Metra Electric District
| Metra Electric District | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
A Metra Electric train pulls out of 59th Street station | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Overview | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Type | Commuter Rail | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| System | Metra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Operational | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Locale | Chicago, Illinois, United States | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Termini |
Millennium Station University Park, South Chicago (93rd Street), Blue Island | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stations | 49 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Services | Three | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Daily ridership | 34,000 (Avg. Weekday 2014)[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Owner | Metra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operator(s) | Metra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Technical | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Line length | 31 mi (50 km) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Track gauge | 4 ft 8 1⁄2 in (1,435 mm) standard gauge | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrification | Overhead catenary, 1500 V DC | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
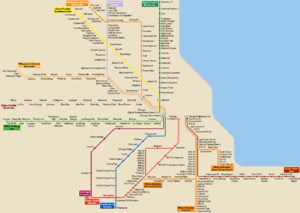
The Metra Electric District is an electrified commuter rail line owned and operated by Metra which connects Millennium Station (formerly Randolph Street Station), in downtown Chicago, with the city's southern suburbs. As of 2014, it is the second busiest of Metra's 11 lines, after the BNSF, with nearly 9.5 million annual riders.[2] While Metra does not explicitly refer to any of its lines by color, the timetable accents for the Metra Electric District are printed in bright "Panama orange" to reflect the line's origins with the Illinois Central Railroad (IC) and its Panama Limited passenger train.[3] It is the only Metra line that is solely a commuter route, which means no freight trains operate on this route. Instead, freight trains operate on tracks that are adjacent to the route. Its suburban operations line is the shortest on Metra's system, only running to fare zone G. If all the branches were combined, they would reach to zone J. It is also the only line with two downtown stations. During rush hours some trains do not reach Van Buren Street or Millennium Station.
It is the only Metra line powered by overhead catenary, and the only one with three branches. Trains operate on 1500 volts direct current, and all stations have high-level platforms. Its main line north of Kensington is shared by NICTD's South Shore Line, an electric interurban line through northern Indiana to South Bend.
It is the only Metra line with significant off-peak and Saturday service. In total, 92 trains depart Millennium Station according to the Monday-Saturday public timetable. Of these, 39 run on the main line. Of these, 29 reach University Park, with 5 terminating at Flossmoor and 5 terminating at Harvey. The stretch of the line from Millennium Station to 55th-56th-57th Street is the most heavily traveled section on the entire Metra system. Suburban operations along the line are the most frequent in the entire Metra system. The Metra Electric District also has the best on-time performance of all Metra lines, averaging only one late train a month in 2014.[4]
History
Steam era
The line was built by the Illinois Central Railroad, one of the first commuter services outside the major metropolitan areas of the northeastern United States. It opened on July 21, 1856 between the IC's downtown station (now Millennium Station) and Hyde Park. Part of the line was elevated for the World's Columbian Exposition of 1893 in Jackson Park.
The line predates the 1871 Great Chicago Fire, and ran on a trestle just offshore in Lake Michigan. After the fire, remains of buildings destroyed by the fire were dumped into the lake, creating landfill that forms the foundation of Grant Park, which the Metra Electric District runs through.
Two branches were added: from Brookdale southeast to South Chicago in the early 1880s, and from Kensington southwest to Blue Island in the early 1890s, both later electrified and still operated by Metra.
Electrical IC era

By the early 20th century the IC operated up to 300 steam trains each day. In 1919, the IC and the Chicago government collaborated to build a berm from the far south suburb of Homewood into the city. They also dug a trench from the near south side into the city proper, eliminating all grade crossings on the main line except one just south of the Richton Park station. The University Park extension required the line to cross a very long private driveway. The South Chicago branch runs at grade, crossing many city streets.
