n-Butylamine
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Butan-1-amine | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
| 109-73-9 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| Abbreviations | NBA |
| 605269 | |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:43799 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL13968 |
| ChemSpider | 7716 |
| DrugBank | DB03659 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.364 |
| EC Number | 203-699-2 |
| 1784 | |
| MeSH | n-butylamine |
| PubChem | 8007 |
| RTECS number | EO29750002 |
| UNII | N2QV60B4WR |
| UN number | 1125 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H11N | |
| Molar mass | 73.14 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | fishy, ammoniacal |
| Density | 740 mg mL−1 |
| Melting point | −49 °C; −56 °F; 224 K |
| Boiling point | 77 to 79 °C; 170 to 174 °F; 350 to 352 K |
| Miscible | |
| log P | 1.056 |
| Vapor pressure | 9.1 kPa (at 20 °C) |
| Henry's law constant (kH) |
570 μmol Pa−1 kg−1 |
| Refractive index (nD) |
1.401 |
| Viscosity | 500 µPa s (at 20 °C) |
| Thermochemistry | |
| 188 J K−1 mol−1 | |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH |
−128.9–−126.5 kJ mol−1 |
| Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH |
−3.0196–−3.0174 MJ mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | hazard.com |
| GHS pictograms |  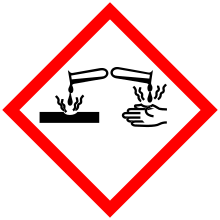  |
| GHS signal word | DANGER |
| H225, H302, H312, H314, H332 | |
| P210, P280, P305+351+338, P310 | |
| EU classification (DSD) |
|
| R-phrases | R11 R20/21/22, R35 |
| S-phrases | S3, S16, S26, S29 S36/37/39 S45 |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Flash point | −7 °C (19 °F; 266 K) |
| 312 °C (594 °F; 585 K) | |
| Explosive limits | 1.7–9.8% |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (median dose) |
|
| LCLo (lowest published) |
4000 ppm (rat, 4 hr) 263 ppm (mouse, 2 hr)[1] |
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |
| PEL (Permissible) |
C 5 ppm (15 mg/m3) [skin][2] |
| REL (Recommended) |
C 5 ppm (15 mg/m3) [skin][2] |
| IDLH (Immediate danger) |
300 ppm[2] |
| Related compounds | |
| Related alkanamines |
|
| Related compounds |
2-Methyl-2-nitrosopropane |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
n-Butylamine is an organic compound (specifically, an amine) with the formula CH3CH2CH2CH2NH2. This colourless liquid is one of the four isomeric amines of butane, the others being sec-butylamine, tert-butylamine and isobutylamine. At standard temperature and pressure, n-butylamine is a liquid having the fishy, ammonia-like odor common to amines. The liquid acquires a yellow color upon storage in air. It is soluble in all organic solvents.
Like other simple aliphatic amines, n-butylamine is a weak base with a pKa of 10.59 in its protonated form.[3]
Uses
This compound is used as an ingredient in the manufacture of pesticides (such as thiocarbazides), pharmaceuticals, and emulsifiers. It is also a precursor for the manufacture of N,N'-dibutylthiourea, a rubber vulcanization accelerator, and n-butylbenzenesulfonamide, a plasticizer of nylon.
N-Butylamine was used in the synthesis of Fengabine.
Safety
The LD50 to rats through the oral exposure route is 366 mg/kg.[4]
In regards to occupational exposures to n-Butylamine, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration and National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health have set occupational exposure limits at a ceiling of 5 ppm (15 mg/m3) for dermal exposure.[5]
References
- 1 2 "N-Butylamine". Immediately Dangerous to Life and Health. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- 1 2 3 "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards #0079". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ↑ H. K. Hall (1957) J. Am. Chem. Soc. 79 5441.
- ↑ n-Butylamine MSDS
- ↑ CDC - NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards
