Hants County, Nova Scotia
| Hants County | |
|---|---|
| County | |
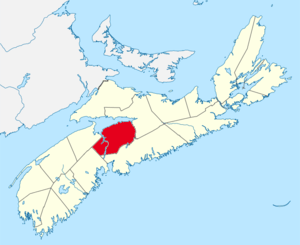 Location of Hants County, Nova Scotia | |
| Coordinates: 45°06′N 63°54′W / 45.1°N 63.9°WCoordinates: 45°06′N 63°54′W / 45.1°N 63.9°W | |
| Country |
|
| Province |
|
| Municipal district (s) | East Hants / West Hants |
| Towns | Hantsport / Windsor |
| Established | June 17, 1781 |
| Electoral Districts Federal |
Kings—Hants |
| Provincial | Hants East / Hants West |
| Area[1] | |
| • Land | 3,049.08 km2 (1,177.26 sq mi) |
| Population (2006)[1][2] | |
| • Total | 41,182 |
| • Density | 13.5/km2 (35/sq mi) |
| • Change 2001-06 |
|
| • Census Rankings - Municipal districts East Hants West Hants - Towns Hantsport Windsor - Reserves Indian Brook 14 |
21,387 (179 of 5,008) 13,881 (272 of 5,008) 1,191 (1,839 of 5,008) 3,709 (862 of 5,008) 1,014 (2,039 of 5,008) |
| Time zone | AST (UTC-4) |
| • Summer (DST) | ADT (UTC-3) |
| Area code(s) | 902 |
| Dwellings | 17,277 |
| Median Income* | $49,630 |
| |
Hants County is a county in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia.
History
Boundaries
The county of Hants was created June 17, 1781, and consisted of the townships of Windsor, Falmouth and Newport. Originally getting its name from the English county of Hampshire, abbreviated to Hants from the Old English name Hantescire, the County was established out of part of what had been Kings County.[3] Subsequently in 1861, Hants County was divided into two Districts called East Hants and West Hants.
18th century - origins
Mi'kmaq

The Mi'kmaq are the aboriginal people who lived on these lands for centuries. In the course of their historical relationship with the Acadian people, many Mi'kmaq became Catholic and therefore played an active role in the Acadian resistance to the Protestant British annexation of Hants County. They were clearly supporters of Abbe LeLoutre's work in protecting Acadian and Mi'kmaq and ultimately Catholic interests in the region. Within Hants County, they fought in the Battle at St. Croix on the St. Croix River.
There is a long history of missionary work in Hants County, such as the work of Silas Tertius Rand's work on a reserve near Hantsport. There are still Mi'kmaq communities in Hants County such as Indian Brook 14, Nova Scotia (the home of the famous activist Anna Mae Aquash) and Shubenacadie 13, Nova Scotia. Shubenacadie is the oldest community in Hants County. There is a significant monument in the middle of the reserve to Major Jean-Baptiste Cope, the signatory to the Peace Treaty of 1752 with the British, which was recently upheld by the Supreme Court of Canada (1985).
Acadians
The first Acadians to settle in present-day Hants County (known as Pisiguit) established farms at (present day Falmouth) in the early 1680s, as the 1686 census shows a number of families on well established farms utilizing dyked pastures. More Acadian villages soon followed spreading along the shores of the Piziquid and St. Croix rivers. One of these was at present day Windsor, Nova Scotia. With an expanding population the region by 1722 was split into two parishes (see Pisiquit). The l'Assomption parish church was situated on a hill overlooking the confluence of the Pisiquit and Saint Croix rivers where in 1750 it was pulled down by the Acadians under orders from the British to make way for Fort Edward. By the early 1700s Acadians migrated all along the shore of Hants County to the Shubenacadie River. One of the most prominent Acadians from this area was Noel Doiron who is the namesake of the community of Noel. With the founding of both Halifax (1749) and Fort Edward, there was an Acadian Exodus that involved an emigration of most of the Acadians from the Municipality of East Hants (1750) and from West Hants (Pisiguit) as well. They left British Nova Scotia for French occupied Prince Edward Island.[4] During the 1755 Expulsion of the Acadians the majority of those Acadians remaining were deported to various locations along the eastern seaboard of the Thirteen Colonies, most notably New England and Maryland. The Expulsion of the Acadians from Hants County began at exactly the same time as it happened at Grand-Pré, with the Acadian men being imprisoned within the walls of Fort Edward. Fort Edward was one of four British forts in Acadia to imprison Acadians throughout the nine years of the expulsion.