The grade crossing elimination project was followed by electrification. The IC electrified the commuter tracks in 1926, from downtown to Matteson. In addition to the removal of all grade crossings, the tracks were separated from, and moved to the west side of, the two freight and inter-city tracks. At McCormick Place just south of downtown Chicago, the two non-electrified tracks to Central Station (opened 1893) crossed over the new electric alignment. The electric tracks continued north to the new Randolph Street Station, on the site of the IC's original terminal.
The "IC Electric" was once Chicago's busiest suburban railroad, and carried a great deal of traffic within the city as well as to suburban communities. The three lines carried 26 million passengers in 1927, the first full year of electrified operation. Ridership rose to 35 million in 1929, and reached an all-time peak of 47 million in 1946.
Service was extended 1.1 miles (1.8 km) southward from Matteson to Richton Park, a new station at the south end of the coach storage yard, in 1946.[5]
The main line had six tracks between Roosevelt Road (Central Station) and 53rd Street (reduced to four in 1962), four to 111th Street, then two, as does the South Chicago branch; the Blue Island branch is single track.
1972 collision
The Illinois Central Gulf commuter rail crash, the worst rail accident in Chicago history, occurred on October 30, 1972. A new lightweight bi-level commuter train inbound to Chicago during the morning rush hour overshot the 27th Street platform and backed up into the station. The bi-level train had already tripped the signals to green for the next train, an older, heavy steel single-level express train. As the bi-level train was backing up at 11 miles per hour (18 km/h), it was struck by the single-level train at full speed. The single-level train telescoped the bi-level train, killing 45 passengers and injuring hundreds more, primarily in the bi-level train. A major contributing factor was that Illinois Central Gulf used a dark gray color scheme on the front ends of the Highliner fleet which was very difficult to see on the cloudy morning of the accident. After the accident the ends of all of the ICG 1926 heavyweight still in use and Highliner MU fleet were partially painted with bright orange added for additional visibility.
RTA era

In 1976 the Regional Transportation Authority signed a contract with Illinois Central Gulf to fund its commuter service. The next year an extension of 2.3 miles (3.7 km) was built to the current terminal at University Park (originally named Park Forest South). On May 1, 1987 Metra bought the line and its branches for $28 million. Two inter-city freight tracks retained by the ICG are now part of the Canadian National Railway, used by Amtrak's City of New Orleans, Illini and Saluki trains.
The Metra Electric District is the only line on the Metra system in which all stations (except 18th and 47th Streets, both flag stops) have ticket vending machines. The machines originally sold magnetically encoded tickets which unlocked the turnstiles. People with paper tickets or weekend passes, on reduced fares or who had trouble with the vending machines had to use a blue or orange pal phone to contact an operator who would unlock the turnstiles. Complaints from passengers who missed their trains caused Metra to remove the turnstiles in November 2003.
The main line and South Chicago branch run daily, but the Blue Island Branch does not operate on Sundays or holidays. A unique feature of the Metra Electric schedule is the similarity of the weekday and Saturday timetables. Many express trains run throughout the day in both directions. On other Metra lines, express service operates exclusively during the morning and afternoon rush hours. It is the only Metra line where all trackage is used exclusively for commuter service. Freight trains and Amtrak trains run on a pair of adjacent tracks owned by the Canadian National Railroad.
Off-peak and Saturday service is frequent, while Sunday service operates hourly north of 63rd Street and every 2 hours south of 63rd.
