Marcel Proust
| Marcel Proust | |
|---|---|
 Proust in 1900 | |
| Born |
Valentin Louis Georges Eugène Marcel Proust 10 July 1871 Auteuil, France |
| Died |
18 November 1922 (aged 51) Paris, France |
| Occupation | Novelist, essayist, critic |
| Notable work | In Search of Lost Time |
| Parent(s) |
Achille Adrien Proust Jeanne Clémence Weil |
| Signature | |
|
| |
Valentin Louis Georges Eugène Marcel Proust (/pruːst/;[1] French: [maʁsɛl pʁust]; 10 July 1871 – 18 November 1922) was a French novelist, critic, and essayist best known for his monumental novel À la recherche du temps perdu (In Search of Lost Time; earlier rendered as Remembrance of Things Past), published in seven parts between 1913 and 1927: The Walk by Swann's Place, In the Shade of Blooming Young Girls, The Guermantes Walk, Sodom and Gomorrah, The Captive Girl, Vanished Albertine, Time Found Again.[2] He is considered by English critics and writers to be one of the most influential authors of the 20th century.[3][4]
Biography
Proust was born in Auteuil (the south-western sector of Paris's then-rustic 16th arrondissement) at the home of his great-uncle on 10 July 1871, two months after the Treaty of Frankfurt formally ended the Franco-Prussian War. His birth took place during the violence that surrounded the suppression of the Paris Commune, and his childhood corresponded with the consolidation of the French Third Republic. Much of In Search of Lost Time concerns the vast changes, most particularly the decline of the aristocracy and the rise of the middle classes that occurred in France during the Third Republic and the fin de siècle.
Proust's father, Adrien Proust, was a prominent pathologist and epidemiologist, studying cholera in Europe and Asia. He was the author of numerous articles and books on medicine and hygiene. Proust's mother, Jeanne Clémence Weil, was the daughter of a wealthy Jewish family from Alsace.[5] Literate and well-read, she demonstrates a well-developed sense of humour in her letters, and her command of English was sufficient to help with her son's translations of John Ruskin.[6] Proust was raised in his father's Catholic faith.[7] He was baptized (on 5 August 1871, at the church of Saint-Louis d'Antin) and later confirmed as a Catholic but he never formally practised that faith.
By the age of nine, Proust had had his first serious asthma attack, and thereafter he was considered a sickly child. Proust spent long holidays in the village of Illiers. This village, combined with recollections of his great-uncle's house in Auteuil, became the model for the fictional town of Combray, where some of the most important scenes of In Search of Lost Time take place. (Illiers was renamed Illiers-Combray in 1971 on the occasion of the Proust centenary celebrations.)
In 1882, at the age of eleven, Proust became a pupil at the Lycée Condorcet, but his education was disrupted by his illness. Despite this he excelled in literature, receiving an award in his final year. Thanks to his classmates, he was able to gain access to some of the salons of the upper bourgeoisie, providing him with copious material for In Search of Lost Time.[8]

Despite his poor health, Proust served a year (1889–90) enlisted in the French army, stationed at Coligny Barracks in Orléans, an experience that provided a lengthy episode in The Guermantes' Way, part three of his novel. As a young man, Proust was a dilettante and a social climber whose aspirations as a writer were hampered by his lack of self-discipline. His reputation from this period, as a snob and an amateur, contributed to his later troubles with getting Swann's Way, the first part of his large-scale novel, published in 1913. At this time, he attended the salons of Mme Straus, widow of Georges Bizet and mother of Proust's childhood friend Jacques Bizet, of Madeleine Lemaire and of Mme Arman de Caillavet, one of the models for Madame Verdurin, and mother of his friend Gaston Arman de Caillavet, with whose fiancée (Jeanne Pouquet) he was in love. It is through Mme Arman de Caillavet that he made the acquaintance of Anatole France, her lover.
In an 1892 article published in Le Banquet entitled "L'Irréligion d'État" and again in a 1904 Le Figaro article entitled "La mort des cathédrales", Proust argued against the separation of church and state, declaring that socialism posed a greater threat to society than the Church and emphasizing the latter's role in sustaining a cultural and educational tradition.[9]
Proust had a close relationship with his mother. To appease his father, who insisted that he pursue a career, Proust obtained a volunteer position at Bibliothèque Mazarine in the summer of 1896. After exerting considerable effort, he obtained a sick leave that extended for several years until he was considered to have resigned. He never worked at his job, and he did not move from his parents' apartment until after both were dead.[6]
His life and family circle changed markedly between 1900 and 1905. In February 1903, Proust's brother, Robert Proust, married and left the family home. His father died in November of the same year.[10] Finally, and most crushingly, Proust's beloved mother died in September 1905. She left him a considerable inheritance. His health throughout this period continued to deteriorate.
