Jiva
In Hinduism and Jainism, a jiva (Sanskrit: जीव, jīva, alternative spelling jiwa; Hindi: जीव, jīv, alternative spelling jeev) is a living being, or any entity imbued with a life force.[1]
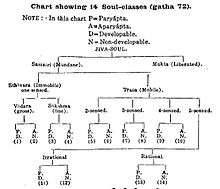
In Jainism, jiva is the immortal essence or soul of a living organism (human, animal, fish or plant etc.) which survives physical death.[2] The concept of Ajiva in Jainism means "not soul", and represents matter (including body), time, space, non-motion and motion.[2] In Jainism, a Jiva is either samsari (mundane, caught in cycle of rebirths) or mukta (liberated).[3]
The concept of jiva in Jainism is similar to atman in Hinduism. However, some Hindu traditions differentiate between the two concepts, with jiva considered as individual self, while atman as that which is universal unchanging self that is present in all living beings and everything else as the metaphysical Brahman.[4][5][6] The latter is sometimes referred to as jiva-atman (a soul in a living body).[4]
The word itself originates from the Sanskrit jivás, with the root jīv- "to breathe". It has the same Indo-European root as the Latin word vivus, meaning "alive".
See also
References
- ↑ Matthew Hall (2011). Plants as Persons: A Philosophical Botany. State University of New York Press. p. 76. ISBN 978-1-4384-3430-8.
- 1 2 J Jaini (1940). Outlines Of Jainism. Cambridge University Press. pp. xxii–xxiii.
- ↑ Jaini, Jagmandar-lāl (1927), Gommatsara Jiva-kanda, p. 54, archived from the original on 2006
- 1 2 Jean Varenne (1989). Yoga and the Hindu Tradition. Motilal Banarsidass. pp. 45–47. ISBN 978-81-208-0543-9.
- ↑ Michael Myers (2013). Brahman: A Comparative Theology. Routledge. pp. 140–143. ISBN 978-1-136-83565-0.
- ↑ The Philosophy of Person: Solidarity and Cultural Creativity, Jozef Tichner and George McClean, 1994, p. 32
External links
- The Science of the Emotions by Bhagavan Das
- 'Jiva' - usage in Bhagavata Purana
- Terms 'jiva' and 'soul' in Western and Eastern philosophy and religion (English)(Czech)