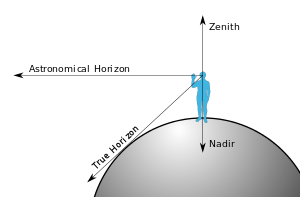
Nadir
| Look up nadir in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
The nadir (/ˈneɪdɪər/) (from Arabic: نظير / ALA-LC: naẓīr, meaning "counterpart") is the direction pointing directly below a particular location; that is, it is one of two vertical directions at a specified location, orthogonal to a horizontal flat surface there. Since the concept of being below is itself somewhat vague, scientists define the nadir in more rigorous terms. Specifically, in astronomy, geophysics and related sciences (e.g., meteorology), the nadir at a given point is the local vertical direction pointing in the direction of the force of gravity at that location. The direction opposite of the nadir is the zenith.
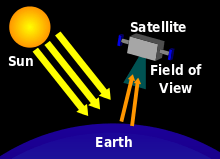
Nadir also refers to the downward-facing viewing geometry of an orbiting satellite,[1] such as is employed during remote sensing of the atmosphere, as well as when an astronaut faces the Earth while performing a spacewalk.
The word is also used figuratively to mean the lowest point of a person's spirits,[2] or the quality of an activity or profession.[3]
The term nadir can also be used to represent the lowest point reached by a celestial body during its apparent orbit around a given point of observation. This can be used to describe the location of the Sun, but it is only technically accurate for one latitude at a time and only possible at the low latitudes. The sun is said to be at the nadir at a location when it is at the zenith at the location's antipode and the sun is 90 degrees below the horizon.
In oncology, the term nadir is used to represent the lowest level of a blood cell count while a patient is undergoing chemotherapy.[4] A diagnosis of neutropenic nadir after chemotherapy typically lasts 7–10 days.[5]
References
- ↑ McLaughlin, Richard J.; Warr, William H. (2001). "The Common Berthing Mechanism (CBM) for International Space Station" (PDF). Society of Automotive Engineers. Retrieved March 23, 2012.
- ↑ Encyclopædia Britannica. 1911. p. 149. Retrieved March 23, 2012.
- ↑ Turner, Janice (December 1, 2007). "The lowest point in British journalism". The Times. Archived from the original on September 5, 2008. Retrieved March 23, 2012.
- ↑ "Bone marrow suppression". Chemotherapy Principles: An In-depth Discussion. American Cancer Society. Archived from the original on July 21, 2010. Retrieved March 5, 2013.
- ↑ Le, Tao; Bhushan, Vikas; Skapik, Julia (2007). First Aid For The USMLE Step 2 CK (6th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Medical. p. 479. ISBN 9780071487955. Retrieved March 23, 2012.