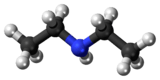
Diethylamine
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
N-Ethylethan-1-amine | |
| Other names
(Diethyl)amine Diethylamine (deprecated[2]) | |
| Identifiers | |
| 109-89-7 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| 605268 | |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:85259 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL1189 |
| ChemSpider | 7730 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.380 |
| EC Number | 203-716-3 |
| MeSH | diethylamine |
| PubChem | 8021 |
| RTECS number | HZ8750000 |
| UNII | B035PIS86W |
| UN number | 1154 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H11N | |
| Molar mass | 73.14 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colourless liquid |
| Odor | fishy, ammoniacal |
| Density | 0.7074 g mL−1 |
| Melting point | −49.80 °C; −57.64 °F; 223.35 K |
| Boiling point | 54.8 to 56.4 °C; 130.5 to 133.4 °F; 327.9 to 329.5 K |
| Miscible | |
| log P | 0.657 |
| Vapor pressure | 24.2–97.5 kPa |
| Henry's law constant (kH) |
150 μmol Pa−1 kg−1 |
| Refractive index (nD) |
1.385 |
| Thermochemistry | |
| 178.1 J K−1 mol−1 | |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH |
−131 kJ mol−1 |
| Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH |
−3.035 MJ mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | hazard.com |
| GHS pictograms |  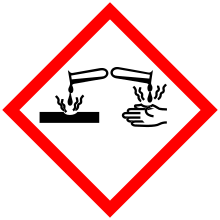  |
| GHS signal word | DANGER |
| H225, H302, H312, H314, H332 | |
| P210, P280, P305+351+338, P310 | |
| EU classification (DSD) |
|
| R-phrases | R11, R20/21/22, R35 |
| S-phrases | (S1/2), S3, S16, S26, S29, S36/37/39 |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Flash point | −23 °C (−9 °F; 250 K) |
| 312 °C (594 °F; 585 K) | |
| Explosive limits | 1.8–10.1% |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (median dose) |
540 mg/kg (rat, oral) 500 mg/kg (mouse, oral)[3] |
| LC50 (median concentration) |
4000 ppm (rat, 4 hr)[3] |
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |
| PEL (Permissible) |
TWA 25 ppm (75 mg/m3)[4] |
| REL (Recommended) |
TWA 10 ppm (30 mg/m3) ST 25 ppm (75 mg/m3)[4] |
| IDLH (Immediate danger) |
200 ppm[4] |
| Related compounds | |
| Related amines |
|
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Diethylamine is a secondary amine with the molecular structure CH3CH2NHCH2CH3 (also written as C4H11N). It is a flammable, weakly alkaline liquid. It is miscible with water and ethanol. It is a colorless liquid which often appears brown due to impurities. It is volatile and has a strong unpleasant odor.
Diethylamine is manufactured from ethanol and ammonia and is obtained together with ethylamine and triethylamine. It is used as a corrosion inhibitor and in the production of rubber, resins, dyes and pharmaceuticals.
Diethylamine is a corrosive chemical and contact with skin may cause irritation or burns.
Diethylamine can be used in the production of LSD and therefore it is strictly monitored in the United States by the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA).
References
- ↑ Merck Index, 12th Edition, 3160
- ↑ Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. p. 671. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- 1 2 "Diethylamine". Immediately Dangerous to Life and Health. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- 1 2 3 "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards #0209". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
