Hariphunchai
| Hariphunchai | ||||||||
| ||||||||
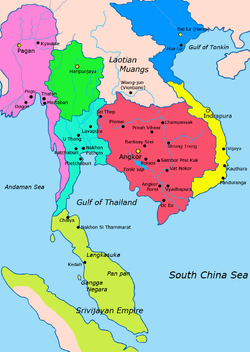 1000–1100 AD Green: Haripunchai Light Blue: Lavo Kingdom Red: Khmer Empire Yellow: Champa Blue: Đại Việt Pink: Pagan Kingdom Light green: Srivijayan Empire | ||||||||
| Capital | Lamphun | |||||||
| Government | Monarchy | |||||||
| King | ||||||||
| • | 661 | Jamadevi (first) | ||||||
| • | c. 1200 | Yip (last) | ||||||
| Historical era | Middle Ages | |||||||
| • | Founding by Suthep | 661 | ||||||
| • | More probable, supposed founding | c. 750 A.D. | ||||||
| • | Besieged and captured by Kingdom of Lanna | 1292 | ||||||
| ||||||||
Part of a series on the |
|---|
| History of Thailand |
 |
|
Legendary Suvarnabhumi Central Thailand Dvaravati Lavo Supannabhum Northern Thailand Singhanavati Ngoenyang Hariphunchai Southern Thailand Pan Pan Raktamaritika Langkasuka Srivijaya Tambralinga Nakhon Si Thammarat Sultanate of Pattani Kedah Sultanate |
| History |
|
Sukhothai Kingdom Ayutthaya Kingdom Thonburi Kingdom Rattanakosin Kingdom Military period Democratic period |
|
Regional history |
|
|
Hariphunchai or Haribhunjaya (from Thai: หริภุญชัย, in turn from Pali: Haribhuñjaya) was a Mon kingdom in the north of present Thailand in the centuries before the Thais moved into the area. Its capital was at Lamphun, which at the time was also called Hariphunchai.[1]:77 In 1292 the city was besieged and captured by Mangrai of the Thai kingdom of Lanna.[1]:208
Founding
According to the Camadevivamsa and Jinakalamali chronicles, the city was founded by a hermit named Suthep in 661 AD, and the Mon ruler of Lavo Kingdom (present-day Lopburi) sent his daughter Jamadevi to become its first queen. However, this date is now considered as too early, and the actual beginning is placed at around 750 AD. At that time, most of what is now central Thailand was under the rule of various Mon city states, known collectively as the Dvaravati kingdom. Queen Jamadevi gave birth to twins, the older succeeding her as the ruler of Lamphun, and the younger becoming ruler of neighboring Lampang.
Flourishing and downfall

The kingdom under King Adityaraja, came into conflict with the Khmers in the twelfth century. Lamphun inscriptions from 1213, 1218, and 1219, mention King Sabbadhisiddhi endowing Buddhist monuments.[1]:195
The chronicles say that the Khmer unsuccessfully besieged Hariphunchai several times during the 11th century. It is not clear if the chronicles describe actual or legendary events, but the other Dvaravati Mon kingdoms did in fact fall to the Khmers at this time. The early 13th century was a golden time for Hariphunchai, as the chronicles talk only about religious activities or constructing buildings, not about wars. Nevertheless, Hariphunchai was besieged in 1292 by the Lanna king Mangrai the Great, who incorporated it into his Lan Na ("One Million Rice Fields") kingdom.
List of rulers
Names of monarchs of the Hariphunchai kingdom according to Tamnan Hariphunchai (History of Kingdom of Hariphunchai):
- Queen Jamadevi
- Hanayos
- Kumanjaraj
- Rudantra
- Sonamanjusaka
- Samsara
- Padumaraj
- Kusadeva
- Nokaraj
- Dasaraj
- Gutta
- Sera
- Yuvaraj
- Brahmtarayo
- Muksa
- Traphaka
- Uchitajakraphad king of Lavo
- Kampol
- Jakaphadiraj, King of Atikuyaburi
- Vasudev
- Yeyyala
- Maharaj, King of Lampang
- Sela
- Kanjana
- Chilanka
- Phunthula
- Ditta
- Chettharaj
- Jeyakaraj
- Phatijjaraj
- Thamikaraj
- Ratharaj
- Saphasith
- Chettharaj
- Jeyakaraj
- Datvanyaraj
- Ganga
- Siribun
- Uthen
- Phanton
- Atana
- Havam
- Trangal
- Yotta
- Yip
References
- 1 2 3 Coedès, George (1968). Walter F. Vella, ed. The Indianized States of Southeast Asia. trans.Susan Brown Cowing. University of Hawaii Press. ISBN 978-0-8248-0368-1.
- 'Historic Lamphun: Capital of the Mon Kingdom of Haripunchai', in: Forbes, Andrew, and Henley, David, Ancient Chiang Mai Volume 4. Chiang Mai, Cognoscenti Books, 2012. ASIN B006J541LE
- Swearer, Donald K. and Sommai Premchit. The Legend of Queen Cama: Bodhiramsi's Camadevivamsa, a Translation and Commentary. New York: State University of New York Press, 1998.