Isocytosine
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-Amino-3H-pyrimidin-4-one | |
| Other names
2-Aminouracil | |
| Identifiers | |
| 108-53-2 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:55502 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL56260 |
| ChemSpider | 60309 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.266 |
| PubChem | 66950 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H5N3O | |
| Molar mass | 111.10 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Isocytosine or 2-aminouracil is a pyrimidine base that is an isomer of cytosine. It is used in combination with isoguanine in studies of unnatural nucleic acid analogues of the normal base pairs in DNA.[1]

Isoguanine-Isocytosine-base-pair
It can be synthesized from guanidine and malic acid.[2]
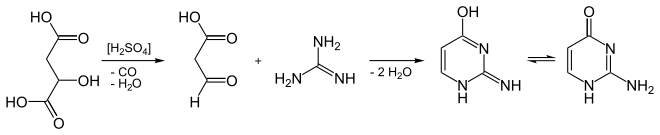
Synthesis of isocytosine from malic acid
It is also used in physical chemical studies involving metal complex binding, hydrogen bonding, and tautomerism and proton transfer effects in nucleobases.[3]
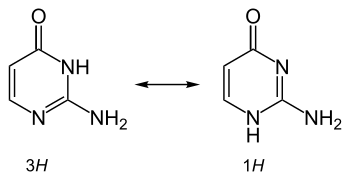
Tautomerism of isocytosine
References
- ↑ "Isocytosine". Molecule of the Week. American Chemical Society. Retrieved November 1, 2012.
- ↑ William T. Caldwell , Harry B. Kime (1940). "A New Synthesis of Isocytosine". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 62 (9): 2365–2365. doi:10.1021/ja01866a028.
- ↑ "Isocytosine". Sigma-Aldrich. Retrieved November 1, 2012.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 7/7/2015. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.