Glycerol phosphate shuttle
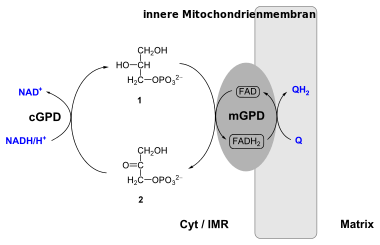
The glycerol-3-phosphate shuttle is a mechanism that regenerates NAD+ from NADH, a by-product of glycolysis. Its importance in transporting reducing equivalents is secondary to the malate-aspartate shuttle.
Reaction
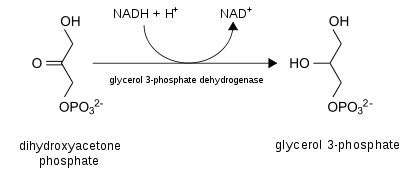
In this shuttle, the enzyme called cytoplasmic glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 1 (GPDH-C) converts dihydroxyacetone phosphate (2) to glycerol 3-phosphate (1) by oxidizing one molecule of NADH to NAD+ as in the following reaction:[1]
Reverse path
Glycerol-3-phosphate gets converted back to dihydroxyacetone phosphate by an inner membrane-bound mitochondrial glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 2 (GPDH-M), this time reducing one molecule of enzyme-bound flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) to FADH2. FADH2 then reduces coenzyme Q (ubiquinone to ubiquinol) which enters into oxidative phosphorylation.[1] This reaction is irreversible.[2]
Function
The glycerol-3-phosphate shuttle allows the NADH synthesized in the cytosol by glycolysis to contribute to the oxidative phosphorylation pathway in the mitochondria to generate ATP.[1] It has been found in animals, fungi, and plants.[2]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 Stryer, Lubert; Berg, Jeremy Mark; Tymoczko, John L. (2007). Biochemistry. San Francisco: W. H. Freeman. ISBN 0-7167-8724-5.
- 1 2 Shen W, Wei Y, Dauk M, et al. (February 2006). "Involvement of a glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase in modulating the NADH/NAD+ ratio provides evidence of a mitochondrial glycerol-3-phosphate shuttle in Arabidopsis". Plant Cell. 18 (2): 422–41. doi:10.1105/tpc.105.039750. PMC 1356549
 . PMID 16415206.
. PMID 16415206.
External links
- http://chemistry.elmhurst.edu/vchembook/601glycolysissum.html (describes the shuttle in the context of glycolysis)