Lake Neusiedl
| Neusiedler See Fertő tó | |
|---|---|
 Satellite image of Lake Neusiedl | |
| Location | Austria, Hungary |
| Coordinates | 47°50′N 16°45′E / 47.833°N 16.750°ECoordinates: 47°50′N 16°45′E / 47.833°N 16.750°E |
| Type | Endorheic lake |
| Primary inflows | precipitation, Wulka |
| Primary outflows | evaporation (90%) Einserkanal (artificial) |
| Catchment area | 1,120 km2 (430 sq mi) |
| Basin countries | Austria, Hungary |
| Max. length | 36 km (22 mi) |
| Max. width | 12 km (7.5 mi) |
| Surface area | 315 km2 (122 sq mi) |
| Average depth | 1 m (3 ft 3 in) |
| Max. depth | 1.8 m (5 ft 11 in) |
| Water volume | 0.325 km3 (0.078 cu mi) |
| Surface elevation | 115.45 m (378.8 ft) |
| Settlements | Neusiedl am See, Rust |
| Official name | Fertő/Neusiedlersee Cultural Landscape |
| Type | Cultural |
| Criteria | v |
| Designated | 2001 (25th session) |
| Reference no. | 772 |
| State Party | Austria and Hungary |
| Region | Europe and North America |

Lake Neusiedl (German: Neusiedler See; Central Bavarian: Neisiedla See) or Fertő (Hungarian: Fertő tó; Croatian: Nežidersko jezero, Niuzaljsko jezero; Slovene: Nežidersko jezero; Slovak: Neziderské jazero) is the largest endorheic lake in Central Europe, straddling the Austrian–Hungarian border. The lake covers 315 km2 (122 sq mi), of which 240 km2 (93 sq mi) is on the Austrian side and 75 km2 (29 sq mi) on the Hungarian side. The lake's drainage basin has an area of about 1,120 km3 (270 cu mi). From north to south, the lake is about 36 km (22 mi) long, and it is between 6 km (3 1⁄2 mi) and 12 km (7 1⁄2 mi) wide from east to west. On average, the lake's surface is 115.45 m (378.8 ft) above the Adriatic Sea and the lake is no more than 1.8 m (5 ft 11 in) deep.
Water level fluctuations
In the past, rainfall and aridity caused significant floods (which in 1768 enlarged the lake to its maximum documented size of 515 km2 [199 sq mi]) and significant decreases in the lake's level, although frequently there seemed to be no apparent connection with the weather situation.
Stratigraphy shows that the lake bed has totally dried up at least 100 times since its formation (18,000–14,000 BC). During recent history the lake's complete disappearance has been documented in considerable detail on several occasions, e.g. in 1740–1742, 1811–1813, and most recently in 1866, when the private diary of a local, Gottlieb Wenzel, noted that he crossed the bed of the lake on 4 June without soiling his boots. Parts of the lake bed were claimed for agriculture; wheat and turnips were being planted. However, in 1871 the lake began to return and by the spring of 1876 it had already reassumed its usual size. The last (brief and partial) vanishing took place during the summer of 1949 when the northern part of the lake bed (to the approximate latitude of Podersdorf) fell dry for a few weeks. Each time the drying-up of the lake bed caused major environmental disruptions because the humidifying and temperature buffering effect of the large water body was absent, and because the winds blew large amounts of salty dust into the surrounding villages. On earlier occasions the lake was sometimes referred to as a "swamp", suggesting a very low water level with an expansion of reeds throughout the lake bed. Two records dated to 1318 and 1324, respectively mention a "river", implying that at this time the lake might have been reduced to a central body of water running from north to south.
Today the water level is controlled by a sluice on Hungarian territory near Fertőújlak, and bilateral issues are dealt with by the Austro-Hungarian water commission which was established in 1956. However, comparatively minor fluctuations of the lake's level continue to occur. In 1965 the lake gained 100 million cubic metres (3.5 billion cubic feet) of water within a single month, raising its level by 35 cm (14 inches). The water level decreased to a similar extent, by 30 cm (12 inches) within one year as a result of the drought of 2003. Both types of events are perfectly within the normal range, and because of the shallowness of the water can be either exacerbated or compensated by the effects of wind pressure, which can temporarily raise or reduce the local water level by as much as 75 cm (30 inches). However, the lake remains sensitive to changes in its equilibrium, as recent climate change scenario simulations have shown.[1][2]
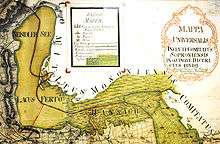
Before the regulation works of the 19th century, the lake extended in the southeast to the marshlands of the Hanság (German: Waasen) which have been increasingly drained and claimed for agriculture from the 16th century onward.[3] Originally, the lake was thus closely connected to the Danube and the Rába river systems.
