EPN (insecticide)
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
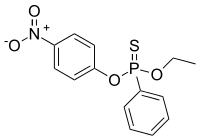
| IUPAC name
O-Ethyl O-(4-nitrophenyl) phenylphosphonothioate | |
| Other names
Ethyl p-nitrophenyl thionobenzenephosphonate, Ethyl p-nitrophenyl benzenethionophosphonate | |
| Identifiers | |
| 2104-64-5 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 15571 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.016.615 |
| PubChem | 16421 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H14NO4PS | |
| Molar mass | 323.30 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Light yellow crystalline powder[1] |
| Density | 1.3 g/cm3[1] |
| Melting point | 36 °C (97 °F; 309 K)[1] |
| Insoluble[1] | |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | noncombustible [2] |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (median dose) |
20 mg/kg (oral, dog) 8 mg/kg (oral, rat) 36 mg/kg (oral, rat) 7 mg/kg (oral, rat) 12.2 mg/kg (oral, mouse)[3] |
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |
| PEL (Permissible) |
TWA 0.5 mg/m3 [skin][2] |
| REL (Recommended) |
TWA 0.5 mg/m3 [skin][2] |
| IDLH (Immediate danger) |
5 mg/m3[2] |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
EPN is an insecticide of the phosphonothioate class.[4] It is used against pests such as European corn borer, rice stem borer, bollworm, tobacco budworm, and boll weevil.[5]
References
- 1 2 3 4 "EPN International Chemical Safety Card". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health.
- 1 2 3 4 "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards #0255". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ↑ "EPN". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). 4 December 2014. Retrieved 19 March 2015.
- ↑ "EPN Data Sheet". alanwood.net.
- ↑ "EPN Chemical Profile". Pesticide Management Education Program, Cornell University.
External links
- EPN, toxipedia.org
- NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards, cdc.gov
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 1/29/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.