Magnesium gluconate
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
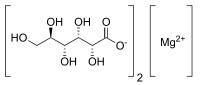
| IUPAC name
Magnesium bis[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxyhexanoate] | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3632-91-5 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL2107145 |
| ChemSpider | 9593457 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.020.772 |
| E number | E580 (acidity regulators, ...) |
| PubChem | 11418570 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H22MgO14 | |
| Molar mass | 414.60 g·mol−1 |
| Pharmacology | |
| A12CC03 (WHO) | |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Magnesium gluconate is a compound with formula MgC12H22O14. It is the magnesium salt of gluconic acid.
According to scientific research, magnesium gluconate shows the highest level of bioavailability of any magnesium salt and is recommended as the optimal salt for human supplementation although of the 10 salts studied, all increased Magnesium levels significantly.[1]
It has E number "E580".
Use in Medicine
There are data on the pharmacological properties of magnesium gluconate. Gluconic acid is the initial substrate for the reactions of pentose phosphate path of oxidation of glucose, so it was suggested that it may affect the energy metabolism of mitochondria. In Ukraine, magnesium gluconate, together with potassium gluconate in the drug Rhythmocor is used to treat heart disease. Pilot studies have shown efficacy in various cardiac arrhythmia. Whether these effects are from the influence of gluconic acid on the metabolism of the heart or from the influence of magnesium and potassium on osmotic pressure is unknown.
References
- ↑ Coudray, C; Rambeau, M; Feillet-Coudray, C; Gueux, E; Tressol, JC; Mazur, A; Rayssiguier, Y (2005). "Study of magnesium bioavailability from ten organic and inorganic Mg salts in Mg-depleted rats using a stable isotope approach". Magnesium research : official organ of the International Society for the Development of Research on Magnesium. 18 (4): 215–23. PMID 16548135.