Druze in Lebanon
| Total population | |
|---|---|
| 215,000[1] | |
| Languages | |
|
Vernacular: Lebanese Arabic | |
| Religion | |
| Druze |
Druze in Lebanon refers to adherents of the Druze faith, an ethnoreligious[2] esoteric group originating from the Near East who self identify as unitarians (Muwahhideen).[3]
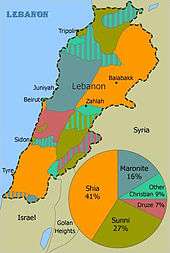
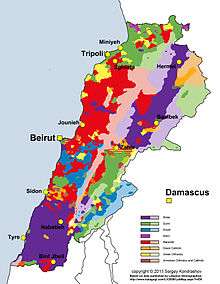
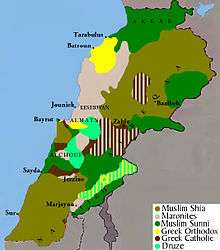
The Lebanese Druze people are believed to constitute about 5%[1] of the total population of Lebanon. The Druze, who refer to themselves as al-Muwahhideen, or "believers in one God," are concentrated in the rural, mountainous areas east and south of Beirut.[1]
Under the Lebanese political division (Parliament of Lebanon Seat Allocation) the Druze community is designated as one of the five Lebanese Muslim communities (Sunni, Shia, Druze, Alawi, and Ismaili).[4][5] Lebanon's constitution was intended to guarantee political representation for each of the nation's ethno-religious groups.[6]
Under the terms of an unwritten agreement known as the National Pact between the various political and religious leaders of Lebanon, the Chief of the General Staff must be a Druze.[7]
History
The Druze faith is a monotheistic Abrahamic religion that does not follow the Five Pillars of Islam, "fasting during the month of Ramadan and making a pilgrimage to Mecca. Thus, they are not regarded by Muslims as Islamic".[8][9] The Druze beliefs incorporate elements of Ismailism, Gnosticism, Neoplatonism and other philosophies. The Druze call themselves Ahl al-Tawhid "People of Unitarianism or Monotheism" or al-Muwaḥḥidūn."
The Druze follow a life style of isolation where no conversion is allowed, neither out of, or into, the religion. When Druze live among people of other religions, they try to blend in, in order to protect their religion and their own safety. They can pray as Muslims, or as Christians, depending on where they are. This system is apparently changing in modern times, where more security has allowed Druze to be more open about their religious belonging."[10]
The Tanukhids inaugurated the Druze community in Lebanon when most of them accepted and adopted the new message that was being preached in the 11th century, due to their leaderships close ties with then Fatimid ruler Al-Hakim bi-Amr Allah.[11]
The Druze community in Lebanon played an important role in the formation of the modern state of Lebanon, and even though they are a minority they play an important role in the Lebanese political scene. Before and during the Lebanese Civil War (1975–90), the Druze were in favor of Pan-Arabism and Palestinian resistance represented by the PLO. Most of the community supported the Progressive Socialist Party formed by their leader Kamal Jumblatt and they fought alongside other leftist and Palestinian parties against the Lebanese Front that was mainly constituted of Christians. After the assassination of Kamal Jumblatt on 16 March 1977, his son Walid Jumblatt took the leadership of the party and played an important role in preserving his father's legacy after winning the Mountain War and sustained the existence of the Druze community during the sectarian bloodshed that lasted until 1990.
