European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization
CENELEC (French: Comité Européen de Normalisation Électrotechnique; English: European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization) is responsible for European standardization in the area of electrical engineering. Together with ETSI (telecommunications) and CEN (other technical areas), it forms the European system for technical standardization. Standards harmonised by these agencies are regularly adopted in many countries outside Europe which follow European technical standards.
CENELEC was founded in 1973. Before that two organizations were responsible for electrotechnical standardization: CENELCOM and CENEL. CENELEC is a non-profit organization under Belgian law, based in Brussels. The members are the national electrotechnical standardization bodies of most European countries.
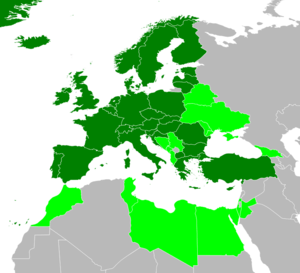
The current members of CENELEC are: Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, the Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Macedonia, Malta, the Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Spain, Slovakia, Slovenia, Sweden, Switzerland, Turkey and the United Kingdom.[1]
Albania, Belarus, Bosnia/Herzegovina, Egypt, Georgia, Israel, Jordan, Libya, Moldova, Montenegro, Morocco, Serbia, Tunisia and Ukraine are currently "affiliate members"[2] with a view to becoming full members.
CENELEC has cooperation agreements with: Canada, China, Japan. South Korea, Russia and informal agreement with the USA.[3]
Although CENELEC works closely with the European Union, it is not an EU institution.
See also
- European Committee for Standardization (CEN)
- European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI)
- European Office of Crafts, Trades and Small and Medium-sized Enterprises for Standardisation (NORMAPME)
- European Norms Electrical Certification (ENEC)
