Multiplexed binary offset carrier
Multiplexed binary offset carrier (MBOC) modulation [1][2][3] is a modulation proposed for Galileo[2] and modernized GPS signals, which combines a sine binary offset carrier SinBOC(1,1) signal with a SinBOC(6,1) signal, either via weighted sum/difference (the CBOC implementation) or via time-multiplexing (the TMBOC implementation).
The main objective of the common GPS and Galileo signal design activity was that the power spectral density (PSD) of the proposed solution would be identical for GPS L1C and Galileo E1 OS when the pilot and data components are computed together.[1] This assures high interoperability between both signals. Its power spectral density 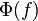 is defined by [4]
is defined by [4]
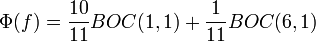
MBOC has two main implementations, the Composite Binary Offset Carrier (CBOC) implementation, currently used in Galileo and the Time-Multiplexed Binary Offset Carrier (TMBOC), currently used in modernized GPS L1C signal.
References
- 1 2 Navipedia information on MBCO Modulation
- 1 2 Galileo Open Service Signal In Space Interface Control Document (OS SIS ICD), GSA, Issue 1.1, September 2010
- ↑ [Hoult, N.; Aguado, L. E. and Xia, P. MBOC and BOC(1,1) Performance Comparison. Journal of Navigation, Volume 61, No. 4, pp613–627, 2008 (NaviJournal08)]
- ↑ Agreement06