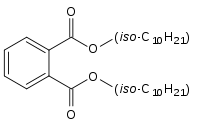
Diisodecyl phthalate
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Bis(8-methylnonyl) benzene-1,2-dicarboxylate | |
| Other names
Bis(8-methylnonyl) phthalate Bis(isodecyl) phthalate | |
| Identifiers | |
| 26761-40-0 68515-49-1 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.043.601 |
| |
| Properties | |
| C28H46O4 | |
| Molar mass | 446.67 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 0.96-0.97 g/cm3 at 20 °C[1] |
| Melting point | −50 °C (−58 °F; 223 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 250 to 257 °C (482 to 495 °F; 523 to 530 K) at 0.5 kPa [2] |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Diisodecyl phthalate (DIDP) is a commonly used plasticizer used in the production of plastic and plastic coating to increase flexibility. It is a mixture of compounds derived from the esterification of phthalic acid and isomeric decyl alcohols.
The coating on furnishings, cookware, pharmaceutical pills, food wrappers and many other products may have DIDP or other phthalates in them. There has been recent concern in the USA and European Union for their toxicity and bioaccumulative quality. The European Union has set a maximum specific migration limit from food contact materials of 9 mg/kg food for the sum of diisodecyl phthalates and diisononyl phthalates.[3]
DIDP has been listed since 2007 under Proposition 65 as a substance known to the state of California to cause reproductive toxicity.[4] The similar compound DINP is also listed.
See also
- DPHP, a similar phthalate ester
References
- 1 2 Record of CAS RN 26761-40-0 in the GESTIS Substance Database of the IFA, accessed on Sep 27, 2007
- ↑ NIOSH. "International Chemical Safety Cards". NIOSH.
- ↑ "EU legislative list for food contact materials".
- ↑ "OEHHA Proposition 65 List of Chemicals".