Flag of Qatar
 | |
| Name | Al-Adaam |
|---|---|
| Use | National flag and ensign |
| Proportion | 11:28 |
| Adopted | 9 July 1971 |
| Design | A white band on the hoist side, separated from a maroon area on the fly side by nine white triangles which act as a serrated line |
The flag of Qatar (Arabic: علم قطر) is in the ratio of 11:28. It is maroon with a broad white serrated band (nine white points) on the hoist side. It was adopted shortly before the country's declaration of independence from Britain on September 3, 1971.
The flag is very similar to the flag of the neighbouring country Bahrain, which has fewer points, a 3:5 proportion, and a red colour instead of maroon. Qatar's flag is the only national flag having a width more than twice its height.[1]
History
Qatar's historic flag was plain red, in correspondence with the red banner traditionally used by the Kharjite Muslims.[2] In the 19th century, the country modified its entirely red flag with the addition of a white vertical stripe at the hoist to suit the British directive.[3] After this addition, Sheikh Mohammed bin Thani officially adopted a patterned purple-red and white flag which bore a strong resemblance to its modern derivative.[4] Several additions were made to the Qatari flag in 1932, with the nine-pointed serrated edge, diamonds and the word "Qatar" being integrated in its design.[4] The maroon color was standardized in 1949. In the 1960s, Sheikh Ali Al Thani removed the wording and diamonds from the flag.[4] The flag was officially adopted on July 9, 1971 and was virtually identical to the 1960s flag, with the exception of the height-to-width proportion.[4]
Characteristics
Pattern
Nine serrated edges separate the colored and white portions. They signify Qatar's inclusion as the 9th member of the 'reconciled Emirates' of the Persian Gulf at the conclusion of the Qatari-British treaty in 1916.[5]
Color
The shade of Qatar's colored portion is referred to as 'Qatar maroon'.[6] The history of purple dye in the country dates back several centuries.[4] It has been asserted that Qatar was the site of the earliest known production of shellfish dye during the rule of the Kassites due to the presence of a purple dye industry on Al Khor Islands.[7][8] Qatar was also known for its production of purple dye during the rule of the Sasanian Empire.[9] Mohammed bin Thani, who ruled from 1847 to 1876, proposed the creation a flag with a purple-red color in order to unify the state, and to highlight its historic role in the production of dye. In 1932, the British Navy suggested an official flag should be designed. They proposed that the flag be white and red, but Qatar rejected the red coloring and continued using a mixture of purple and red instead.[4] Due to the country's subtropical desert climate, the flags colors were prone to being tinted darker by the sun, which resulted in the eventual adoption of a maroon coloring in 1949.[4] The white portion of the flag symbolizes the peace procured from signing anti-piracy treaties with the British.[3]
Historic flags
-
.svg.png)
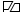 around 1916
around 1916 -
.svg.png)
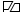 around 1936
around 1936 -
.svg.png)
11:30
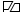 1949 to 1971
1949 to 1971
See also
References
- ↑ ".(28:11) عند استخدام العلم خارج المباني، داخل دولة قطر، فإنه يجب أن تكون النسبة بين طول وعرض العلم" (When using a flag outside of buildings within the State of Qatar, the ratio between the length and the width of the flag should be 11:28.) - Law No. 14 on the Flag of Qatar - Qatar Legal Portal
- ↑ Complete Flags of the World (Dk). DK Publishing. 2014. p. 185. ISBN 978-1409353713.
- 1 2 "Imperial era flag of Qatar". British Empire in the Middle East. Retrieved 7 May 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "Al Adaam.. History of a Nation". Qatar e-Government. Retrieved 28 January 2015.
- ↑ "FIELD LISTING :: FLAG DESCRIPTION". CIA. Retrieved 7 May 2015.
- ↑ "Qatar's flag". World Atlas. Retrieved 7 May 2015.
- ↑ Sterman, Baruch (2012). Rarest Blue: The Remarkable Story Of An Ancient Color Lost To History And Rediscovered. Lyons Press. pp. 21–22. ISBN 978-0762782222.
- ↑ Khalifa, Haya; Rice, Michael (1986). Bahrain Through the Ages: The Archaeology. Routledge. pp. 79, 215. ISBN 978-0710301123.
- ↑ "Qatar - Early history". globalsecurity.org. Retrieved 17 January 2015.

