Field vole
| Field vole | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Rodentia |
| Family: | Cricetidae |
| Subfamily: | Arvicolinae |
| Genus: | Microtus |
| Subgenus: | Microtus |
| Species: | M. agrestis |
| Binomial name | |
| Microtus agrestis (Linnaeus, 1761) | |
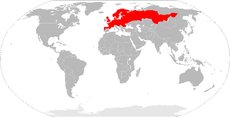
The field vole or short-tailed vole (Microtus agrestis) is a grey-brown vole,[2] around four inches (ten centimetres) in length, with a short tail. It is one of the most common mammals in Europe, with a range extending from the Atlantic coast to Lake Baikal. These voles are found in moist grassy habitats, such as woodland, marsh or on river banks. Although they make shallow burrows, they usually build nests above ground. They are an important food source for owls and some other predators and their population size tends to peak and trough cyclically. Field voles breed prolifically, mainly in summer, but often all year round, even under snow. Females produce up to seven litters a year, each averaging from four to six young which are weaned after about fourteen days. The field vole is both widespread and common and is listed as being of "Least Concern" by the IUCN.
Description
The field vole is a small, dark brown rodent with a short tail, distinguishable from the closely related common vole (Microtus arvalis) by its darker, longer and shaggier hair and by its more densely haired ears. The head and body length varies between 3.75 and 5.25 inches (95 and 133 mm) and the tail between 1 and 1.75 inches (25 and 44 mm). The weight is 0.7 to 1.8 ounces (20 to 51 g). The voice is a faint, low squeak and it also emits a range of chattering sounds.[3]
Distribution and habitat
The field vole has a palearctic distribution. Its range extends throughout Western Europe and eastwards to Lake Baikal in Siberia and north west China and northward to Norway, Sweden and Finland. It is absent from Iceland and Ireland and thins out southwards towards the Mediterranean Sea. It is found in a range of habitats including meadows, field borders, plantations, woodland verges, clearings, upland heaths, dunes, marshes, bogs and river banks and tends to prefer wet areas.[1] It is found at altitudes of up to about 1,700 metres (5,600 ft).[3]
Behaviour

The field vole is more active by day than the common vole. It excavates shallow burrows close to the surface of the ground, under leaf litter and under snow in winter. It also makes surface runs through tall vegetation, routes along which it can scurry back to safety if danger threatens. Off these are dedicated defecation sites and it often leaves little piles of chopped up grass stalks nearby.[3]
The field vole is a herbivore and feeds on grasses, herbs, root tubers, moss and other vegetation and gnaws bark during the winter (it does not hibernate). It occasionally eats invertebrates such as insect larvae.[1] Among the plants it favours are the grasses Agrostis spp. and Festuca rubra, the yarrow (Achillea millefolium), clover (Trifolium spp.), dandelion (Taraxacum officinale) and buttercups (Ranunculus spp.). The voles choose species with high digestibility where possible and avoid some common plants amongst which they live such as the tufted hairgrass (Deschampsia cespitosa) and rosebay willowherb (Chamerion angustifolium). The animals have low energy reserves and these are only able to sustain them for five to fourteen hours. Because of the low availability of food in the winter, drier habitats are unable to sustain populations of much over two hundred animals per hectare. The number of voles expands rapidly with the arrival of spring and the better availability of food supplies.[4]
Field voles are an important part of the diet of barn owls and they are also preyed on by kestrels, other owls, weasels, stoats, foxes and snakes. Though very numerous, they have little impact on man except in plague years when the may cause significant damage to crops.[5]
Breeding
The field vole breeds throughout the year but the breeding season peaks in spring and summer. The nest is made on or just under the surface of the ground, often in a clump of grass or sedge. The gestation period is about three weeks and up to a dozen young are borne. These grow rapidly, suckle for twelve days and leave the nest at twenty one days, reaching sexual maturity soon afterwards. Like the common vole, the field vole is subject to population explosions when conditions are right.[3] Females become pregnant again soon after parturition. The pregnancy rate is nearly 100% in late spring but falls during midsummer only to rise again later. Mortality in the nest is about 20% but may rise to 50% in the middle of summer when the digestibility of the food supplies fall. Life expectancy is about two years but is lower for spring-born individuals than for ones born later in the year.[6]
Male field voles maintain a territory but females just have a home range which may overlap with that of a neighbour. After leaving the nest, young female voles remain in or near their mother's home range but young males are forced to disperse by the aggressiveness of the adult males. Female field voles sometimes spontaneously move in the time gap between weaning one litter and producing the next, a phenomenon typical of this species. One of the causes of the large population swings that occur in the field vole is the scramble competition which comes into play when the most desirable food plants are less available in mid summer.[7] At this time litter sizes may fall, growth rates slow down, there may be increased mortality of young in the nest, adults may lose weight and some may die. Similar competition can occur in winter when the availability of greenstuff fails and starvation ensues.[7]
Status
The field vole is common over most of its very wide range, although thinning out towards the peripheries and may be locally scarce where conditions are less suitable. The population seems stable over the long term though there are marked fluctuations from year to year. The IUCN in its Red List of Threatened Species has therefore listed it as being of "Least Concern".[1]
References
- 1 2 3 4 Kryštufek, B.; Vohralík, V.; Zima, J.; Zagorodnyuk, I. (2008). "Microtus agrestis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2008. International Union for Conservation of Nature. Retrieved 2013-08-11.
- ↑ Musser, G.G.; Carleton, M.D. (2005). "Superfamily Muroidea". In Wilson, D.E.; Reeder, D.M. Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 990–991. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- 1 2 3 4 Konig, Claus (1973). Mammals. Collins & Co. p. 119. ISBN 978-0-00-212080-7.
- ↑ Hansson, Lennart (1971). "Habitat, food and population dynamics of the field vole Microtus agrestis (L.) in south Sweden". Viltrevy. 8: 268–278. ISSN 0505-611X.
- ↑ "Field vole: Microtus agrestris". Young People's Trust for the Environment. Retrieved 2013-08-10.
- ↑ Myllymäki, A. (1977). "Demographic Mechanisms in the Fluctuating Populations of the Field Vole Microtus agrestis". Oikos. 29 (3): 463–493. doi:10.2307/3543588. JSTOR 3543588.
- 1 2 Myllymäki, A. (1977). "Intraspecific Competition and Home Range Dynamics in the Field Vole Microtus agrestis". Oikos. 29 (3): 553–569. doi:10.2307/3543594. JSTOR 3543594.