Proust spent the last three years of his life mostly confined to his bedroom, sleeping during the day and working at night to complete his novel.[11] He died of pneumonia and a pulmonary abscess in 1922. He was buried in the Père Lachaise Cemetery in Paris.
Early writing
| French literature |
|---|
| by category |
| French literary history |
| French writers |
|
| Portals |
|
Proust was involved in writing and publishing from an early age. In addition to the literary magazines with which he was associated, and in which he published, while at school, La Revue verte and La Revue lilas, from 1890 to 1891 Proust published a regular society column in the journal Le Mensuel.[6] In 1892 he was involved in founding a literary review called Le Banquet (also the French title of Plato's Symposium), and throughout the next several years Proust published small pieces regularly in this journal and in the prestigious La Revue Blanche.
In 1896 Les Plaisirs et les Jours, a compendium of many of these early pieces, was published. The book included a foreword by Anatole France, drawings by madame Lemaire in whose salon Proust would be a frequent guest, and who was a model for Mme Verdurin. She invited him and Reynaldo Hahn to her château de Réveillon (the model for Mme Verdurin's La Raspelière) in summer 1894 and three weeks in 1895. This book was so sumptuously produced that it cost twice the normal price of a book its size.
That year Proust also began working on a novel, which was eventually published in 1952 and titled Jean Santeuil by his posthumous editors. Many of the themes later developed in In Search of Lost Time find their first articulation in this unfinished work, including the enigma of memory and the necessity of reflection; several sections of In Search of Lost Time can be read in the first draft in Jean Santeuil. The portrait of the parents in Jean Santeuil is quite harsh, in marked contrast to the adoration with which the parents are painted in Proust's masterpiece. Following the poor reception of Les Plaisirs et les Jours, and internal troubles with resolving the plot, Proust gradually abandoned Jean Santeuil in 1897 and stopped work on it entirely by 1899.
Beginning in 1895 Proust spent several years reading Carlyle, Emerson, and John Ruskin. Through this reading Proust began to refine his own theories of art and the role of the artist in society. Also, in Time Regained Proust's universal protagonist recalls having translated Ruskin's Sesame and Lilies. The artist's responsibility is to confront the appearance of nature, deduce its essence and retell or explain that essence in the work of art. Ruskin's view of artistic production was central to this conception, and Ruskin's work was so important to Proust that he claimed to know "by heart" several of Ruskin's books, including The Seven Lamps of Architecture, The Bible of Amiens, and Praeterita.[6]
Proust set out to translate two of Ruskin's works into French, but was hampered by an imperfect command of English. To compensate for this he made his translations a group affair: sketched out by his mother, the drafts were first revised by Proust, then by Marie Nordlinger, the English cousin of his friend and sometime lover[12] Reynaldo Hahn, then again finally polished by Proust. Confronted about his method by an editor, Proust responded, "I don't claim to know English; I claim to know Ruskin".[6][13] The Bible of Amiens, with Proust's extended introduction, was published in French in 1904. Both the translation and the introduction were very well reviewed; Henri Bergson called Proust's introduction "an important contribution to the psychology of Ruskin" and had similar praise for the translation.[6] At the time of this publication, Proust was already at work on translating Ruskin's Sesame and Lilies, which he completed in June 1905, just before his mother's death, and published in 1906. Literary historians and critics have ascertained that, apart from Ruskin, Proust's chief literary influences included Saint-Simon, Montaigne, Stendhal, Flaubert, George Eliot, Fyodor Dostoyevsky, and Leo Tolstoy.