In August 2001, Maronite Catholic Patriarch Nasrallah Boutros Sfeir toured the predominantly Druze Chouf region of Mount Lebanon and visited Mukhtara, the ancestral stronghold of Druze leader Walid Jumblatt. The tumultuous reception that Sfeir received not only signified a historic reconciliation between Maronites and Druze, who fought a bloody war in 1983–84, but underscored the fact that the banner of Lebanese sovereignty had broad multi-confessional appeal[12] and was a cornerstone for the Cedar Revolution in 2005. Jumblatt's post-2005 position diverged sharply from the tradition of his family. He also accused Damascus of being behind the 1977 assassination of his father, Kamal Jumblatt, expressing for the first time what many knew he privately suspected. The BBC describes Jumblatt as "the smartest leader of Lebanon's most powerful Druze clan and heir to a leftist political dynasty".[13] The second largest political party supported by Druze is the Lebanese Democratic Party led by Prince Talal Arslan, the son of Lebanese independence hero Emir Majid Arslan.
Demographics

The Druze, who refer to themselves as al-Muwahhideen, or "believers in one God," are concentrated in the rural, mountainous areas east and south of Beirut.[1] The Lebanese Druze are estimated to constitute 5% of Lebanon's population of approximately 4.3 million, which means they amount to 215,000.[1]
Notable people
-2.png) |  |  |  |  |  |  |
- Fakhr-al-Din II, a Druze prince and an early leader of the Emirate of Chouf.
- Emir Majid Arslan, a Druze leader and head of the Arslan feudal Druze ruling family.
- Emir Shakib Arslan, a Druze prince and notable Islamic scholar.
- Emir Talal Arslan, Lebanese politician and the head of the mostly Druze Lebanese Democratic Party.
- Kamal Jumblatt, an important Lebanese politician.
- Walid Jumblatt, a Lebanese politician and the current leader of the Progressive Socialist Party (PSP).
- Nabil Kanso, a Lebanese-American painter.
- Akram Chehayeb, a Lebanese politician, member of parliament,and Minister of Agriculture.
- Ghazi Aridi, a Lebanese politician, and member of parliament.
- Raghida Dergham, a Lebanese-American journalist based in New York.
- Amal Clooney, a London-based British-Lebanese lawyer, activist, and author. (Druze father and Sunni mother.)
- Mona Abou Hamze, TV presenter
- Ramy Ayach, singer/ popstar
- Samir Kuntar, convicted murderer, terror chief and member of the Palestine Liberation Front representing Hezbollah
See also
Druze |
|---|
 |
|
Important figures |
|
Texts
|
|
Holy places |
|
Holy days |
|
- Chouf District
- Druze
- Shia Islam in Lebanon
- Sunni Islam in Lebanon
- Maronite Christianity in Lebanon
- Christianity in Lebanon
- Roman Catholicism in Lebanon
- Melkite Christianity in Lebanon
- Eastern Orthodox Christianity in Lebanon
- Protestantism in Lebanon
- Religion in Lebanon
- Lebanese Democratic Party
- Progressive Socialist Party
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Lebanon - International Religious Freedom Report 2008 U.S. Department of State. Retrieved on 2013-06-13.
- ↑ Chatty, Dawn. Displacement and Dispossession in the Modern Middle East. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521817927.
- ↑ Doniger, Wendy. Merriam-Webster's Encyclopedia of World Religions. Merriam-Webster, Inc. ISBN 0877790442.
- ↑ Lebanon Country Study Guide Volume 1 Strategic Information and Developments
- ↑
- ↑
- ↑ United Nations Development Programme : Programme on Governance in the Arab Region : Elections : Lebanon. Retrieved 25 January 2010.
- ↑ "Druze". druze.org.au. 2015.
- ↑ James Lewis (2002). The Encyclopedia of Cults, Sects, and New Religions. Prometheus Books. Retrieved 13 May 2015.
- ↑ "Druze". druze.org.au. 2015.
- ↑ William Harris (19 Jul 2012). Lebanon: A History, 600-2011 (illustrated ed.). Oxford University Press. p. 46. ISBN 9780195181111.
- ↑ Nasrallah Boutros Sfeir, Meib, May 2003, archived from the original (dossier) on July 20, 2009
- ↑ "Who's who in Lebanon". BBC News. 14 March 2005. Retrieved 13 August 2011.