libvirt
 | |
| Developer(s) | Red Hat |
|---|---|
| Initial release | December 19, 2005 |
| Stable release |
2.4.0
/ 1 November 2016[1] |
| Preview release |
2.4.0-rc2
/ October 31, 2016 |
| Repository |
libvirt |
| Written in | C |
| Operating system | Linux |
| Type | Library |
| License | GNU Lesser General Public License |
| Website |
libvirt |
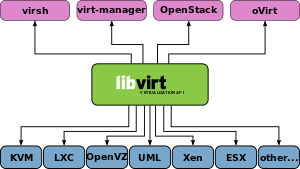
libvirt is an open source API, daemon and management tool for managing platform virtualization.[2] It can be used to manage KVM, Xen, VMware ESX, QEMU and other virtualization technologies. These APIs are widely used in the orchestration layer of hypervisors in the development of a cloud-based solution.
Internals
libvirt itself is a C library, but it has bindings in other languages, notably in Python,[3] Perl,[4] OCaml,[5] Ruby,[6] Java,[7] JavaScript (via Node.js)[8] and PHP.[9] libvirt for these programming languages is composed of wrappers around another class/package called libvirtmod. libvirtmod's implementation is closely associated with its counterpart in C/C++ in syntax and functionality.
Supported Hypervisors
- LXC – lightweight Linux container system
- OpenVZ – lightweight Linux container system
- Kernel-based Virtual Machine/QEMU (KVM) – open source hypervisor for Linux and SmartOS[10]
- Xen – Bare-Metal hypervisor
- User-mode Linux (UML) paravirtualized kernel
- VirtualBox – hypervisor by Oracle (formerly Sun) for Windows, Linux, Mac OS X, and Solaris
- VMware ESX and GSX – hypervisors for Intel hardware
- VMware Workstation and Player – hypervisors for Windows and Linux
- Hyper-V – hypervisor for Windows by Microsoft
- PowerVM – hypervisor by IBM for AIX, Linux and IBM i
- Parallels Workstation – hypervisor for Mac by Parallels IP Holdings GmbH
- Bhyve – hypervisor for FreeBSD 10+.[11] (Support added with Libvirt 1.2.2)
User Interfaces
Libvirt is used by various virtualization programs and platforms. Graphical Interfaces are provided by Virtual Machine Manager and others. The most popular command line interface is 'virsh', and higher level tools like oVirt.[12]
GNOME Boxes uses libvirt.
Corporate
Development of libvirt is backed by Red Hat,[13] with significant contributions by other organisations and individuals. Libvirt is available on most Linux distributions; remote servers are also accessible from Apple Mac OS X and Microsoft Windows clients.[14]
See also
- List of libvirt feature policies
- SPICE
- libguestfs
- Linux range of use § Virtualization
References
- ↑ "v2.2.0: Sep 02 2016". libvirt. 2016-09-02. Retrieved 2016-09-02.
- ↑ "libvirt home page description".
- ↑ "Python bindings".
- ↑ "Perl bindings".
- ↑ "OCaml bindings".
- ↑ "Ruby bindings".
- ↑ "Java bindings".
- ↑ "Node.js module".
- ↑ "PHP bindings".
- ↑ http://dtrace.org/blogs/bmc/2011/08/15/kvm-on-illumos/
- ↑ https://wiki.freebsd.org/bhyve#line-19
- ↑ "oVirt Virtualization Management Platform".
- ↑ "Innovation Without Disruption: Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5.4 Now Available".
- ↑ "Windows availability".
Books
- Warnke, Robert; Ritzau, Thomas. qemu-kvm & libvirt (in German). Norderstedt, Germany: Books on Demand. ISBN 978-3-8370-0876-0.