New England Planters
After the Acadians were removed from the area of present-day Hants County, New England Planters began to arrive and settle the vacated lands (1760). They formed the townships of Windsor, Falmouth and Newport. Many arrived from Rhode Island.[5] One of the Planters of note during this period was Henry Alline who led the New Light revival of the Great Awakening in the region. Alline's movement had a significant impact on the stance the New Englander Planters took with respect to the troubles building in the colonies to the west, between their British masters, and brethren who remained in New England, that led to the Revolutionary War. Alline's Newlight congregations were the progenitors of the Baptist movement in Canada.[6][7][8]
Ulster Irish
The next wave of immigration to Hants County was the Ulster Scots people who settled all along the Cobequid shore such as the O'Briens in Noel, Nova Scotia (1771) and the Putnams in Maitland, Nova Scotia.
American Loyalists
During the American Revolution, Fort Edward (Nova Scotia) played a pivotal role defending Halifax from a possible land attack and serving as the headquarters in Atlantic Canada for 84th Regiment of Foot (Royal Highland Emigrants). After the American Revolution, the Rawdon Township and Douglas Township were created for American Loyalists (1884). The Douglas Township (Kennetcook, Nova Scotia and area) was settled by the 84th Regiment of Foot (Royal Highland Emigrants). The Rawdon Township was settled by loyalists from South Carolina whose lives had been saved in the Siege of Ninety-Six by Lord Rawdon and the 84th Regiment of Foot.
19th century - shipbuilding and confederation
Plaster War
Windsor developed its gypsum deposits, usually selling it to American markets at Passamaquoddy Bay. Often this trade was illegal. In 1820 an effort to stop this smuggling trade resulted in the "Plaster War", in which local smugglers resoundingly defeated the efforts of New Brunswick officials to bring the trade under their control.[9]
Shipbuilding
Productive timber lands and tidal building sites made Hants County an important shipbuilding centre in the 19th century. Loyalist merchant Abraham Cunard was an early shipbuilder in the county. Cunard's efforts were surpassed by much larger yards by the mid 19th century, including the William Dawson Lawrence shipyard in Maitland which built the William D. Lawrence, the largest wooden ship ever built in Canada, and Ezra Churchill's in Hantsport.
The Great Hants Campaign (1869)
The Honourable Joseph Howe was the first member of parliament for Hants County (1867).[10] He campaigned in the county with an agenda to punish those politicians who have forced Nova Scotia to participate in the formation, and become a part of Canada without a mandate or referendum from the people. Over the next two years in office, deciding not to mobilize to join America or become a colony independent of Britain, Howe determined that Nova Scotia's best option was to remain in Canada and to fight for "better terms. While most Nova Scotians remained supportive of the Anti-Confederation Campaign during this time period, Howe ran in Hants County bi-election of 1869 to get a mandate from the people to see if they wanted him to continue to support Nova Scotia's entry into Canada. What ensued was one of the most expensive political campaigns in Nova Scotia's history.[10] The whole country watched to see if Howe would be returned to Ottawa to lead Nova Scotia into Confederation on the best terms possible. Howe toured the whole county and eventually won, which eventually led to all of Nova Scotia accepting Canada.[11]
20th century
Hants County produced two Olympians, both of whom came from along the Noel shore (See Athletics at the 1928 Summer Olympics – Men's marathon). Along with the great literary figure in Nova Scotia's history, Thomas Chandler Haliburton, Hants produced Alden Nowlan, George Elliot Clarke and others. Folk Singer Stan Rogers made the community of Rawdon famous by writing the song "The Rawdon Hills" (See Video).
