Epipubic bone

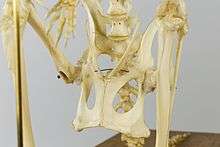
Epipubic bones are a pair of bones projecting forward from the pelvic bones of modern marsupials and most non-placental fossil mammals: multituberculates, monotremes, and even basal eutherians (the ancestors of placental mammals).[1] They first occur in tritylodontids, suggesting that they are a synapomorphy between them and Mammaliformes.
Only placentals, and possibly the early mammaliformes Megazostrodon and Erythrotherium, lack them;[2] in thylacines and sparassodonts, they appear to have become primarily cartilaginous and the osseous element has become strongly reduced or even absent.[3][4] Trichosurus mimicked placentals in shifting hypaxial muscles attachment sites from the epipubic to the pelvis, losing the respiratory benefits (see below), but otherwise retains large epipubics.[5]
In modern marsupials the epipubic bones are often called "marsupial bones" because they support the mother's pouch ("marsupium" is Latin for "pouch"), but their presence on other groups of mammals indicates that this was not their original function, which some researchers think was to assist locomotion by supporting some of the muscles that flex the thigh.[6]
The epipubic bones were first described in 1698 but their functions have remained unresolved. It has been suggested[7] that they form part of a kinetic linkage stretching from the femur on one side to the ribs on the opposite side. This linkage is formed by a series of muscles: each epipubic bone is connected to the femur by the pectineus muscle, and to the ribs and vertebrae by the pyramidalis, rectus abdominis, and external and internal obliques. According to this hypothesis, the epipubic bones act as levers to stiffen the trunk during locomotion, and aid in breathing.[8] It has been suggested that epipubic bones may constrain asymmetrical gaits, though this appears to not be the case.[9]
Placentals are the only mammal lineage which lacks epipubic bones, and this absence has been considered to be correlated to the development of the placenta itself; epipubic bones stiffen the torso, preventing the expansion necessary for prolonged pregnancy.[10] However, vestiges of the epipubic bone may survive in a common placental characteristic, the baculum.[11]
See also
| Look up epipubic bone in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
References
- ↑ Novacek, M.J.; Rougier, G.W.; Wible, J.R.; McKenna, M.C.; Dashzeveg, D; Horovitz, I (1997). "Epipubic bones in eutherian mammals from the late Cretaceous of Mongolia". Nature. 389 (6650): 440–1. doi:10.1038/39020. PMID 9333234.
- ↑ Jason A. Lillegraven, Zofia Kielan-Jaworowska, William A. Clemens, Mesozoic Mammals: The First Two-Thirds of Mammalian History, University of California Press, 17/12/1979 - 321
- ↑ Marshall, L. Evolution of the Borhyaenidae, extinct South American predaceous marsupials. Berkeley: University of California Press, 1978.
- ↑
- ↑ Reilly SM, McElroy EJ, White TD, Biknevicius AR, Bennett MB, Abdominal muscle and epipubic bone function during locomotion in Australian possums: insights to basal mammalian conditions and Eutherian-like tendencies in Trichosurus, J Morphol. 2010 Apr;271(4):438-50. doi: 10.1002/jmor.10808.
- ↑ White, T.D. (August 9, 1989). "An analysis of epipubic bone function in mammals using scaling theory". Journal of Theoretical Biology. 139 (3): 343–57. doi:10.1016/S0022-5193(89)80213-9. PMID 2615378.
- ↑ Reilly SM, White TD. (2003-01-17). "Hypaxial motor patterns and the function of epipubic bones in primitive mammals". Science. 299 (5605): 400–2. doi:10.1126/science.1074905. PMID 12532019.
- ↑ Stephen M Reilly, Eric Mcelroy and Thomas D White, Abdominal muscle function in ventilation and locomotion in new world opossums and basal eutherians: Breathing and running with and without epipubic bones, Journal of Morphology 270(8):1014-28 · August 2009 Impact Factor: 1.74 · DOI: 10.1002/jmor.10735 · Source: PubMed
- ↑ Nadja Schilling, Rémi Hackert, Sagittal spine movements of small therian mammals during asymmetrical gaits, Journal of Experimental Biology 2006 209: 3925-3939; doi: 10.1242/jeb.02400
- ↑ Michael L. Power,Jay Schulkin. The Evolution Of The Human Placenta. pp. 68–.
- ↑ Frederick S. Szalay (11 May 2006). Evolutionary History of the Marsupials and an Analysis of Osteological Characters. Cambridge University Press. pp. 293–. ISBN 978-0-521-02592-8.