1908 was an important year for Proust's development as a writer. During the first part of the year he published in various journals pastiches of other writers. These exercises in imitation may have allowed Proust to solidify his own style. In addition, in the spring and summer of the year Proust began work on several different fragments of writing that would later coalesce under the working title of Contre Sainte-Beuve. Proust described what he was working on in a letter to a friend: "I have in progress: a study on the nobility, a Parisian novel, an essay on Sainte-Beuve and Flaubert, an essay on women, an essay on pederasty (not easy to publish), a study on stained-glass windows, a study on tombstones, a study on the novel".[6]
From these disparate fragments Proust began to shape a novel on which he worked continually during this period. The rough outline of the work centered on a first-person narrator, unable to sleep, who during the night remembers waiting as a child for his mother to come to him in the morning. The novel was to have ended with a critical examination of Sainte-Beuve and a refutation of his theory that biography was the most important tool for understanding an artist's work. Present in the unfinished manuscript notebooks are many elements that correspond to parts of the Recherche, in particular, to the "Combray" and "Swann in Love" sections of Volume 1, and to the final section of Volume 7. Trouble with finding a publisher, as well as a gradually changing conception of his novel, led Proust to shift work to a substantially different project that still contained many of the same themes and elements. By 1910 he was at work on À la recherche du temps perdu.
In Search of Lost Time
Begun in 1909, when Proust was 38 years old, À la recherche du temps perdu consists of seven volumes totaling around 3,200 pages (about 4,300 in The Modern Library's translation) and featuring more than 2,000 characters. Graham Greene called Proust the "greatest novelist of the 20th century", and W. Somerset Maugham called the novel the "greatest fiction to date". Proust died before he was able to complete his revision of the drafts and proofs of the final volumes, the last three of which were published posthumously and edited by his brother, Robert.
The book was translated into English by C. K. Scott Moncrieff, appearing under the title Remembrance of Things Past between 1922 and 1931. Scott Moncrieff translated volumes one through six of the seven volumes, dying before completing the last. This last volume was rendered by other translators at different times. When Scott Moncrieff's translation was later revised (first by Terence Kilmartin, then by D. J. Enright) the title of the novel was changed to the more literal In Search of Lost Time.
In 1995 Penguin undertook a fresh translation of the book by editor Christopher Prendergast and seven translators in three countries, based on the latest, most complete and authoritative French text. Its six volumes, comprising Proust's seven, were published in Britain under the Allen Lane imprint in 2002.
Personal life
Proust was homosexual, and his sexuality and relationships with men are often discussed by his biographers.[14] Although his housekeeper, Céleste Albaret, denies this aspect of Proust's sexuality in her memoirs,[15] her denial runs contrary to the statements of many of Proust's friends and contemporaries, including his fellow writer André Gide[16] as well as his valet Ernest A. Forssgren.[17]
During his life, Proust never openly admitted to his homosexuality, though his family and close friends either knew or suspected it. In 1897, he even fought a duel with writer Jean Lorrain, who publicly questioned the nature of Proust's relationship with Lucien Daudet. (Both duelists survived.)[18] Despite Proust's own public denial, his romantic relationship with composer Reynaldo Hahn,[12] and his infatuation with his chauffeur and secretary, Alfred Agostinelli, are well documented.[19]
The exact influence of Proust's sexuality on his writing is a topic of debate.[20] However, In Search of Lost Time discusses homosexuality at length and features several principal characters, both men and women, who are either homosexual or bisexual: the Baron de Charlus, Robert de Saint-Loup, and Albertine Simonet.[21] Homosexuality also appears as a theme in Les plaisirs et les jours and his unfinished novel, Jean Santeuil.
Gallery
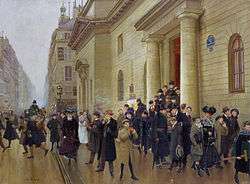 Jean Béraud, La Sortie du lycée Condorcet
Jean Béraud, La Sortie du lycée Condorcet- 102 Boulevard Haussmann, Paris, where Marcel Proust lived from 1907 to 1919
