Mucic acid
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2S,3R,4S,5R)-2,3,4,5-Tetrahydroxyhexanedioic acid | |
| Other names
Galactaric acid; Galactosaccharic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| 526-99-8 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL1232958 |
| ChemSpider | 2301286 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.641 |
| PubChem | 3037582 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H10O8 | |
| Molar mass | 210.14 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 230 °C (446 °F; 503 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
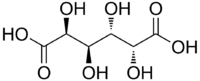
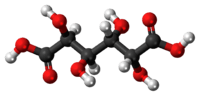
Mucic acid, C6H10O8 or HOOC-(CHOH)4-COOH, (also known as galactaric or meso-galactaric acid) is an aldaric acid obtained by nitric acid oxidation of galactose or galactose-containing compounds such as lactose, dulcite, quercite, and most varieties of gum.
Properties
Mucic acid forms a crystalline powder, which melts at 230 °C. It is insoluble in alcohol, and nearly insoluble in cold water. Due to the symmetry in the molecule, it is optically inactive even though it has chiral carbon atoms (i.e., it is a meso compound).
Reactions
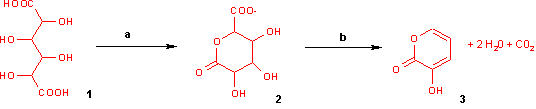
When heated with pyridine to 140 °C, it is converted into allomucic acid.[1] When digested with fuming hydrochloric acid for some time it is converted into a furfural dicarboxylic acid while on heating with barium sulfide it is transformed into a thiophene carboxylic acid. The ammonium salt yields on dry distillation carbon dioxide, ammonia, pyrrol and other substances. The acid when fused with caustic alkalis yields oxalic acid.
With potassium bisulfate mucic acid forms 3-hydroxy-2-pyrone by dehydration and decarboxylation.
Use
Mucic acid can be used to replace tartaric acid in self-rising flour or fizzies.
It has been used as a precursor of adipic acid en route to nylon by a rhenium-catalyzed deoxydehydration reaction.[2]
See also
- Saccharic acid - an optical isomer
- Muconic acid - a structurally related compound which is dehydrated and unsaturated
References
- ↑ Butler, C. L.; Cretcher, L. H. (1929). "The Preparation of Allomucic Acid and Certain of Its Derivatives". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 51 (7): 2167. doi:10.1021/ja01382a029.
- ↑ Li, X.; Wu, D.; Lu, T.; Yi, G.; Su, H.; Zhang, Y. (2014). "Highly Efficient Chemical Process to Convert Mucic Acid into Adipic Acid and DFT Studies of the Mechanism of the Rhenium-Catalyzed Deoxydehydration". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 53 (16): 4200. doi:10.1002/anie.201310991.
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "article name needed". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "article name needed". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.