Joan Blaeu
.jpg)
Joan Blaeu (23 September 1596 – 21 December 1673) was a Dutch cartographer born in Alkmaar, the son of cartographer Willem Blaeu.
Life
In 1620 he became a doctor of law but he joined the work of his father. In 1635 they published the Atlas Novus (full title: Theatrum orbis terrarum, sive, Atlas novus) in two volumes. Joan and his brother Cornelius took over the studio after their father died in 1638. Joan became the official cartographer of the Dutch East India Company.

Blaeu's world map, Nova et Accuratissima Terrarum Orbis Tabula, incorporating the discoveries of Abel Tasman, was published in 1648.[1] This map was revolutionary in that it "depicts the solar system according to the heliocentric theories of Nicolaus Copernicus, which show the earth revolving around the sun.... Although Copernicus's groundbreaking book On the Revolutions of the Spheres had been first printed in 1543, just over a century earlier, Blaeu was the first mapmaker to incorporate this revolutionary heliocentric theory into a map of the world."[2]
Blaeu's map was copied for the map of the world set into the pavement of the Groote Burger-Zaal of the new Amsterdam Town Hall, designed by the Dutch architect Jacob van Campen (now the Amsterdam Royal Palace), in 1655.[3]
Blaeu's Hollandia Nova was also depicted in his Archipelagus Orientalis sive Asiaticus published in 1659 in the Kurfürsten Atlas (Atlas of the Great Elector). and used by Melchisédech Thévenot to produce his map, Hollandia Nova—Terre Australe (1664).[4]
As "Jean Blaeu", he also published the 12 volume "Le Grand Atlas, ou Cosmographie blaviane, en laquelle est exactement descritte la terre, la mer, et le ciel". One edition is dated 1663. That was folio (540 x 340 mm), and contained 593 engraved maps and plates. In March 2015, a copy was on sale for £750,000.[5]
Around 1649 Joan Blaeu published a collection of Dutch city maps named Toonneel der Steeden (Views of Cities). In 1651 he was voted into the Amsterdam council. In 1654 Joan published the first atlas of Scotland, devised by Timothy Pont. In 1662 he reissued the Atlas Novus, also known as Atlas Maior, in 11 volumes, and one for oceans.
A cosmology was planned as their next project, but a fire destroyed the studio completely in 1672. Joan Blaeu died in Amsterdam the following year.[6] He is buried in the Westerkerk there.
Gallery
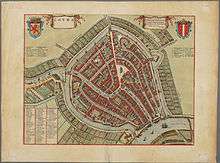 City centre of Gouda, ca. 1650
City centre of Gouda, ca. 1650.jpg) Nova et Accuratissima Terrarum Orbis Tabula (J. Blaeu, 1664).
Nova et Accuratissima Terrarum Orbis Tabula (J. Blaeu, 1664). Title page of the Atlas Novus
Title page of the Atlas Novus Coat of arms of the Bosnian kingdom as illustrated by Blaeu
Coat of arms of the Bosnian kingdom as illustrated by Blaeu Wageningen, 1649 (J. Blaeu)
Wageningen, 1649 (J. Blaeu).jpg) "Lessinia Vrbs" from the book "Toonneel der Steden" by Joan Blaeu c. ± 1649 (Amsterdam)
"Lessinia Vrbs" from the book "Toonneel der Steden" by Joan Blaeu c. ± 1649 (Amsterdam)
See also
Literature
- Krogt, van der, Peter CJ (2000), Koeman's Atlantes Neerlandici II: The Folio Atlases Published by Willem Jansz. Blaeu and Joan Blaeu, Houten: Hes & De Graaf publishers BV, ISBN 90-6194-438-4
- BROTTON, Jerry, A History of the World in Twelve Maps, London: Penguin, 2012.
References
- ↑ Brian Hooker, “New Light on the Mapping and Naming of New Zealand”, The New Zealand journal of history, vol.6, no.2, 1972, pp.158–67, p.159; William Eisler and Bernard Smith, Terra Australis: The Furthest Shore, Sydney, International Cultural Corporation of Australis, 1988, pp.67-84, p.80; Glyndwr Williams and Alan Frost, Terra Australis to Australia, Oxford University Press in association with the Australian Academy of the Humanities, 1988, p. 103; Byron Heath, Discovering the Great South Land, Rosenberg, 2005, p.117.
- ↑ Brotton, Jerry. A History of the World in Twelve Maps. London: allen Lane, 2012, p. 262.
- ↑ National Library of Australia, Maura O'Connor, Terry Birtles, Martin Woods and John Clark, Australia in Maps: Great Maps in Australia's History from the National Library's Collection, Canberra, National Library of Australia, 2007, p.32; this map is reproduced in Gunter Schilder, Australia Unveiled, Amsterdam, Theatrum Orbis Terrarum, 1976, p.402; and in William Eisler and Bernard Smith, Terra Australis: The Furthest Shore, Sydney, International Cultural Corporation of Australia, 1988, pp.67-84, p.81. Martin Woods , "New Holland’s Birth Certificate", National Library of Australia, Mapping our World: Terra Incognita to Australia, Canberra, National Library of Australia, 2013, p.138.
- ↑ Melchisedech Thévenot, Relations de divers Voyages curieux qui n 'ont point esté publiées, Paris, Thomas Moette, IV, 1664.
- ↑ http://www.peterharrington.co.uk/rare-books/catalogue-107/le-grand-atlas-ou-cosmographie-blaviane-en-laquelle-est-exactement-descritte-la-terre-la-mer-et-le-ciel/ as seen online 29 Mar 2015
- ↑ "Joan Blaeu". www.biografischportaal.nl. Retrieved 2016-08-16.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Maps by Willem and Johannes Blaeu. |
- Utrecht University
- Arader Galleries' Collection of Maps from Blaeu's Atlas Major.
- Brazil map by Joan Blaeu, Amsterdam 1650 (high resolution zoomable scan)
- Plan of Delft from Joan Blaeu' Town book, Amsterdam 1660 (high resolution zoomable scan)
- Blaeu on the Dutch map
- Jonathan Potter Maps