Ischiocavernosus muscle
| Ischiocavernosus muscle | |
|---|---|
 Muscles of the female perineum (ischiocavernosus visible at upper right) | |
 Muscles of male perineum (ischiocavernosus visible at upper left) | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Ischial Tuberosity |
| Insertion | Crus of penis |
| Artery | Perineal artery |
| Nerve | Pudendal nerve |
| Actions | Assists the bulbospongiosus muscle (in males, empties the urethra; in females, clenches the vagina) |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus ischiocavernosus |
| TA | A09.5.02.004 |
| FMA | 19730 |
The ischiocavernosus muscle is a muscle just below the surface of the perineum, present in both men and women.[1]
Structure
It arises by tendinous and fleshy fibers from the inner surface of the tuberosity of the ischium, behind the crus penis; and from the rami of the pubis and ischium on either side of the crus.
From these points fleshy fibers succeed, and end in an aponeurosis which is inserted into the sides and under surface of the crus penis.
Function
It helps flex the anus, and (in males) stabilize the erect penis or (in females) tense the vagina during orgasm. Kegel exercises (also known as pelvic floor exercises) can help tone the ischiocavernosus muscle.
Ischiocavernosus compresses the crus penis, and retards the return of the blood through the veins, and thus serves to maintain the organ erect.
Additional images
 Right hip bone. Internal surface.
Right hip bone. Internal surface.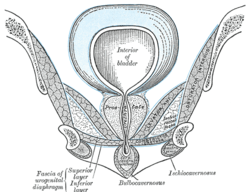 Coronal section of anterior part of pelvis, through the pubic arch. Seen from in front.
Coronal section of anterior part of pelvis, through the pubic arch. Seen from in front. The superficial branches of the internal pudendal artery.
The superficial branches of the internal pudendal artery.
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- -194314163 at GPnotebook
- Anatomy photo:41:11-0101 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "The Female Perineum: Muscles of the Superficial Perineal Pouch"
- Anatomy figure: 41:05-01 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Muscles of the female superficial perineal pouch."
- Anatomy figure: 42:04-01 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Muscles of the male superficial perineal pouch. "