Intrusion Detection Message Exchange Format
Used as part of computer security, IDMEF (Intrusion Detection Message Exchange Format) is a data format used to exchange informations between software enabling intrusion detection, intrusion prevention, security information collection and management systems that may need to interact with them. IDMEF messages are designed to be processed automatically. The details of the format are described in the RFC 4765. This RFC presents an implementation of the XML data model and the associated DTD. The requirements for this format are described in RFC 4766, and the recommended transport protocol (IDXP) is documented in RFC 4767
IDMEF Format
The purpose of IDMEF is to define data formats and exchange procedures for sharing information of interest to intrusion detection and response systems and to the management systems that may need to interact with them. It is used in computer security for incidents reporting and exchanging. It is intended for easy automatic processing.
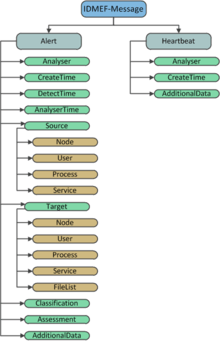
IDMEF is a well-structured object-oriented format, which consists of 33 classes containing 108 fields including three mandatory:
- The classification
- The unique login
- The date of creation of the alert.
There are currently two types of IDMEF messages that can be created, Heartbeat or Alert
Heartbeat
The Heartbeats are sent by the analyzers to indicate their status. These messages are sent at regular intervals which period is defined in the Heartbeat Interval Field. If none of these messages are received for several periods of time, consider that this analyzer is not able to trigger alerts.
Alert
Alerts are used to describe an attack that took place, the main areas that create the alert are:
- CreateTime: Date of creation of the alert
- DetectTime: alert detection time by the analyzer
- AnalyzerTime: The time the alert was sent by the analyzer
- Source: Details about the origin of the attack can be a service, a user, a process and / or a node
- Target: Details on the target of the attack can be a service, a user, a process and / or a node and a file
- Classification: Name of the attack and references, as CVEs
- Assessment: Evaluation of the attack (severity, potential impact, etc.)
- AdditionalData: Additional information on the attack
There are three other alert types that inherit from this scheme:
- CorrelationAlert: Grouping of alerts related to one another
- ToolAlert: alerts from the same Grouping tool
- OverflowAlert: Alert resulting from attack so-called buffer overflow
Example
IDMEF report of ping of death attack can look as follows:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<idmef:IDMEF-Message xmlns:idmef="http://iana.org/idmef" version="1.0">
<idmef:Alert messageid="abc123456789">
<idmef:Analyzer analyzerid="bc-sensor01">
<idmef:Node category="dns">
<idmef:name>sensor.example.com</idmef:name>
</idmef:Node>
</idmef:Analyzer>
<idmef:CreateTime ntpstamp="0xbc71f4f5.0xef449129">2000-03-09T10:01:25.93464Z</idmef:CreateTime>
<idmef:Source ident="a1a2" spoofed="yes">
<idmef:Node ident="a1a2-1">
<idmef:Address ident="a1a2-2" category="ipv4-addr">
<idmef:address>192.0.2.200</idmef:address>
</idmef:Address>
</idmef:Node>
</idmef:Source>
<idmef:Target ident="b3b4">
<idmef:Node>
<idmef:Address ident="b3b4-1" category="ipv4-addr">
<idmef:address>192.0.2.50</idmef:address>
</idmef:Address>
</idmef:Node>
</idmef:Target>
<idmef:Target ident="c5c6">
<idmef:Node ident="c5c6-1" category="nisplus">
<idmef:name>lollipop</idmef:name>
</idmef:Node>
</idmef:Target>
<idmef:Target ident="d7d8">
<idmef:Node ident="d7d8-1">
<idmef:location>Cabinet B10</idmef:location>
<idmef:name>Cisco.router.b10</idmef:name>
</idmef:Node>
</idmef:Target>
<idmef:Classification text="Ping-of-death detected">
<idmef:Reference origin="cve">
<idmef:name>CVE-1999-128</idmef:name>
<idmef:url>http://www.cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-1999-128</idmef:url>
</idmef:Reference>
</idmef:Classification>
</idmef:Alert>
</idmef:IDMEF-Message>
Tools implementing the IDMEF protocol
- Prelude (Intrustion Detection System)
- NIDS Snort
- NIDS Suricata ()
- HIDS Ossec ()
- HIDS Samhain ()
- Sagan
- Barnyard 2
- Orchids
- LibPrelude : Part of the Prelude OSS Project, libprelude permits to communicate between agents using the IDMEF format. Libprelude is coded in C but multiple bindings are available (python, lua, perl, etc.). It can be used in any open-source IDS tools.
- LibIDMEF : LibIDMEF is an implementation of the IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force), IDWG ( Intrusion Detection Exchange Format Charter Working Group), draft standard IDMEF protocol.
- IDMEF Framework Dotnet : Dotnet library to create IDMEF objects and export them in XML.
- DILCA – Distributed IDMEF Logical Correlation Architecture : DILCA is a distributed logical correlation and reaction architecture featuring collection and correlation of IDMEF formatted log events (Intrusion Detection Message Exchange Format – RFC 4765) through a multi-step signature based system.
- XML::IDMEF – A perl module for building/parsing IDMEF messages : IDMEF.pm is an interface for simply creating and parsing IDMEF messages. IDMEF is an XML based protocol designed mainly for representing Intrusion Detection (IDS) alert messages.
- Other module for creating/parsing IDMEF messages
- Snort IDMEF Plugin : Snort IDMEF is an IDMEF XML plugin for Snort to output alert events in the form of IDMEF messages. The plugin is compatible with Snort 2.x
- A Broccoli server to send IDMEF alerts via Prelude
- Converter for the IDMEF format
- IDMEF Parser
- An IDMEF alerting library for distributed IDPS
References
External links
- (English) RFC 4765, The Intrusion Detection Message Exchange Format (IDMEF)
- (English) RFC 4766, Intrusion Detection Message Exchange Requirements (IDMEF)
- (English) RFC 4767, The Intrusion Detection Exchange Protocol (IDXP)
- (English) Pravin Kothari, Intrusion Detection Interoperability and Standardization, SANS Institute InfoSec Reading Room, 19 février 2002
- (English) SECEF, Project for the promotion of the IDMEF and IODEF formats
 sécurité informatique portal
sécurité informatique portal
Tutorials
- Formats, Quick introduction on alert formats and what they are
- Comparison of alert formats, Long comparison of existing formats (CEF, LEEF, SDEE, etc.)
- Format IDMEF, Detailed description of the IDMEF Format
- Format SDEE, Detailed schema of SDEE format
- How to use IDMEF, Tutorial on IDMEF content and how to use it
- How to use LibPrelude, Detailed tutorial on how to use LibPrelude and code an IDMEF client (Python, C, Ruby, etc.)
- How to build a sensor, Detailed tutorial on how to create a new sensor that can communicate in IDMEF through the LibPrelude Library.
- LibPrelude IDMEF, Detailed description of all IDMEF fields