Esperanto symbols
|
Culture and media |
|
Related topics |
|
Wikimedia Portal · Task force Esperanto Wikipedia (Vikipedio) Vikivortaro · Vikicitaro · Vikifontaro Vikilibroj · Vikikomunejo Vikispecoj · Vikinovaĵoj |
Since the earliest days of Esperanto, the colour green has been used as a symbol of mutual recognition, and it appears prominently in all Esperanto symbols.
The Verda Stelo (Esperanto: Green Star) was first proposed in an 1892 article in La Esperantisto for use as a symbol of mutual recognition among esperantists.
In a letter to The British Esperantist in 1911, L. L. Zamenhof, the creator of Esperanto, wrote: "It seems to me, that my attention was drawn to the color green by Mr. [R. H.] Geoghegan and from that time I began to publish all of my works with green covers . . . Looking at one of my pamphlets that I had entirely by chance printed with a green cover, he pointed out that this was the color of his homeland, Ireland; at that time it came to me, that we could certainly look at that color as a symbol of HOPE. About the five-pointed star, it seems to me, that at first Mr. de Beaufront had it imprinted on his grammar [of Esperanto]. I liked that and I adopted it as a symbol. Afterward by association of ideas, the star appeared with a green color."
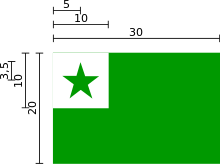
The Esperanto flag is composed of a green background with a white square in the upper lefthand corner, which in turn contains a green star. The green field symbolizes hope, the white symbolizes peace and neutrality, and the five-pointed star represents the five continents (Europe, America, Asia, Oceania, Africa). The flag was created by the Esperanto Club of Boulogne-sur-Mer, initially for their own use, but was adopted as the flag of the worldwide Esperanto movement by a decision of the first Universal Congress of Esperanto, which took place in 1905 in that town.
By recommendation of the board of the World Esperanto Association, the flag should have the following proportions: The ratio of the width of the flag to the height of the flag to a side of the white square should be 3 to 2 to 1. The ratio of a side of the white square to the radius of a circle enclosing the star should be 10 to 3.5.[1]
Some Esperanto speakers consider the traditional flag too nationalistic for an international language, so many organizations no longer recommend its use and, instead, use the jubilea simbolo (jubilee symbol, two green "E"s facing each other—or alternatively a Latin-alphabet "E" facing a Cyrillic-alphabet "Э", the first letter of "Эсперанто", the Russian name for Esperanto—on a white field). This symbol was created in 1987 by a Brazilian Esperantist to mark the centenary of the creation of Esperanto. On the other hand, this new symbol is derogatively called la melono (Esperanto: the melon) by some.
Most Esperantists, however, continue to hold the verda stelo dear as a symbol of international or supranational solidarity, and regard the preference of one symbol over another as a purely personal choice. At most Esperanto congresses, all three main symbols can be seen in use on displays or being worn as badges.
Sometimes, Esperanto travelers will display the flag, wear a badge with one of the above symbols, or even wear green clothes, to make themselves known to other Esperanto speakers.
Flag variants
In 1905, delegates to the first conference of Esperantists at Boulogne-sur-Mer, unanimously approved a version, differing from the modern only by the superimposition of an "E" over the green star.[2] Other variants include that for Christian Esperantists, with a white Christian cross superimposed upon the green star, and that for Leftists, with the color of the field changed from green to red.[3]
Appearance
On December 15, 2009, the Esperanto flag flew on the Google home search page "Google" logo to mark L.L. Zamenhof's 150th birthday. The flagstaff was the "L" of the search-company name.[4]
Influence
One hypothesis of the red star as a symbol of socialism relates to an alleged encounter between Leon Trotsky and Nikolai Krylenko. Krylenko, an Esperantist, was wearing a green-star lapel badge; Trotsky enquired as to its meaning and received an explanation that each arm of the star represented one of the five traditional continents. On hearing this, he specified that a similar red star should be worn by soldiers of the Red Army.[5]
References
- ↑ eo:Esperanta Flago
- ↑ https://web.archive.org/web/20070831015356/http://www.fotw.net/flags/qy-eo.html#vars. Archived from the original on August 31, 2007. Retrieved September 2, 2007. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ https://web.archive.org/web/20070831015356/http://www.fotw.net/flags/qy-eo.html#vars. Archived from the original on August 31, 2007. Retrieved September 2, 2007. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ 150th Birthday of LL Zamenhof.
- ↑ Pri La Stelo: Militista simbolo
See also
-

The Esperanto Flag
-

Jubilee symbol
-

A green star