Natural resources: wood, fish, gypsum, oil and gold
The wood in the county was both used to build the many wooden ships, but it was also used as an export resource on the wooden ships. For this purpose, the Midland Railway was also built through the County (1901), connecting Windsor and Truro.
The county is noted for very large deposits of gypsum, some of which was at one time shipped from Walton, Nova Scotia. The world's largest open pit Gypsum mine is located in Milford, East Hants and currently produces approximately 8,000 tons of gypsum daily. George Elliot Clarke's poem, "West Hants County", tells of the difficult condition of black workers in the gypsum mines.
Gold was mined at Renfrew, Nova Scotia, near Nine Mile River, Nova Scotia, The village was the home of one of the largest gold mines in the province. There were other gold mines in the community of Rawdon Gold Mines, Nova Scotia. There is currently oil exploration in and around Kennetcook, Nova Scotia.
Notable Residents
- Henry Alline
- Thomas Chandler Haliburton
- Alden Nowlan
- Noel Doiron
- George Elliot Clarke
- William Dawson Lawrence
- Ezra Churchill
- Anna Mae Aquash
- Jean-Baptiste Cope
- Trevor Andrew
- Buck 65
Isaac Douglas
Communities
For a list of communities in Hants County, see List of communities.
Towns
District municipalities
Native reserves
Demographics
|
Mother tongue language (2011)[14]
|
Ethnic Groups (2006)[15]
|
Access routes
Highways and numbered routes that run through the county, including external routes that start or finish at the county limits:[16]
|
See also
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Hants County, Nova Scotia. |
- 1 2 2006 Statistics Canada Community Profile: Hants County, Nova Scotia
- ↑ Statistics Canada Population and dwelling counts, for Canada and census subdivisions (municipalities), 2006 and 2001 censuses - 100% data
- ↑ The words of the minutes of the Council of Nova Scotia for June 17, 1781 make it clear that the distance from Horton (the County town of Kings County) and the inconvenience of crossing the Avon River to transact county business were factors which led to a separate county being formed. Four and a half years later its boundaries were more precisely defined and set forth by the Governor and Council in 1785. The boundary lines of Hants were duly surveyed and confirmed by the Lieutenant Governor 1828.
- ↑ Stephen Patterson. Colonial Wars and Aboriginal Peoples: 1744-1763. p. 141
- ↑ Rhode Island Settlers in Nova Scotia
- ↑ Beverley, James and Barry Moody, Editors. The Journal of Henry Alline. Lancelot Press for the Acadia Divinity School and the Baptist Historical Committee. 1982.
- ↑ Bumsted, J. M. Henry Alline. Lancelot Press, Hantsport, 1984.
- ↑ Rawlyk, George. The Sermons of Henry Alline. Lancelot Press for Acadia Divinity College and The Baptist Historical Committee of the United Baptist Convention of the Atlantic Provinces. 1986.
- ↑ Smith, Joshua (2007). Borderland Smuggling: Patriots, Loyalists, and Illicit Trade in the Northeast, 1780-1820. Gainesville, FL: UPF. pp. passim. ISBN 0-8130-2986-4.
- 1 2 Joseph Howe: The Briton Becomes Canadian, 1848-1873 By J. Murray Beck
- ↑ Joseph Schull. "The Night They Killed Joe Howe" Ottawa Citizen - Jun 30, 1956
- ↑ Censuses 1871-1941
- ↑ Statistics Canada: 1996, 2001, 2006 census
- ↑ Statistics Canada: 2011 census
- ↑ 2006 Statistics Canada Census Ethnocultural Portrait of Canada: Hants County, Nova Scotia
- ↑ Atlantic Canada Back Road Atlas ISBN 978-1-55368-618-7 Pages 67-68, 80-81
External links
 |
Kings County | Minas Basin |  | |
| Lunenburg County | |
Colchester County | ||
| ||||
| | ||||
| Halifax Regional Municipality |