Health in Hungary
Public Health Measures
In 2016 Hunbisco produced a critical report on the implementation of the sugar tax which was introduced in Hungary in 2011. It reported that the consumption of products subject to the sugar tax had decreased. They argued that manufacturers now have a smaller budget to explore healthier alternatives to sugar. Innovation and new marketing initiatives have reduced since 2011. The effect of the health tax, in addition to 27% VAT, increases the price of products by as much as 40%, and has led to redundancies. They say that the consumption of other products not subject to the tax but with similar nutritional contents, like popcorn, has not dropped. The advocate abolition of the tax in favour of educational measures.[1]
Statistics
Despite recent improvements, life expectancy in Hungary is still among the lowest in the European Union.[2] Romani people have a life expectancy up to ten years lower than ethnic Hungarians.[3]
| Year | Life expectancy (years, Man/Woman) | Infant mortality rate (‰) | Suicide rate
(per 100,000 people) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1949 | 59.28 / 63.40 | 91.0 | 23.9 |
| 1960 | 65.89 / 70.10 | 47.6 | 26.0 |
| 1970 | 66.31 / 72.08 | 35.9 | 34.6 |
| 1980 | 65.45 / 72.70 | 23.2 | 44.9 |
| 1990 | 65.13 / 73.71 | 14.8 | 39.8 |
| 2001 | 68.15 / 76.46 | 8.1 | 29.2 |
| 2011 | 70.93 / 78.23 | 4.9 | 24.3 |
| 2012 | 71.45 / 78.38 | 4.9 | 23.7 |
| 2013 | 72.01 / 78.73 | 5.1 | 21.1 |
Major death causes
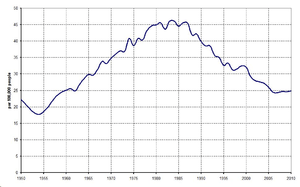
62,979 deaths (49.4% of all) in Hungary were caused by cardiovascular disease in 2013.[4] Number of cardiovascular disease deaths peaked in 1985 with 79,355, declining continuously since the fall of Communism.[4] The second most important cause of death was cancer with 33,274 (26.2% of all), stagnating since the 1990s.[4] Number of accident deaths dropped from 8,760 in 1990 to 3,654 in 2013, number of suicides from 4,911 in 1983 to 2,093 (21.1 per 100,000 people) in 2013 (the lowest data registered since 1956).[4][5] According to Péter Polt, Chief Prosecutor of Hungary, there were only 133 homicides in 2012, which is the lowest number registered in the last 50 years in Hungary.[6] Homicide rate was 1.3 per 100,000 people, which is among the lowest in the World.
Major health issues
Despite recent improvements, alcoholism is still a major problem in Hungary, inherited from the Socialist era.[7] According to KSH estimations number of alcohol addicts were 1,052,000 (10% of the total population) in 1995, declined to 432,000 (4.3% of the total population) in 2005.[8] Hungarians drank 9.5 litres of pure alcohol per capita in 2012 (40% wine, 35% beer and 24% spirit in 2005[9]), annual alcohol consumption is constantly between 9 and 11.5 litres of pure alcohol since the 1970s.[10]
Smoking also causes significant losses to Hungarian society. 28% of the adult population smoked in 2012, dropped to 19% in 2013 due to strict regulation.[11] Nationwide smoking bans expanded to every indoor public place (inculing pubs), the sale of tobacco is limited to state-controlled (but privately owned) tobacco shops[12] called Nemzeti dohánybolt (National Tobacco Shop). The number of stores where people can buy tobacco reduced from 40,000–42,000 to 5,300.[13] In 2013 WHO awarded Prime Minister Viktor Orbán in "accomplishments in the area of tobacco control".[14]
Regional differences
According to the last Országos Lakossági Egészségfelmérés ("National Population Health Survey") held in 2003 the most healthy region is Western Transdanubia and the least is the Southern Great Plain. There are huge differences between the western and eastern parts of Hungary, heart disease, hypertension, stroke and suicide is prevalent in the mostly agricultural and low-income characteristic Great Plain (can be described as the Hungarian Stroke Belt), but infrequent in the high-income and middle class characteristic Western Transdanubia. Central Hungary (region of Budapest) is between east and west by health.[15]
See also
References
- ↑ "Better health but side effects persist". Budapest Times. 21 February 2016. Retrieved 21 February 2016.
- ↑ Eurostat - Life expectancy at birth
- ↑ Hungary’s Healthcare System
- 1 2 3 4 5 Vital statistics, Hungarian Central Statistical Office (KSH)
- 1 2 Rudolf Andorka - Harcsa István: Deviáns viselkedés, TÁRKI, Budapest 1990, pp. 9-11 (Hungarian)
- ↑ Polt Péter: rég volt ilyen alacsony itthon a gyilkosságok száma ("Péter Polt: number of homicides is the lowest for a long time"), HVG (Hungarian)
- ↑ Judit Kiss - Edina Gábor: Az alkoholfogyasztás hazai tendenciái a 80-as évektől napjainkig I. ("Tendencies of the Hungarian alcohol consumption from the 1980s"), Országos Egészségfejlesztési Intézet ("National Institute for Health Development") (Hungarian)
- ↑ Number of alcohol addicts in Hungary, 1990–2005
- ↑ WHO Global Alcohol Report, Europe (English)
- ↑ Alcohol, coffee, tea and tobacco consumption in Hungary (1970–2011), Hungarian Central Statistical Office (KSH)
- ↑ Egy év alatt kilenc százalékkal csökkent a dohányosok száma ("Number of smokers declined by 9% in the last year") mno.hu (Hungarian)
- ↑ Govt allocates HUF 450 mln to company facilitating tobacco sales monopoly, Budapest Business Journal (English)
- ↑ Itt vannak a nemzeti dohányboltok ("Here are the national tobacco shops"), index.hu (Hungarian)
- ↑ WHO awards Orbán in fight against “tobacco industry tactics”, Budapest Business Journal (English)
- ↑ Országos Lakossági Egészségfelmérés ("National Population Health Survey"), 2003, Dr. Dóra Hermann: Krónikus betegségek (Chronic illnesses)