Nature and wildlife
Most of the lake is surrounded by reeds which serve as a habitat for wildlife (making the lake an important resting place for migratory birds)[4] and are harvested in winter as soon as the ice is solid enough.[5] This serves a double purpose, one ecological (removal of the bulk of organic matter that would otherwise decay in the lake) and one economic (the reed is sold for various purposes, mostly related to construction and housing). During the summer months, there are occasional reed fires, as dry reed is easily flammable, and fires spread quickly because of the almost constant wind. Water quality is determined by temperature, wind, and by the amount of salt and mud emanating with the ground water from the sediments.
Several plans for dams and other intrusive construction works which would have destroyed the lake and its biotopes were discussed during the first half of the 20th century but came to nothing. Detailed plans to divide the lake bed with earthworks so that certain parts with reasonably fertile soil could be permanently drained and claimed for agriculture while the remaining parts would be used for intensive aquaculture had been finalized and approved in 1918 but were abandoned when most of the lake became Austrian territory after World War I. In 1971 plans for a bridge across the Austrian part of the lake were thwarted by environmentalists.
In 1993 the National Park Neusiedler See-Seewinkel gained international acceptance as an IUCN Category II preserve. In 2001 the national parks in Austria and Fertő-Hanság in Hungary were together accepted as a World Heritage Site. Lake Neusiedl See and its surrounding areas in Austria also enjoy protection through the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands.[6]
Towns and villages around the lake
Traces of human settlement around Lake Neusiedl go back to the neolithic period. The area became densely populated from the 7th century BC onward, initially by people of the Hallstatt culture and remained so throughout Roman times. In 454 Theodoric the Great, the preeminent king of the Ostrogoths, was born here. Near Fertőrákos there are two Roman villas and a 3rd-century Mithras temple open to visitors.
The more important extant towns lying on the lake's shore are Illmitz (Illmic), Podersdorf am See (Pátfalu), Weiden (Védeny), Neusiedl am See (Nezsider), Jois (Nyulas), Winden (Sásony), Breitenbrunn (Fertőszéleskút), Purbach am Neusiedlersee (Feketeváros), Donnerskirchen (Fertőfehéregyháza), Oggau (Oka), Rust (Ruszt) and Mörbisch (Fertőmeggyes) in Austria, and Fertőrákos, Fertőboz, Fertőd, Balf and Fertőújlak in Hungary, with the communities of Illmitz, Apetlon (Mosonbánfalva) and Podersdorf am See forming the so-called Seewinkel (lake corner), which is located between the lake and the Hungarian border. Hungarian names of Austrian towns lying on the lake's shore are given in parentheses.
Gallery

 Donnerskirchen / Austria
Donnerskirchen / Austria Stork's nest typical of the region
Stork's nest typical of the region- Frauenkirchen / Austria
- Schloss Esterházy / Austria
 Lake Neusiedl at Podersdorf during sunset
Lake Neusiedl at Podersdorf during sunset- Cave in Fertőrákos / Hungary
 Fertőszéplak / Hungary
Fertőszéplak / Hungary Széchenyi Palace in Nagycenk / Hungary
Széchenyi Palace in Nagycenk / Hungary Sarród / Hungary
Sarród / Hungary- Esterházy Palace / Hungary
 Fertő-tó
Fertő-tó
Tourism
Despite remaining a protected wildlife habitat, the region of Lake Neusiedl, particularly in its Austrian part, draws significant numbers of tourists. The lake is known as the "Sea of the Viennese", as it offers ample opportunities for sailing and windsurfing at a reasonable distance from Vienna. There is also some commercial fishing.
Low water levels pose a problem for sailing and commercial shipping, as boats hit the ground more frequently and mooring sites can become temporarily unusable. However, it somewhat facilitates the annual freestyle mass crossing of the lake from Mörbisch to Illmitz. Everybody who can swim and is more than 160 cm (5 ft 3 in) in height can participate in this event, which was revived in 2004.
See also
References
- ↑ "Impact of Climate Change on Lake Neusiedl and potential adaptation strategies". 2006-10-04. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-03-16. Retrieved 2013-03-16.
- ↑ "Climate impacts on water balance of a shallow steppe lake in Eastern Austria (Lake Neusiedl)". 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-03-16. Retrieved 2013-03-16.
- ↑ "Utilization of the inundation area at Lake Fertö before regulation works: Example of Sarród and its surroundings". 2005. Archived from the original on 2013-03-16. Retrieved 2013-03-16.
- ↑ "Monitoring of bird populations in the Lake Neusiedl area". 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-03-16. Retrieved 2013-03-16.
- ↑ "Workers harvest reeds on Austria's Neusiedler See". 2012-02-04. Archived from the original on 2013-03-16. Retrieved 2013-03-16.
- ↑ "Austria hosts international conference on transboundary Ramsar sites". 2004-11-26. Archived from the original on 2013-03-16. Retrieved 2013-03-16.
External links
- Official website (English)
- Lake Neusiedl at funiq.hu (English)
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Fertő / Neusiedlersee. |
