgene that forms is converted into diethyl carbonate.
See also
References
- ↑ "DIETHYL CARBONATE". Retrieved 2010-02-01.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 6/27/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.