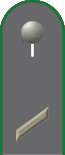
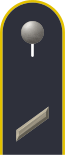
Gefreiter
Gefreiter (abbr. Gefr. [ German > "Exempted"]) is a German, Swiss and Austrian military rank that has existed since the 16th century. It is usually the second rank or grade to which an enlisted soldier, airman or sailor could be promoted.[1][2]
Within the combined NATO rank scale, the modern-day rank of Gefreiter is usually equivalent to the NATO-standard rank scale OR-2. The word has also been lent into the Russian language, and is in use in several Russian and post-Soviet militaries.
History
Historically the military rank of Gefreiter (also Gefreite)[3] emerged in 16th-century Europe for the German Landsknechte foot soldiers,[4] predominantly made up of German and Swiss mercenary pikemen and supporting infantry foot soldiers.[5][6][7][8] Those soldiers who proved especially reliable and experienced were appointed to gefreyten Knechten (exempted Servants/Soldiers; a cognate to 'knight') and were installed in critical battlefield positions, among their extra rank privileges they were exempted in general from guard watch duties.[1][5][6][9]
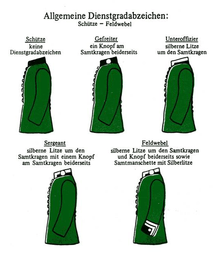
From the 18th century, Gefreiters were the first line members of a military company, and every Gefreiter led and commanded a section or squad of Gemeine[10] (ordinary-rank soldiers), the rank existed in the cavalry, infantry, pioneers, and artillery where the Gefreiter rank received a greater rank-class status.[5][6] Gefreiter was the only enlisted rank until 1918 within the Royal Prussian Army and respectively the imperial army of the German Empire to which an exceptional enlisted soldier could be promoted on the recommendation of the Hauptmann (Captain) or Rittmeister (Cavalry-Master otherwise Captain) and ultimately endorsed by the Regiments-Commandeur (Regimental Colonel), with exception of the rank Obergefreiter (since 1859) in the foot artillery which later replaced the artillery Bombardier (Corporal) rank.[5] The Gefreiter rank was also considered a transition rank for promotion to and wherefrom replacements were selected to the Unteroffizier (Corporal)[11] rank.[5] Within the Royal Prussian Army and respectively the imperial army of the German Empire, the rank Gefreiter was a deputy to the Unteroffizier (Corporal), and were distinguished by the wearing of a Auszeichnungsknopf (rank Distinction-button) known as the Gefreitenknopf (Gefreiter-button) on each side of their uniform collar, similar to the slightly larger rank collar side-buttons worn by both the Sergeant and Feldwebel ranks.[5]
In the Royal Prussian Army until its reorganization after 1806, there existed along with Gefreiter the rank of Gefreite-Korporale[5] who wore a silver Portepee (sword lanyard) and were officer cadets specifically selected for higher advancement, they stood equal with their officer cadet counterpart the Portepee-Fähnriche.[5] The Gefreite-Korporale was a rank that also existed along with Gefreiter in the Austrian Army during the Thirty Years' War.[5]
From the 1920s the German rank of Gefreiter has expanded into several additional ranks and duties, those being Obergefreiter (Senior Lance Corporal otherwise Second Corporal; Prussian Army since 1859), Hauptgefreiter (Leading Lance Corporal; Luftwaffe during 1935-1944, Kriegsmarine during 1938-1945, Heer from 1955), Stabsgefreiter (Staff Lance Corporal; Reichswehr since 1927. Kriegsmarine until 1945. Luftwaffe from 1944 temporarily replacing Hauptgefreiter rank) and Oberstabsgefreiter (Senior Staff Lance Corporal; Kriegsmarine since 1940. Not Heer or Luftwaffe until 1996). All Gefreiter ranks are now in use with the German Army, Airforce and Navy.
Germany
Bundeswehr
(Army, Air Force, Navy) | ||||||
| ||||||
| Rank insignia | German enlisted rank | |||||
| Introduction | 1955 | |||||
| Rank group | Enlisted ranks | |||||
| Army | Gefreiter | |||||
| Air Force | Gefreiter | |||||
| Navy | Gefreiter | |||||
| NATO equivalent | OR-2 | |||||
Gefreiter (abbr. Gefr. or G.) is the second enlisted rank grade within the modern-day Army (Heer), Air Force (Luftwaffe) and Navy (Marine) of the Bundeswehr.[12] Following the NATO ranking system, Gefreiter equates to OR-2 on the NATO-standard rank scale, the rank is thus equivalent to either private, private first class, vice corporal or corporal rank depending on the chosen NATO-allied force used for the comparison.[2] It is grade A4 in the pay scale of the Federal Ministry of Defence.
The sequence of ranks (top-down approach) in this particular group is as follows:
- OR-4a: Oberstabsgefreiter
- OR-4b: Stabsgefreiter
- OR-3a: Hauptgefreiter
- OR-3b: Obergefreiter
- OR-2: Gefreiter
- OR-1: Soldat/Schütze (Army), Flieger (Air Force), Matrose (Navy)
In line with Bundeswehr rank advancement conditions, enlisted personnel OR-1 may be promoted to OR-2 level after passing primary recruit training (usually after three to six months, depending on branch of service and curriculum) to the rank of Gefreiter.
| junior Rank Soldat (rank) |
(German enlisted rank)
|
senior Rank Obergefreiter |
Wehrmacht
Throughout the periods of the Royal Prussian Army, Imperial Army of the German Empire, Reichswehr and the German Wehrmacht, the rank of Gefreiter was considered in English the equivalent to a British Army Lance Corporal rank, with Obergefreiter as senior lance corporal or rather second corporal in the artillery, and a full corporal rank known as Unteroffizier[11] (subordinate non-commissioned officer) which replaced the Korporal rank from 1856. Within the army branch of the German Wehrmacht, a rank of Oberschütze (senior rifleman) once existed between the ranks of Gefreiter and Schütze/Soldat ("[enlisted] ordinary-rank rifleman/soldier"). In modern times the Unteroffizier rank is now considered in English the equivalent to a sergeant and less a corporal rank, under the NATO rank scale OR-5.
One of the best-known holders of the rank of Gefreiter was Adolf Hitler, who held the rank in the Bavarian Reserve Infantry Regiment 16 of the Royal Bavarian Army during World War I.
Switzerland

