Gliese 1132 b
| Exoplanet | List of exoplanets | |
|---|---|---|
 | ||
| Parent star | ||
| Star | Gliese 1132 | |
| Right ascension | (α) | 10h 14m 51.1s |
| Declination | (δ) | −47° 09′ 12″ |
| Apparent magnitude | (mV) | 14.7 |
| Distance | 39 ly (12 pc) | |
| Spectral type | M3.5D | |
| Orbital elements | ||
| Orbital period | (P) | 1.6 d |
| Physical characteristics | ||
| Mass | (m) | 1.6 M⊕ |
| Radius | (r) | 1.2 R⊕ |
| Stellar flux | (F⊙) | 19 ⊕ |
| Temperature | (T) | 410 K (137 °C; 278 °F) |
| Discovery information | ||
| Discovery date | May 10, 2015 (announced)[1] November 12, 2015 (confirmed)[2] | |
| Discoverer(s) | MEarth-South Array Team | |
| Discovery method | Transit | |
| Discovery site | Chile | |
| Discovery status | Confirmed | |
| Other designations | ||
| Gliese 1132 b, Gl 1132 b, GJ 1132 b
| ||
Gliese 1132 b (often shortened to GJ 1132 b) is an exoplanet orbiting a red dwarf star (Gliese 1132) 39 light years (12 parsecs) from Earth.[3] The planet is considered uninhabitable but cool enough to possess an atmosphere.[1] Gliese 1132 b was discovered by the MEarth-South array in Chile.[4]
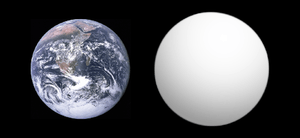
It has been called "one of the most important planets ever discovered beyond the Solar System": Gliese 1132 b is three times closer to Earth than any other known rocky exoplanet and telescopes should be able to determine the composition of its atmosphere, the speed of its winds and the color of its sunsets.[5][6][7] This is due in part to the small diameter of its parent star (21% that of the Sun), which increases the effect on the star's light of its transits. The planet's diameter is approximately 20% larger than that of the Earth[3] and its mass is estimated at 1.6 times that of Earth,[1] implying that it is a has an Earth-like rocky composition.[8] Gliese 1132 b orbits its star every 1.6 days at a distance of 1.4 million miles.[4]
The planet receives 19 times more stellar radiation than Earth.[3] The temperature of the top of its atmosphere is estimated at 500 °F (260 °C; 533 K). The planet is estimated to be hotter than Venus, as higher temperatures may prevail near the surface.[8] (cf. Atmosphere of Venus, Colonization of Venus) It is possible that one side of the planet is cooler, because it is presumed to be tidally locked due to its proximity to its star; however, under most circumstances where an atmosphere is thick, it would be able to transfer heat to the far side.
See also
References
- 1 2 3 Chu, Jennifer (November 11, 2015). "New exoplanet in our neighborhood". MIT News. Retrieved 2015-11-12.
- ↑ NASA Exoplanet Archive New ticker slide 1
- 1 2 3 Berta-Thompson, Zachory K.; Irwin, Jonathan; Charbonneau, David; Newton, Elisabeth R.; Dittmann, Jason A.; Astudillo-Defru, Nicola; Bonfils, Xavier; Gillon, Michaël; Jehin, Emmanuël. "A rocky planet transiting a nearby low-mass star". Nature. 527 (7577): 204–207. arXiv:1511.03550
 . Bibcode:2015Natur.527..204B. doi:10.1038/nature15762.
. Bibcode:2015Natur.527..204B. doi:10.1038/nature15762. - 1 2 "Astronomers Eager to Get a Whiff of Newfound Venus-like Planet". Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics. November 11, 2015. Retrieved 2015-11-12.
- ↑ Sample, Ian. "Earth-like world could be 'most important planet found outside solar system'". The Guardian. Retrieved 2015-11-11.
- ↑ Burgess, Matt. "Exoplanet GJ 1132b: the 'most important' ever found (Wired UK)". Wired UK. Retrieved 2015-11-12.
- ↑ "Getting Up Close and Personal with an Earth-Sized Exoplanet". The Kavli Foundation. November 11, 2015. Retrieved 2015-11-13.
- 1 2 Eva Botkin-Kowacki (2015-11-11). "Spotted: A rocky Earth-sized planet close by". Christian Science Monitor.
Coordinates: ![]() 10h 14m 51.100s, −47° 09′ 12.00″
10h 14m 51.100s, −47° 09′ 12.00″