Meryre II
| |||||
| Meryre in hieroglyphs |
|---|
| Meryre II Steward of Queen Nefertiti | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Dynasty | 18th Dynasty |
| Pharaoh | Akhenaten |
| Burial | Amarna Tomb 2 |
The Ancient Egyptian noble known as Meryre II was superintendent of the queen Nefertiti, and had the title Royal scribe, Steward, Overseer of the Two Treasuries, Overseer of the Royal Harim of Nefertiti.[1] He had a tomb constructed at Amarna, Tomb 2, although his remains have never been identified. The tomb has the last dated appearance of Akhenaten and the Amarna family, dating from second month, year 12 of his reign.[2]
Inscribed Scenes

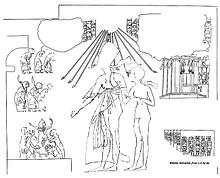
South Wall West Side: The Queen filling the King's cup. Nefertiti is shown standing before a seated Akhenaten, pouring a drink through a sieve for the king. Meritaten stands between Akhenaten and Nefertiti, facing her father and offering him something. Behind Nefertiti we see Meketaten offering a perfume cone, while Ankhesenpaaten offers a bouquet of flowers. Below this scene we see female musicians and male servants.[3]
South Wall, East Side: Reward of Meryra Meryra is shown before the window of appearance. Akhenaten and Nefertiti are shon handing out collars of gold. In the palace behind the window we see Merytaten and Meketaten handing gold collars to their mother. Ankhesenpaaten is shown standing before Neferneferuaten Tasherit and Neferneferure. Ankhesenpaaten is shown wearing large earrings and three bracelets on each arm. She also appears to be wearing a rather elaborate cape or collar. [3]
East Wall: Presentation of tribute. On the east wall of the main chamber is a scene depicting the tribute of 'the chieftains of every foreign land'. Akhenaten and Nefertiti are shown sitting on a throne in a kiosk with all six of their daughters standing behind them. This tribute takes place in year 12 (second month of the seed season, day 8). Their six daughters are shown behind them. Meritaten, Meketaten and Ankhesenpaaten are shown holding hands. Neferneferuaten is holding something in her hands. Neferure is shown holding a gazelle. The youngest daughter, Setepenre, holds a bouquet of flowers while petting the gazelle her older sister is holding. [3]
North Wall East Side: Meryre rewarded by the King Meryre is shown before "The Lord of the Two Lands (Ankheperure)| Son of Re (Smenkhare- Dejeser-Kheperu)| and the great Royal Wife (Meritaten)|." [3] Meritaten appears as a Great Royal Wife and is depicted alongside her husband, Pharaoh Ankhkheperure Smenkhare-djeserkheperu. The scene shows the royal couple bestowing honors and gifts on Meryre. The scene appears on the wall adjacent to the wall depicting the Durbar of year 12. [4] Smenkhare may have served as a co-regent to Akhenaten. Meritaten was the Great Royal Wife to Smenkhare, while Nefertiti continued as the consort of Akhenaten.[5] Nefertiti still held the Great Royal Wife title in year 16, hence Smenkhare must have been a co-regent or otherwise ruled with his wife Meritaten sometime after year 16 of Akhenaten. [6]
References
- ↑ "North Tombs". The Amarna Project. Retrieved 2008-07-08.
- ↑ James P. Allen. "The Amarna Succession" (PDF). p. 1. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 1, 2013. Retrieved 2008-06-23.
- 1 2 3 4 The rock tombs of el-Amarna, Parts I and II: Part 1 The tomb of Meryra & Part 2 The tombs of Panehesy and Meyra II, Egypt Exploration Society (2004)
- ↑ Dodson, Aidan, Amarna Sunset: Nefertiti, Tutankhamun, Ay, Horemheb, and the Egyptian Counter-reformation, The American University in Cairo Press, 2009
- ↑ Aldred, Cyril, Akhenaten: King of Egypt ,Thames and Hudson, 1991 (paperback), ISBN 0-500-27621-8
- ↑ Seyfried, Friederike (Editor), In the Light of Amarna: 100 Years of the Nefertiti Discovery, Michael Imhof Verlag, 2013