See Swiss army ranks.
Austria
| |||
| Rank insignia | Austrian Bundesheer | ||
| Introduction | 1857 | ||
| Rank group | Charges | ||
| Army / Air Force | Gefreiter | ||
| Navy | no equivalent | ||
| Lower: Higher: | Rekrut | ||
| Korporal | |||
| NATO equivalent | OR-2 | ||
Gefreiter (abbr. Gfr) is a military rank of the Austrian Bundesheer. It might be comparable to enlisted men OR2/ private 1st Class ranks in Anglophone armed forces. However, in the Bundesheer it belongs to the so-called charges rank group (OR2 to OR4).
Austro-Hungarian Army
In the k.u.k. Austro-Hungarian Army (1867–1918) Gefreiter (Hungarian: Őrvezetö) was corresponding to Patrouilleführer, and Vormeister. It was used by the k.u.k. Kaiserjäger as well as the Feldjäger, Standschützen troops, k.u.k. Cavalry, Medical corps, and Infantry.
Then rank insignia was a single white celluloid-star on the stand-up collar of the so-called Waffenrock (en: Tunic) on gorget patch (de: Paroli). Stand-up collar and background of the gorget patch showed a particular egalisation colour.
| Junior rank Soldat (Honvéd) |
Rank insignias of the Austro-Hungarian armed forces Gefreiter Patrouilleführer Vormeister |
Senior rank Korporal |
- Rank insignia
| Desigahntion | Austrian k.u.k. Army enlisted men | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
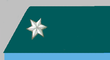 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | ||||
| insignia | ||||||||||
| description | Patrouilleführer | Gefreiter | Vormeister | |||||||
| k.u.k. Mountain troops |
k.u.k. Rifles |
Machine-gun units |
Infantry IR 7 |
|||||||
| branch | Rifles | Cavalry | Infantry | Military engineering |
Artillery | |||||
| (equivalent) | (Rifle 1st class) | (Private 1st class) | (Gunner 1st class) | |||||||
- Gefreiter in adjustation of the infantry
-

