Immunosurgery
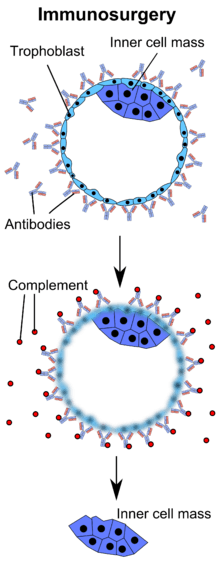
Immunosurgery is a method of removing an external cell layer of an object. Immunosurgery is to expose the specimen to a solution containing antibodies against the object, remove that solution and subsequently expose the object to complement. When only the external layer is marked with antibodies, these cells are the only ones to be destroyed by the complement.
This technique is used to isolate the inner cell mass of mouse blastocysts from the trophoblast layer. It can be used to obtain large quantities of pure inner cell masses in a relatively short period of time. The inner cell mass can be used for stem cell research. They are the best cells to use for research compared to adult and fetal stem cells.This is because the inner cell mass has not been affected by external factors.[2]
References
- ↑ Häggström, Mikael (2014). "Allogeneic component to overcome rejection in interspecific pregnancy". WikiJournal of Medicine. 1 (1). doi:10.15347/wjm/2014.004.
- ↑ Solter, D; Knowles, BB (1975). "Immunosurgery of mouse blastocyst". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 72 (12): 5099–102. Bibcode:1975PNAS...72.5099S. doi:10.1073/pnas.72.12.5099. PMC 388883
 . PMID 1108013.
. PMID 1108013.