 Robert de Montesquiou, the main inspiration for Baron de Charlus in À la recherche du temps perdu
Robert de Montesquiou, the main inspiration for Baron de Charlus in À la recherche du temps perdu
.jpg) Grave of Marcel Proust at Père Lachaise Cemetery
Grave of Marcel Proust at Père Lachaise Cemetery
Bibliography
- Pleasures and Days (Les plaisirs et les jours; illustrations by Madeleine Lemaire, preface by Anatole France, and four piano works by Reynaldo Hahn) (1896)
- In Search of Lost Time (À la recherche du temps perdu published in seven volumes, previously translated as Remembrance of Things Past) (1913–1927)
- Swann's Way (Du côté de chez Swann, sometimes translated as The Way by Swann's) (1913)
- In the Shadow of Young Girls in Flower (À l'ombre des jeunes filles en fleurs, also translated as Within a Budding Grove) (1919)
- The Guermantes Way (Le Côté de Guermantes originally published in two volumes) (1920/1921)
- Sodom and Gomorrah (Sodome et Gomorrhe originally published in two volumes, sometimes translated as Cities of the Plain) (1921/1922)
- The Prisoner (La Prisonnière, also translated as The Captive) (1923)
- The Fugitive (Albertine disparue, also titled La Fugitive, sometimes translated as The Sweet Cheat Gone or Albertine Gone) (1925)
- Time Regained (Le Temps retrouvé, also translated as Finding Time Again and The Past Recaptured) (1927)
- Pastiches, or The Lemoine Affair (Pastiches et mélanges – a novella) (1919)
- Jean Santeuil (three volumes published posthumously 1952)
- Against Sainte-Beuve (Contre Sainte-Beuve: suivi de Nouveaux mélanges) (published posthumously 1954)
Translations
- La Bible d'Amiens (translation of John Ruskin's The Bible of Amiens) (1896)
- Sésame et les lys: des trésors des rois, des jardins des reines (translation of John Ruskin's Sesame and Lilies) (1906)
See also
- Albertine, a novel based on a character in À la recherche du temps perdu by Jacqueline Rose London 2001
- Céleste, a German film dramatising part of Proust's life, seen from the viewpoint of his housekeeper Céleste Albaret
- Involuntary memory
- Le Temps Retrouvé, d'après l'œuvre de Marcel Proust (Time Regained), film by director Raul Ruiz,1999
- Mme Proust and the Kosher Kitchen, a novel by Kate Taylor that includes a fictional diary written by Proust's mother
- "Proust", an essay by Samuel Beckett
- Proust Questionnaire
References
- ↑ "Proust". Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary.
- ↑ Nabokov, Vladimir (1982). Lectures on Literature. New York: A Harvest Book. p. 207. ISBN 9780156027755.
- ↑ Harold Bloom, Genius, pp. 191–224.
- ↑ "Marcel Proust". New York Times. Retrieved 13 October 2016.
- ↑ Allan Massie – Madame Proust: A Biography By Evelyne Bloch-Dano, translated by Alice Kaplan Literary Review.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Tadié, J-Y. (Euan Cameron, trans.) Marcel Proust: A life. New York: Penguin Putnam, 2000.
- ↑ NYSL TRAVELS: Paris: Proust's Time Regained Archived 27 January 2012 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Painter, George D. (1959) Marcel Proust: a biography; Vols. 1 & 2. London: Chatto & Windus
- ↑ Hughes, Edward J. (2011). Proust, Class, and Nation. Oxford University Press. pp. 36–40.
- ↑ Carter (2002)
- ↑ Marcel Proust: Revolt against the Tyranny of Time. Harry Slochower .The Sewanee Review, 1943.
- 1 2 Carter, William C. (2006), Proust in Love, Yale University Press, pp. 31–5, ISBN 0-300-10812-5
- ↑ Karlin, Daniel (2005) Proust's English; p. 36
- ↑ Painter (1959), White (1998), Tadié (2000), Carter (2002 and 2006)
- ↑ Albaret (2003)
- ↑ Harris (2002)
- ↑ Forssgren (2006)
- ↑ Hall, Sean Charles (12 February 2012). "Dueling Dandies: How Men Of Style Displayed a Blasé Demeanor In the Face of Death". Dandyism.
- ↑ Whitaker, Rick (1 June 2000). "Proust's dearest pleasures: The best of a slew of recent biographies points to the author's conscious self-closeting". Salon.
- ↑ Sedgwick (1992) and O'Brien (1949)
- ↑ Sedgwick (1992), Ladenson (1999), and Bersani (2013)
Further reading
- Aciman, André (2004), The Proust Project. New York: Farrar, Straus and Giroux
- Adorno, Theodor (1967), Prisms. Cambridge, Mass.: MIT Press
- Adorno, Theodor, "Short Commentaries on Proust," Notes to Literature, trans. S. Weber-Nicholsen (New York: Columbia University Press, 1991).
- Albaret, Céleste (Barbara Bray, trans.) (2003), Monsieur Proust. New York: The New York Review of Books
- Beckett, Samuel, Proust, London: Calder
- Benjamin, Walter, "The Image of Proust," Illuminations, trans. Harry Zohn (New York: Schocken Books, 1969) 201–215.