Potential expansion or service alterations
The proposed Gold Line, derived from the earlier and more extensive Gray Line plan[6] would have the Electric District operate more like a rapid transit line, by running trains more frequently (every ten minutes between 6am and midnight) with reduced-fare transfers to CTA buses and trains. Unlike the current service, which bypasses many stations to reach suburban stations more quickly, it would make all stops within the city. It would run from Millennium Station to South Chicago (93rd Street) at an estimated cost at $160 million.[7] Since the Gold Line was proposed, the idea of providing rapid transit service along Chicago's south lakefront has gained considerable support from neighborhoods along its route. Despite its popular support, officials from CTA and Metra have largely dismissed the plan, focussing on other expansion projects. In response to this and other concerns, in 2009 the RTA and the Chicago Department of Transportation authorized $450,000 for a "South Lakefront Study" that is anticipated to yield either one or two new transit projects that are eligible for Federal transit funding.[8]
An extension to Peotone, Illinois has been considered since the SouthWest Service was extended to Manhattan.[9][10]
Fleet
| Metra Electric District | |
|---|---|
| Specifications | |
| Coupling system | Scharfenberg or Tomlinson? |
The Metra Electric District uses second-generation bi-level Highliner multiple unit cars built by Nippon Sharyo. These will be supplemented by additional EMU's built at Nippon Sharyo's new Rochelle, IL facility opened in 2012.[11] In 2005, these began to replace the original Highliner fleet built by St. Louis Car Company and Bombardier in the 1970's.
On February 12, 2016 the original Highliners left on their last run in revenue service. Metra confirmed in a Facebook post that twenty-four cars are being sent to museums around the Midwestern United States, including the Illinois Railway Museum, while an unconfirmed source stated that some cars were sent to Mendota, Illinois to be scrapped.[12]
| Numbers | Type | Year built | Builder | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1227-1387 | EMU | 2012–Present | Nippon Sharyo | In Service |
| 1201-1226 | EMU | 2005 | Nippon Sharyo | In Service |
| 1501-1630 | EMU | 1971-1972 | St. Louis | Retired |
| 1631-1666 | EMU | 1978-1979 | Bombardier | Retired |
Footnotes
- ↑ "Operations and Ridership Data". Metra. Commuter Rail Division of the Regional Transportation Authority. Retrieved 6 November 2015.
- ↑ "COMMUTER RAIL RIDERSHIP TRENDS ANNUAL – 2014" (PDF). Metra: 3. 2014.
- ↑ "Did you know?" (PDF). On the Bi-Level: 3. June 2009.
- ↑ "The best and worst of Metra's on-time performance". Retrieved 10 July 2016.
- ↑ Allen & Benedict.
- ↑ "The Gold Line Proposal". Hyde park Urbanist. October 11, 2007. Retrieved February 28, 2012.
- ↑ Freemark, Yonah (July 6, 2009). "Chicago Transit Advocates Encourage Rapid Transit Conversion of Metra Line". The Transport Politic. Retrieved February 23, 2010.
- ↑ "RTA Releases List of 19 Proposed Transit Projects Throughout the Region for Public Comment" (PDF). Regional Transportation Authority. Retrieved March 3, 2010.
- ↑ Hilkevitch, Jon; Worthington, Rogers (18 April 1999). "Metra Wish List Grows With 3 Ambitious Lines". Chicago Tribune. Retrieved 5 August 2014.
- ↑ Groark, Virginia (8 February 2005). "Metra line extension proposed to Peotone airport". Chicago Tribune. Retrieved 5 August 2014.
- ↑ New Highliners will roll out of the factory, Metra - On the Bi-Level, Commuter Newsletter, January 2011
- ↑ https://www.facebook.com/MetraRail/videos/727365644067148. Missing or empty
|title=(help)
References
- Allen, John G.; Benedict, Roy G. "Chicago's Finest Transportation: The Illinois Central Electric" (PDF).
- Carlson, Norman (2006). "Train from Randolph Street: 150 Years of Service on the Illinois Central and Metra Electric" (PDF) (pdf).
- Ingles, J. David (July 1993). "Metra: "Best Commuter Train"". Trains.
- Middleton, William D. (1970). South Shore: Americas Last Interurban. Golden West Books. ISBN 978-0870950032.
External links
- Metra / Electric District Schedules
- Hyde Park Historical Society Article
- Metra Electric District: History and Pictures
![]() Media related to Metra Electric District at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Metra Electric District at Wikimedia Commons
