Nepenthes merrilliana
| Nepenthes merrilliana | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| A lower (top) and upper pitcher of N. merrilliana from Dinagat | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| (unranked): | Angiosperms |
| (unranked): | Eudicots |
| (unranked): | Core eudicots |
| Order: | Caryophyllales |
| Family: | Nepenthaceae |
| Genus: | Nepenthes |
| Species: | N. merrilliana |
| Binomial name | |
| Nepenthes merrilliana Macfarl. (1911)[1] | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Nepenthes merrilliana (/nᵻˈpɛnθiːz mɛˌrɪliˈɑːnə/; after Elmer Drew Merrill) is a tropical pitcher plant endemic to the Philippines. It produces some of the largest pitchers in the genus, rivalling those of N. rajah.[6]
The species is native to northern and central Mindanao as well as neighbouring Dinagat[6] and Samar.[7] Its presence in southern Mindanao is uncertain.[6] It inhabits coastal forest areas on steep slopes[8] at elevations of 0–1100 m above sea level.[9]
Nepenthes surigaoensis is closely related to N. merrilliana and was for a long time considered a heterotypic synonym of this species.[10] Nepenthes samar is another closely allied species.[11]
 A young plant with lower pitchers growing in an exposed site
A young plant with lower pitchers growing in an exposed site A small lower pitcher from Dinagat
A small lower pitcher from Dinagat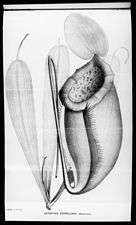
Natural hybrids
- N. alata × N. merrilliana [=N. × merrilliata][7][12]
- ? (N. alata × N. merrilliana) × N. mirabilis [=N. × tsangoya]
- N. bellii × N. merrilliana[6]
- N. merrilliana × N. mindanaoensis[6]
- N. merrilliana × N. mirabilis[6]
References
- ↑ Macfarlane, J.M. 1911. New species of Nepenthes. Contributions from the Botanical Laboratory of the University of Pennsylvania 3(3): 207–210. (plates I–II)
- ↑ Elmer, A.D.E. 1915. Nepenthaceae. [pp. 2785–2787] In: Two hundred twenty six new species—II. Leaflets of Philippine Botany 8: 2719–2883.
- ↑ Danser, B.H. 1928. 26. Nepenthes Merrilliana MACF.. In: The Nepenthaceae of the Netherlands Indies. Bulletin du Jardin Botanique de Buitenzorg, Série III, 9(3–4): 249–438.
- ↑ Jebb, M.H.P. & M.R. Cheek 1997. A skeletal revision of Nepenthes (Nepenthaceae). Blumea 42(1): 1–106.
- ↑ Cheek, M.R. & M.H.P. Jebb 2001. Nepenthaceae. Flora Malesiana 15: 1–157.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 McPherson, S.R. 2009. Pitcher Plants of the Old World. 2 volumes. Redfern Natural History Productions, Poole.
- 1 2 Robinson, A. 2012. Nepenthes merrilliana on Samar. Carnivorous Plants in the tropics, June 29, 2012.
- ↑ Clarke, C.M.; R. Cantley; J. Nerz; H. Rischer & A. Witsuba (2000). "Nepenthes merrilliana". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2006. International Union for Conservation of Nature. Retrieved 11 May 2006. Listed as Vulnerable (VU D2 v2.3).
- ↑ McPherson, S.R. & V.B. Amoroso 2011. Field Guide to the Pitcher Plants of the Philippines. Redfern Natural History Productions, Poole.
- ↑ Danser, B.H. 1928. The Nepenthaceae of the Netherlands Indies. Bulletin du Jardin Botanique de Buitenzorg, Série III, 9(3–4): 249–438.
- ↑ Cheek, M. & M. Jebb 2013. Nepenthes samar (Nepenthaceae), a new species from Samar, Philippines. Blumea 58(1): 82–84. doi:10.3767/000651913X673513
- ↑ Mann, P. 1998. A trip to the Philippines. Carnivorous Plant Newsletter 27(1): 6–11.
Further reading
- Bauer, U., C.J. Clemente, T. Renner & W. Federle 2012. Form follows function: morphological diversification and alternative trapping strategies in carnivorous Nepenthes pitcher plants. Journal of Evolutionary Biology 25(1): 90–102. doi:10.1111/j.1420-9101.2011.02406.x
- Beveridge, N.G.P., C. Rauch, P.J.A. Keßler, R.R. van Vugt & P.C. van Welzen 2013. A new way to identify living species of Nepenthes (Nepenthaceae): more data needed! Carnivorous Plant Newsletter 42(4): 122–128.
- Cantley, R. 2000. Nepenthes of the Philippines. [video] The 3rd Conference of the International Carnivorous Plant Society, San Francisco, USA.
- Cheek, M. & M. Jebb 2013. Nepenthes ramos (Nepenthaceae), a new species from Mindanao, Philippines. Willdenowia 43(1): 107–111. doi:10.3372/wi.43.43112
- Co, L. & W. Suarez 2012. Nepenthaceae. Co's Digital Flora of the Philippines.
- (German) Gronemeyer, T. 2008. Nepenthes auf den Philippinen – Ein Reisebericht. Das Taublatt 60(1): 15–27.
- (German) Gronemeyer, T. & V. Heinrich 2008. Wiederentdeckung von Nepenthes surigaoensis am Naturstandort auf den Philippinen. Das Taublatt 60(1): 28–33.
- Kurata, S. & M. Toyoshima 1972. Philippine species of Nepenthes. The Gardens' Bulletin Singapore 26(1): 155–158. Abstract
- Macfarlane, J.M. 1927. The Philippine species of Nepenthes. The Philippine Journal of Science 33(2): 127–140.
- (Indonesian) Mansur, M. 2001. "Koleksi Nepenthes di Herbarium Bogoriense: prospeknya sebagai tanaman hias." (PDF). In: Prosiding Seminar Hari Cinta Puspa dan Satwa Nasional. Lembaga Ilmu Pengetahuan Indonesia, Bogor. pp. 244–253.
- (German) McPherson, S. & T. Gronemeyer 2008. Die Nepenthesarten der Philippinen Eine Fotodokumentation. Das Taublatt 60(1): 34–78.
- Meimberg, H., A. Wistuba, P. Dittrich & G. Heubl 2001. Molecular phylogeny of Nepenthaceae based on cladistic analysis of plastid trnK intron sequence data. Plant Biology 3(2): 164–175. doi:10.1055/s-2001-12897
- (German) Meimberg, H. 2002. "Molekular-systematische Untersuchungen an den Familien Nepenthaceae und Ancistrocladaceae sowie verwandter Taxa aus der Unterklasse Caryophyllidae s. l.." (PDF). Ph.D. thesis, Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich, Munich.
- Meimberg, H. & G. Heubl 2006. Introduction of a nuclear marker for phylogenetic analysis of Nepenthaceae. Plant Biology 8(6): 831–840. doi:10.1055/s-2006-924676
- (Japanese) Oikawa, T. 1992. Nepenthes merrilliana Macf.. In: Muyū kusa – Nepenthes (無憂草 – Nepenthes). [The Grief Vanishing.] Parco Co., Japan. pp. 58–59.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Nepenthes merrilliana. |
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/30/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.