- Bernard, Anne-Marie (2002), The World of Proust, as seen by Paul Nadar. Cambridge, Mass.: MIT Press
- Bersani, Leo, Marcel Proust: The Fictions of Life and of Art (2013), Oxford: Oxford U. Press
- Bowie, Malcolm, Proust Among the Stars, London: Harper Collins
- Capetanakis, Demetrios, "A Lecture on Proust", in Demetrios Capetanakis A Greek Poet in England (1947)
- Carter, William C. (2002), Marcel Proust: a life. New Haven: Yale University Press
- Carter, William C. (2006), Proust in Love. New Haven: Yale University Press
- Chardin, Philippe (2006), Proust ou le bonheur du petit personnage qui compare. Paris: Honoré Champion
- Chardin, Philippe et alii (2010), Originalités proustiennes. Paris: Kimé
- Compagnon, Antoine, Proust Between Two Centuries, Columbia U. Press
- Davenport-Hines, Richard (2006), A Night at the Majestic. London: Faber and Faber ISBN 9780571220090
- De Botton, Alain (1998), How Proust Can Change Your Life. New York: Vintage Books
- Deleuze, Gilles (2004), Proust and Signs: the complete text. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press
- De Man, Paul (1979), Allegories of Reading: Figural Language in Rousseau, Nietzsche, Rilke, and Proust ISBN 0-300-02845-8
- Descombes, Vincent, Proust: Philosophy of the Novel. Stanford, CA: Stanford U. Press
- Forssgren, Ernest A. (William C. Carter, ed.) (2006), The Momoirs of Ernest A. Forssgren: Proust’s Swedish Valet. New Haven: Yale University Press
- Genette, Gérard, Narrative Discourse: An Essay in Method. Ithaca, NY: Cornell U. Press
- Gracq, Julien, "Proust Considered as An End Point," in Reading Writing (New York: Turtle Point Press,), 113–130.
- Green, F. C. The Mind of Proust (1949)
- Harris, Frederick J. (2002), Friend and Foe: Marcel Proust and André Gide. Lanham: University Press of America
- Hillerin, Laure La comtesse Greffulhe, L'ombre des Guermantes, Paris, Flammarion, 2014. Part V, La Chambre Noire des Guermantes. About Marcel Proust and comtesse Greffulhe's relationship, and the key role she played in the genesis of La Recherche.
- Karlin, Daniel (2005), Proust's English. Oxford: Oxford University Press ISBN 978-0199256884
- Kristeva, Julia, Time and Sense. Proust and the Experience of Literature. New York: Columbia U. Press, 1996.
- Ladenson, Elisabeth (1991), Proust’s Lesbianism. Ithaca, NY: Cornell U. Press
- Landy,Joshua, Philosophy as Fiction: Self, Deception, and Knowledge in Proust. Oxford: Oxford U. Press
- O'Brien, Justin. "Albertine the Ambiguous: Notes on Proust's Transposition of Sexes", PMLA 64: 933–52, 1949.
- Painter, George D. (1959), Marcel Proust: a biography; Vols. 1 & 2. London: Chatto & Windus
- Poulet, Georges, Proustian Space. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins U. Press
- Prendergast, Christopher Mirages and Mad Beliefs: Proust the Skeptic ISBN 9780691155203
- Sedgwick, Eve Kosofsky (1992), "Epistemology of the Closet". Berkeley: University of California Press
- Shattuck, Roger (1963), Proust's Binoculars: a study of memory, time, and recognition in "À la recherche du temps perdu". New York: Random House
- Spitzer, Leo, "Proust's Style," [1928] in Essays in Stylistics (Princeton, Princeton U. P., 1948).
- Shattuck, Roger (2000), Proust's Way: a field guide to "In Search of Lost Time". New York: W. W. Norton
- Tadié, Jean-Yves (2000), Marcel Proust: A Life. New York: Viking
- White, Edmund (1998), Marcel Proust. New York: Viking Books
External links
| Wikilivres has original media or text related to this article: |
- Marcel Proust at DMOZ
- BBC audio file. In Our TIme discussion, Radio 4.
- The Kolb-Proust Archive for Research. University of Illinois.
- Works by Marcel Proust at Project Gutenberg
- Works by Marcel Proust at Project Gutenberg Australia
- Works by or about Marcel Proust at Internet Archive
- Works by Marcel Proust at LibriVox (public domain audiobooks)

- Works by Marcel Proust at Open Library

- The Album of Marcel Proust, Marcel Proust receives a tribute in this album of "recomposed photographs".
- Swann's Way Exhibited at The Morgan Library
- "Why Proust? And Why Now?" Essay on the lasting relevance of Proust and his work. 13 April 2000 New York Times
- University of Adelaide Library French text of volumes 1–4 and the complete novel in English translation