IR 7 -

IR 25 -

IR 33 -

IR 37 -

IR 41 -

IR 50 -

IR 62 -

IR 69 -

IR 77 -

IR 87 -

IR 92 -

IR 99 -

IR 101
- See also
- Main articles: Rank insignias of the Austro-Hungarian armed forces, Waffenfarbe (Austria), and Adjustierung
Yefreytor in Russia and the post-Soviet states
Yefreytor (Russian: Ефрейтор) is a German loanword in Russian and denotes a similar rank in the Russian army.
In Russia, the rank of yefreytor was introduced by Peter I in 1716 to the infantry, cavalry and engineer forces. The rank was not used after 1722. During the reign of Paul I it was made an equivalent rank to private, which after the reign of Alexander I was used only for the Imperial Guard. Yefreytor was re-introduced in the course of the military reforms of 1826.
In the armed forces of the Soviet Union (and later the Russian Federation) yefreytor is the highest rank of enlisted personnel. According to NATO-ranksystem the rank might be comparable to OR-2 in Anglophone armed forces.
| junior rank: Rjadovoy |
Yefreytor |
senior rank: Junior sergeant |
Rank insignia IRA, Red Army (RA), Soviet Army (SA), armed forces of the Russian Federation (RF)
-
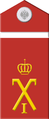
shoulder insignia yefreytor to IRA until 1917
-
gorget insignia to gymnastjorka yefreytor RA (1940−1943)
-

shoulder board yefreytor
Air Force
RA (1943−1955) and SA (1946-1955) -
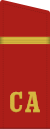
... yefreytor
infantry SA -
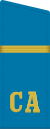
... yefreytor Air Force, aviation Air defence and Navy, Airborne troops SA
(1955−1963) -

... service uniform Kursant with OR2-rank yefreytor, of the RF AF or airborne troops (1994-2010)
-

... yefreytor
land forces and SMT
PF Army
(1994−2010) -

... filed uniform yefreytor
land forces, airborne troops, SMT, RSF
Marines,
AF, AD, etc.
(1994—2010)
See also
- Ranks of the Imperial German Army
- World War II German Army ranks and insignia
- Rank insignia of the German armed forces
- Ranks and insignia of NATO armies enlisted
References
- 1 2 Duden; Definition of Gefreiter, in German.
- 1 2 Official Website (Bundeswehr): Dienstgrade und Uniformen der Bundeswehr (Service Ranks and Uniforms of the German Federal Defence Forces), in German.
- ↑ Duden; Alternative Spelling and Definition of Gefreite, in German.
- ↑ Duden; Origin and meaning of "Landsknecht", in German.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 "Gefreiter" - Allgemeine Encyclopädie der Wissenschaften und Künste, Erste Section, A-G, (Universal Encyclopaedia of the Sciences and Arts, First Section, A-G), Author: Johann Samuel Ersch and Johann Gottfried Gruber, Publisher: F. A. Brockhaus, Leipzig, 1852, Page 471-472, in German.
- 1 2 3 Corpus Juris Militaris Des Heiliges Römisches Reich (Military Law of the Holy Roman Empire), Volume 2, Author: Johann Christian Lünig, Leipzig, 1723, in German.
- ↑ The Landsknechts, Author: Douglas Miller, Publisher: Osprey Publishing, Great Britain, 1976, ISBN 0850452589.
- ↑ Landsknecht Soldier 1486-1560, Author: John Richards, Publisher: Osprey Publishing, Great Britain, 2002, ISBN 1841762431.
- ↑ Lutz Mackensen. Vom Ursprung der Wörter. Etymologisches Wörterbuch der deutschen Sprache.
- ↑ Duden; Origin and meaning of "Gemeine", in German.
- 1 2 Duden; Origin and meaning of "Korporal", in German.
- ↑ BROCKHAUS, The encyclopedia in 24 volumes (1796–2001), Volume 8: 3-7653-3668-8, page 231; definition "Gefreiter".